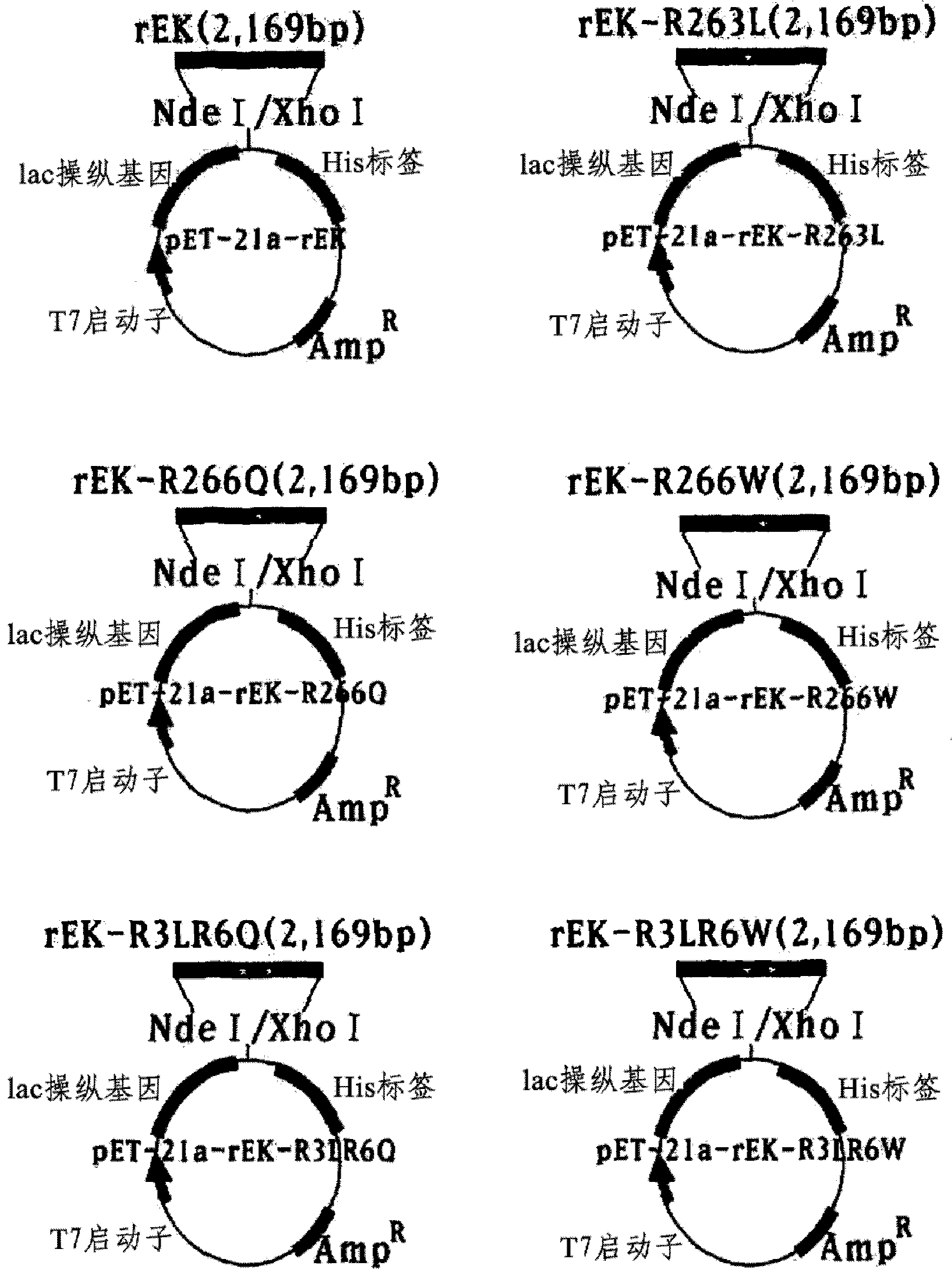Method for preparing recombinant glycoproteins with high sialic acid content
A technology of sialic acid and glycoprotein, applied in the field of preparing recombinant glycoprotein with high sialic acid content, which can solve the problems of shortening the life span of blood cells or glycoproteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Example 1: Induction of Point Mutations in the UDP-GlcNAc 2-Epimerase / ManNAc Kinase (GNE / MNK) Gene
[0076] Substitution of amino acid 263 or amino acid 266 of GNE / MNK gene
[0077] by PCR using the forward primer (5'-ATGGAGAAGAACGGGAATAACCGG-3', SEQ ID NO: 6) and the reverse primer (5'-CTAGTGGATCCTGCGGGTCGTGTAG-3', SEQ ID NO: 7) from Rattus norvegicus The wild-type GNE / MNK gene (SEQ ID NO: 1) was amplified in liver tissue (obtained from Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology), and then, the primers for inducing point mutations and QuickChange Site-Directed Mutagenesis shown in Table 1 Kit (Stratagene), utilizing forward primer (5'-GGAGATGGTTCTAGTGATGCGAAG-3', SEQ ID NO:8) and reverse primer (5'-CCTCTACCAAGATCACTACGCCTTC-3', SEQ ID NO:9) for point mutation, Arginine at position 263 is replaced with leucine (SEQ ID NO: 2); or arginine at position 266 is replaced with glutamine or tryptophan.
[0078] Substitution of amino acid 263 or amino acid 266 of GNE...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Embodiment 2: Preparation of expression vector
[0088] Preparation of α-2,3-sialyltransferase expression vector
[0089] A forward primer (5'-ATGGGACTCTTGGT-3', SEQ ID NO: 14) and a reverse primer ( 5'-TCAGATGCCACTGCTTAG-3', SEQ ID NO: 15), human alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase was amplified from a human fibroblast cell line (HF cell line) by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Such as image 3 As shown in , in order to introduce the amplified gene into Chinese hamster ovary cells as host cells, the amplified gene was ligated to the BamHI / HindIII site of the expression vector pcDNA3.1 / Zeo(+) to prepare the expression vector pcSTz( image 3 ).
[0090] Preparation of expression vector for cytidine monophosphate (CMP)-sialic acid transporter
[0091] A forward primer (5'-CAGCTAGCGCCACCATGGCTCAGG-3', SEQ ID NO: 16) and a reverse primer ( 5′-TCCGAATTCTCACACACCAATGACTC-3′, SEQ ID NO: 17), amplified by PCR from Chinese hamster ovary cells (EC2-1H9: obtained from Korea Resear...
Embodiment 3
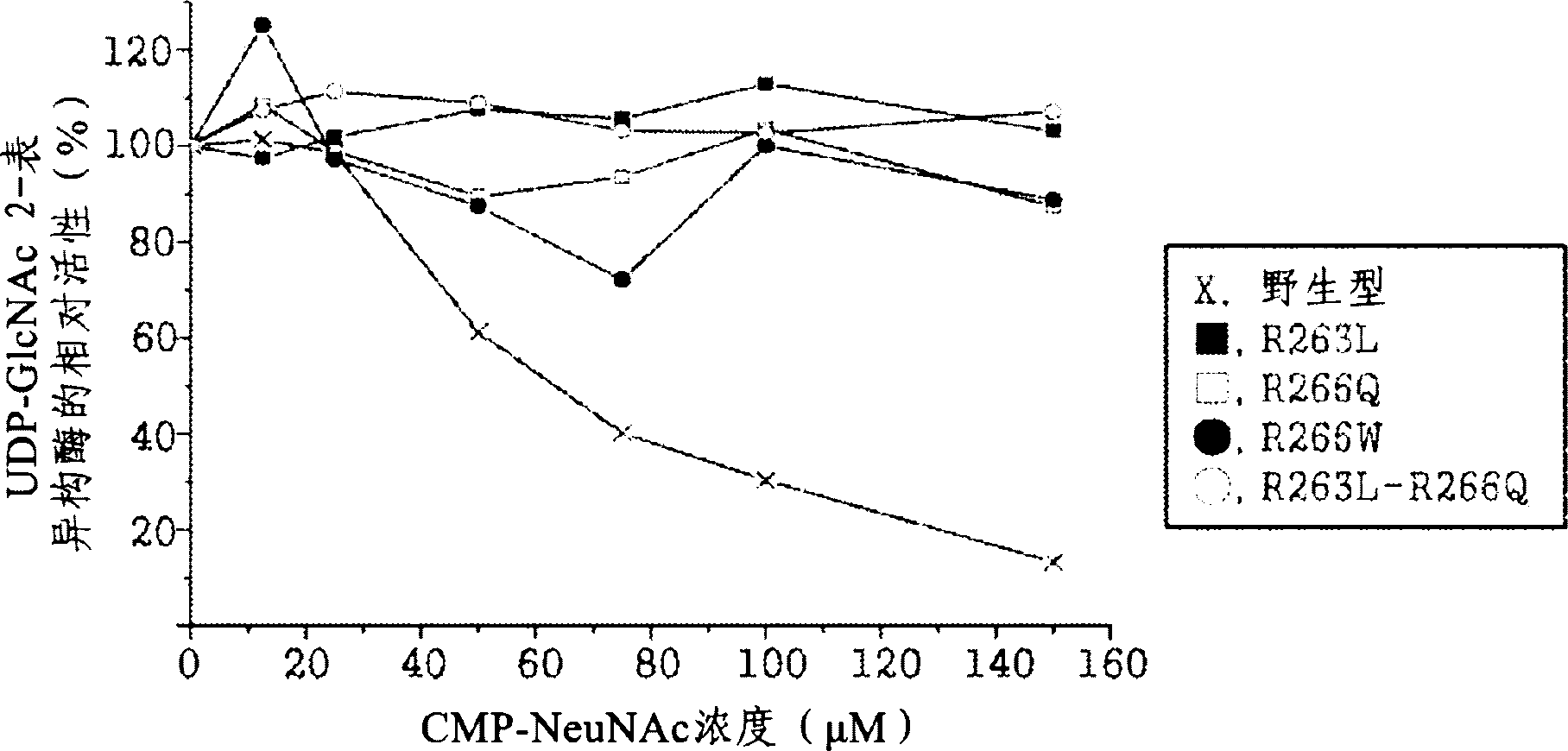
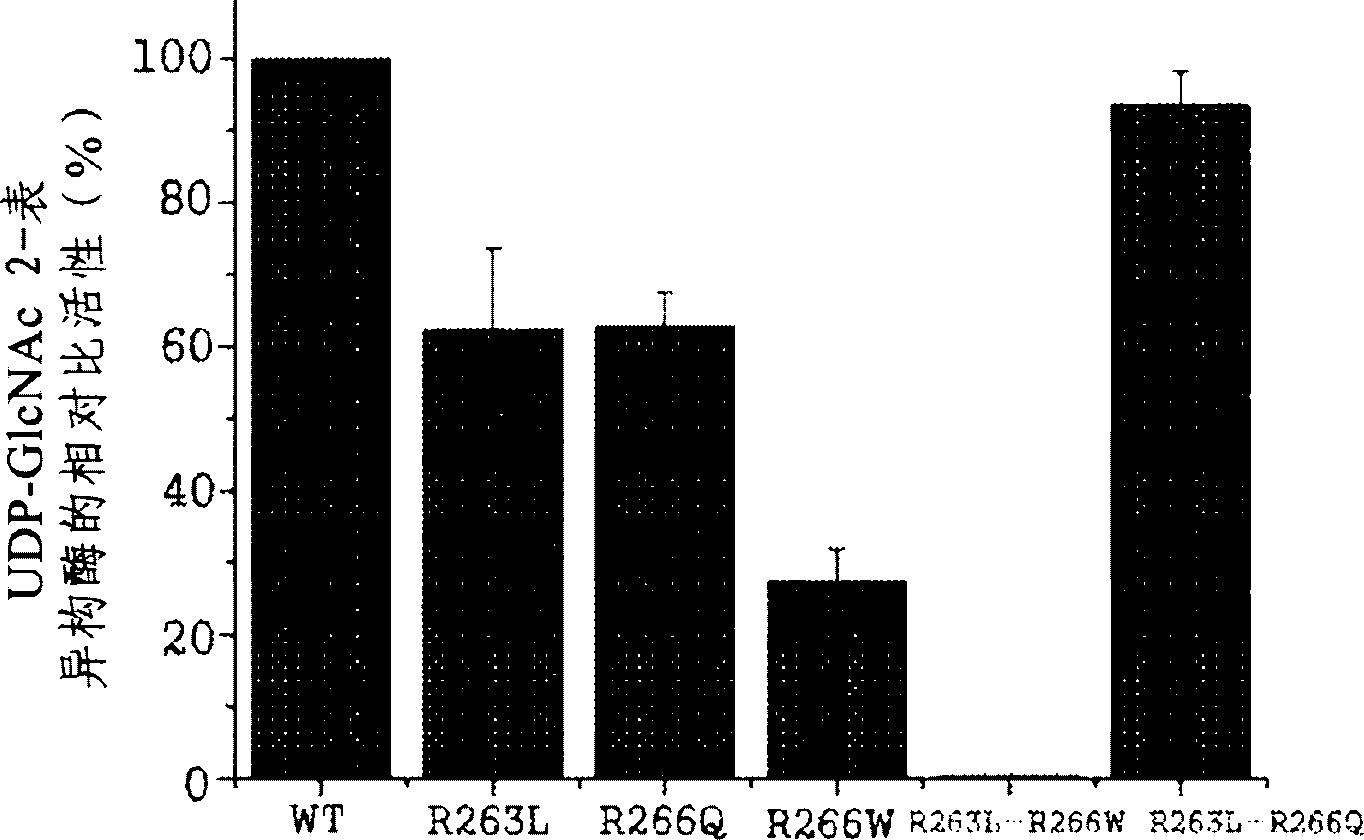
[0094] Example 3: Identification of changes in sialic acid content caused by overexpression of GNE / MNK genes that induce point mutations
[0095] Introducing the expression vector of the GNE / MNK gene that induces point mutations into Chinese hamster ovary cells
[0096] By using Lipofectamine TM LTX and PLUS TM Reagent (Invitrogen), the vectors produced in Example were respectively transfected into Chinese hamster ovary cells, which are host cells producing recombinant erythropoietin. The transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells cultured in medium (MEM-α medium containing 400 μg / ml hygromycin B, 10% dFBS, 1% antibiotic-antimycotic, 20 nM MTX) were cultured in a culture medium with 5 %CO 2 Incubate in an incubator at 37°C, and repeat screening and subculture of surviving cells.
[0097] Identification of GNE / MNK gene expression
[0098] In order to identify the expression of the GNE / MNK gene introduced into the cells screened in Example , total RNA was isolated from the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com