Fructosyl amino acid oxidase
An amino acid, fructosyl technology, applied in the direction of enzymes, biochemical equipment and methods, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as affecting the measurement results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Preparation and Characterization of N1-1 FAOD Mutant
[0076] Structure-function studies of monomeric sarcosine oxidase (MSOX) revealed that the proton transfer system (PRS) involved in transferring electrons from FAD to oxygen contains Thr48 and Lys 265 as well as four H 2 O molecules (Trickey et al., Structure, 7, 331-345, 1999). The active site of fructosyl amino acid oxidase from Pichia pastoris N1-1 strain (N1-1 FAOD, SEQ ID NO: 2) has high homology to MSOX, especially in the conserved residues expected to be responsible for the proton transport system .
[0077] Using the MSOX structure, a predicted structural model of N1-1 FAOD was constructed, predicting that amino acid residues Asn44, Ser46, Asn47, Lys48 and Lys269 are involved in proton and electron transport from FAD. Single or double mutations were introduced into those amino acid residues with the aim of modifying the electron acceptor availability of N1-1 FAOD.
[0078] Use QuickChange ? Methods (Strat...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Purification of N1-1 wild type and N47 mutant FAOD
[0085] Recombinant FAOD was purified as follows. First, an enzyme-containing water-soluble fraction was prepared from recombinant Escherichia coli. Escherichia coli containing the expression vector was cultured in 7L LB medium (37°C, 50 μg / ml ampicillin in a 10L fermenter), and then at about OD 660 = 0.7, the expression was induced with IPTG (final concentration: 0.3 mM), and the culture temperature was lowered to 30°C. Cells were suspended in 100 mM PPb (pH 7.0) and disrupted 4 times with a French cell press. The supernatant was subjected to ultracentrifugation (40,000 g, 90 minutes) and dialyzed against 10 mM PPb (pH 7.0) overnight at 4°C to prepare a water-soluble fraction.
[0086] The water-soluble fraction was further subjected to liquid chromatography to prepare purified enzyme. The enzyme was further purified by anion-exchange chromatography (DEAE-5PW). The water-soluble fraction was adsorbed onto an ani...
Embodiment 3
[0093] Preparation of PnFPOX mutants
[0094] prepared and characterized from Phaeosphaeria nolorum A mutant of fructosyl amino acid oxidase (PnFPOX , SEQ ID NO: 1).
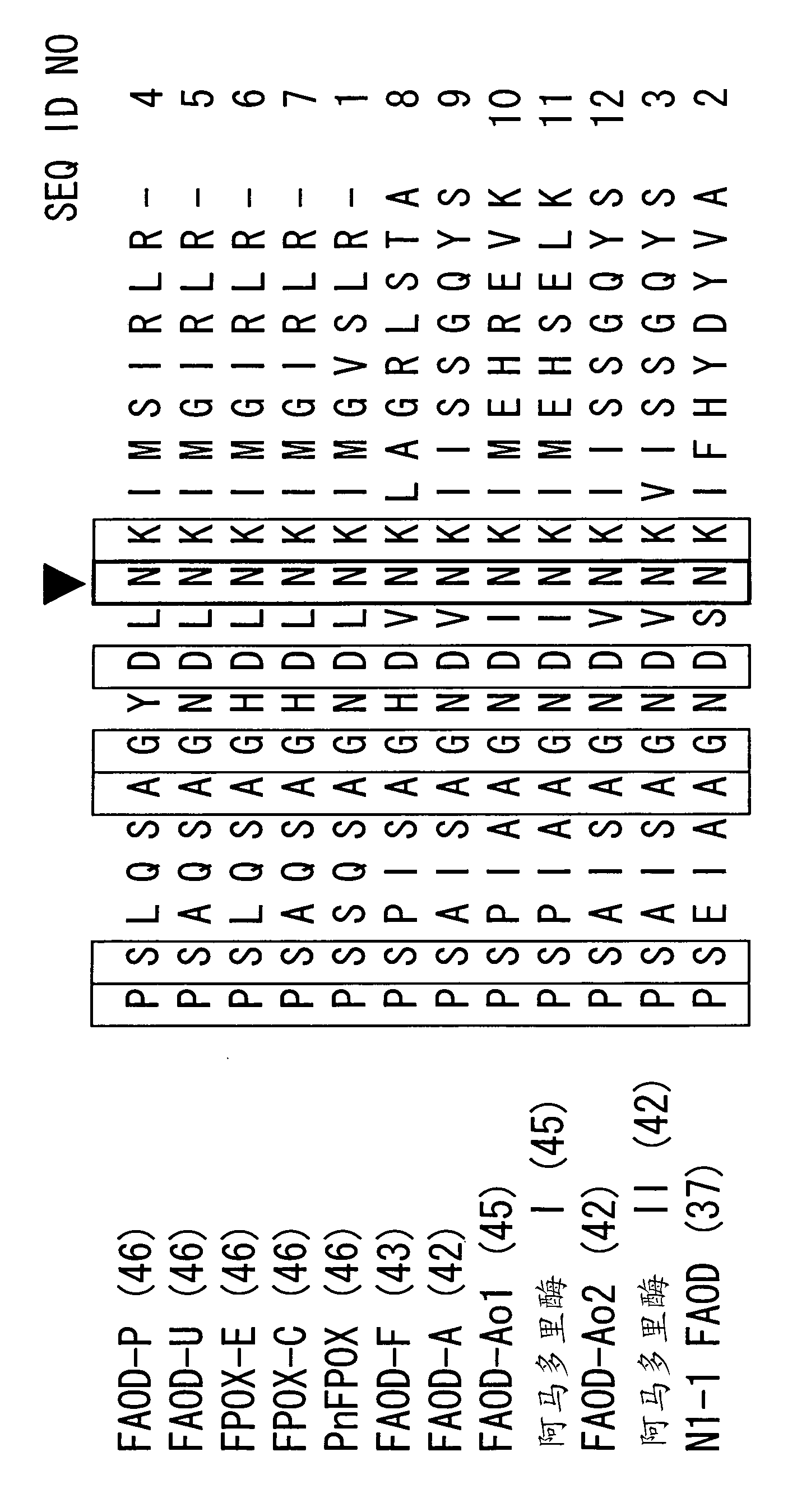
[0095] Alignment based on N1-1 FAOD and PnFPOX ( figure 1 ) and results from Examples 1 and 2 predict that Asn56 is involved in proton and electron transfer from FAD. Different mutations were introduced into Asn56 with the aim of modifying the electron acceptor availability of PnFAOD.
[0096] Mutations were introduced using site-directed mutagenesis as described in Example 1, and BL21 (DE3) cells were transformed with expression vectors containing wild-type or mutant PnFPOX. Cultured cells were resuspended in 10 mM PPB, pH 7.0, and lysed by sonication. Centrifuge the lysate at 10,000 g for 20 min at 4°C and the supernatant at 50,000 rpm for 60 min at 4°C. Oxidase and dehydrogenase activities were measured as described in Example 1.
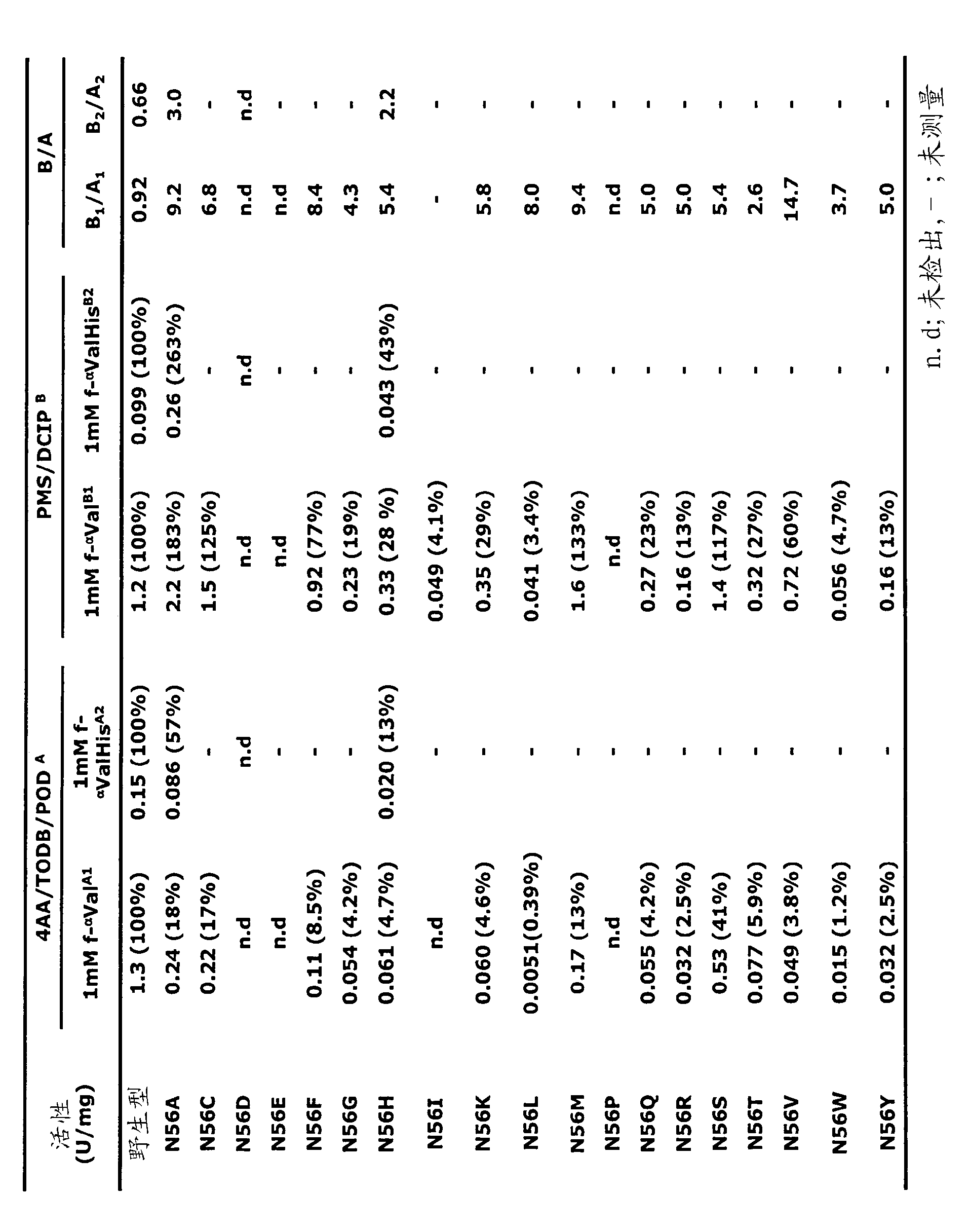
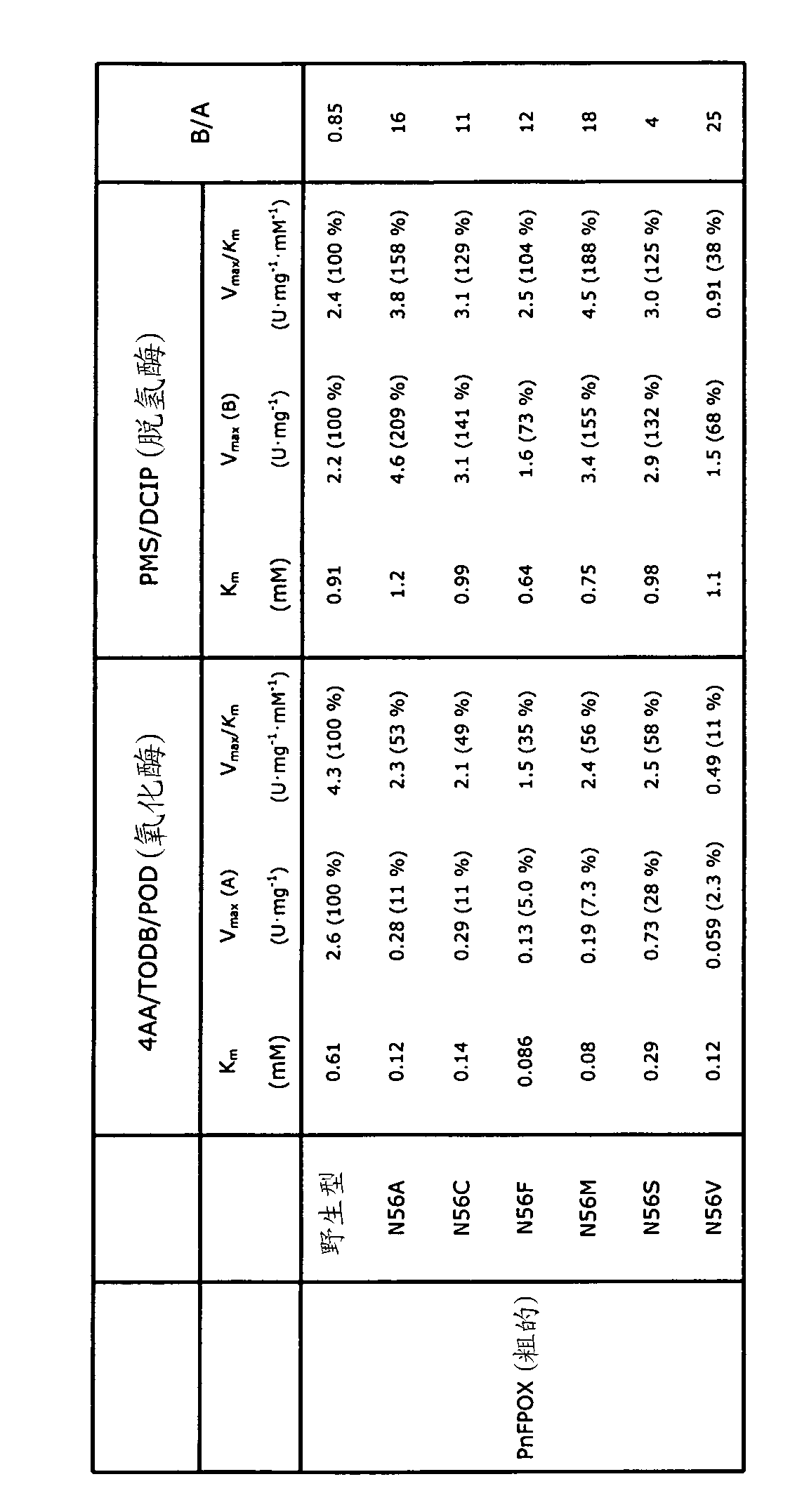
[0097] The activities of crude PnFPOX wild-type and Asn56 variants are...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com