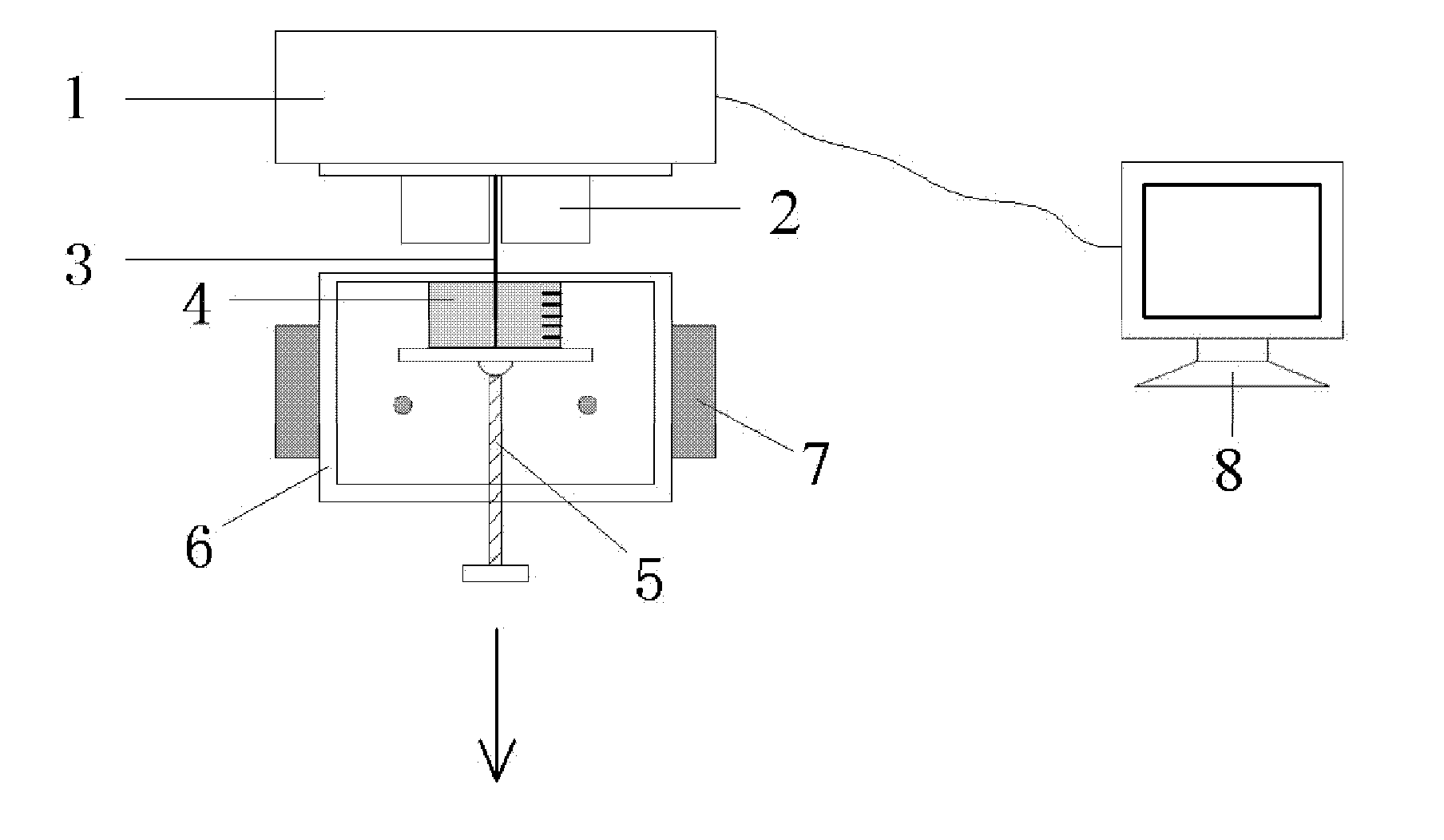
Device for testing bonding performance of synthetic fiber and cement based material during plastic stage
A technology of cement-based materials and synthetic fibers, which is applied in the direction of applying stable tension/pressure to test the strength of materials, etc., can solve the problems that synthetic fibers cannot be applied, and achieve the goal of preventing inaccurate test curves, ensuring accuracy, and high-precision measuring range Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
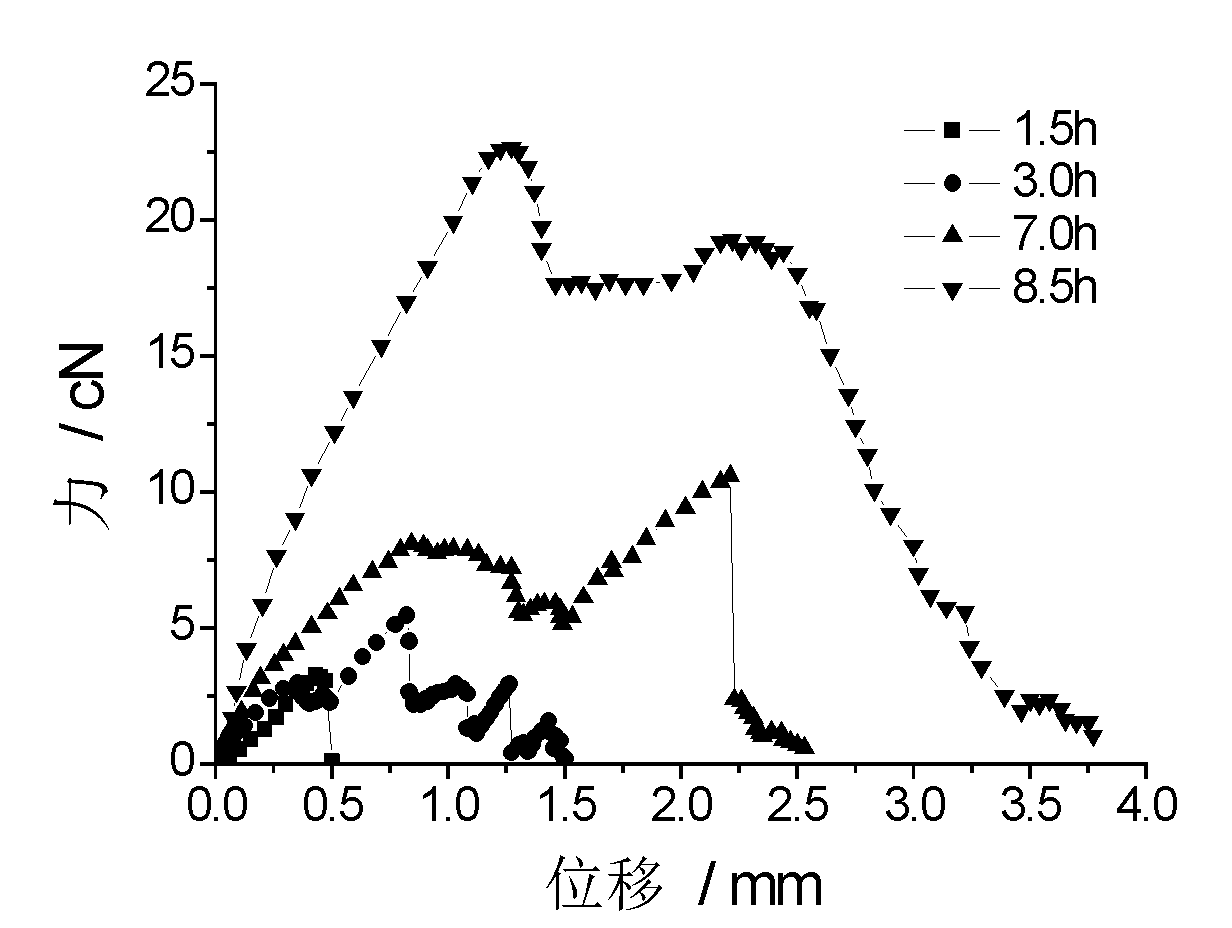
[0031] In this example, polypropylene (PP) fibers were used to investigate the influence of the test time after molding on the fiber pull-out load-displacement curve, interface bond strength and fiber energy consumption. The bottom area of the cement matrix holding the mold is 500mm 2 , the height is 7.5mm, that is, the fiber embedding depth is 7.5mm, and the braking control speed is 0.01mm / s. Fiber performance parameters, see Table 1; matrix mix ratio, see Table 2.
[0032] Table 1 Fiber performance parameters
[0033]
[0034] Table 2 Matrix mix ratio
[0035] water-binder ratio
[0036] The interface bond strength can be calculated according to formula (1):
[0037] τ=P max / πdL e (1)
[0038] Where: P max is the maximum load when the fiber is pulled out; d is the fiber diameter; L e is the fiber embedding depth.
[0039] During the drawing process, the fiber will go through two stages of debonding and pulling out, absorbing a lot of energy. Fib...
Embodiment 2
[0045] In this example, polypropylene (PP) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fibers were used to investigate the effect of fiber types on the interfacial bond strength as the test time prolongs. The bottom area of the cement matrix holding the mold is 500mm 2 , the height is 7.5mm, that is, the fiber embedding depth is 7.5mm, and the braking control speed is 0.01mm / s. The fiber performance parameters are shown in Table 4; the matrix mix ratio is the same as in Example 1, see Table 2.
[0046] Table 4 Fiber types and properties
[0047]
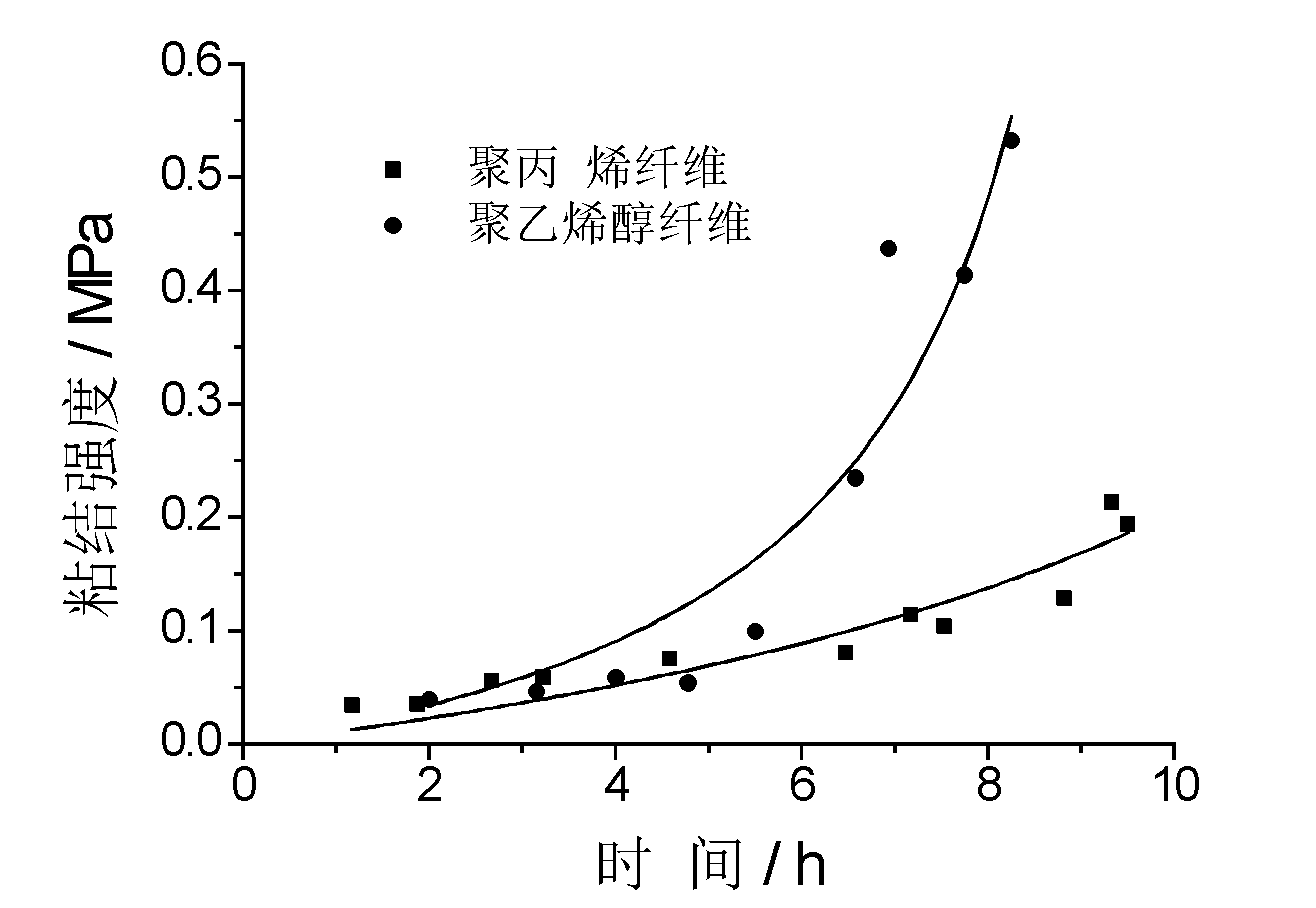
[0048] In this embodiment, the influence of the type of synthetic fiber on the interfacial bond strength is shown in image 3 .
[0049] From image 3 It can be seen that the interfacial bond strength between PVA and PP fibers is not much different within 6 hours after the cement matrix is formed, but after 6 hours, the interfacial bond strength has been significantly improved, and the increase rate is relatively large. The reason why PV...
Embodiment 3
[0051] In this example, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fibers were used to investigate the influence of the matrix type on the bonding performance of the fiber-matrix interface. The bottom area of the cement paste holding mold is 500mm 2 , the height is 7.5mm; the bottom area of the mortar holding mold is 700mm 2 , with a height of 7.5mm. The brake control speed is 0.01mm / s. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fiber performance parameter, with embodiment 2, sees Table 4; Matrix mix ratio, sees Table 5, and wherein sand is the standard sand that saturated surface is dry.
[0052] Table 5 Matrix mix ratio
[0053] water-binder ratio
[0054] From Figure 4 Two points can be seen, (1) After chemical debonding, the interfacial friction between PVA fiber and matrix continues to increase; (2) The interfacial bonding strength between fiber and mortar is higher than that of cement paste. This may be because the surface of the PVA fiber is continuously worn during the pulling out pro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bottom area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com