Manufacture technology for improving toughness of non-quenched and tempered steel forging
A manufacturing process, non-quenched and tempered steel technology, applied in the field of manufacturing process to improve the toughness of non-quenched and tempered steel forgings, can solve the problems of poor material toughness, slow cooling rate, no clear requirements, etc., to improve toughness, plasticity and impact toughness. improved effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
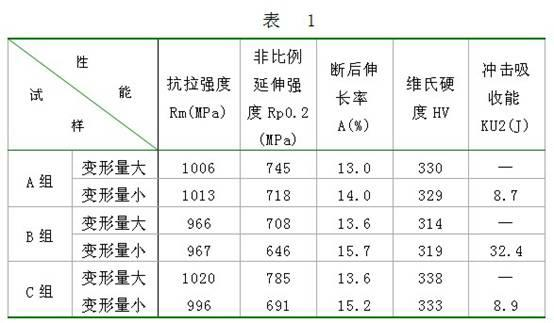
[0023] This embodiment is a manufacturing process for improving the toughness of non-quenched and tempered steel forgings, including the following steps: blanking → induction heating → pre-forging → final forging → edge trimming → controlled cooling → feeding box stack cooling → shot blasting → magnetic force Flaw detection→machining;
[0024] In the induction heating process, the workpiece heating temperature is usually 1120°C; in the final forging process, the final forging temperature of the workpiece is controlled at 980°C; in the trimming process, the temperature of the workpiece after edge trimming is 850°C.
[0025] In the controlled cooling process, the workpieces are immediately dispersed on the conveyor belt moving at a speed of 0.5 m / min after edge trimming, and are cooled to 520 °C at 2.0 °C / s under the cooling condition of forced air, and enter the material box for stack cooling; In the charging box stack cooling process, the workpiece is slowly cooled to room tem...
Embodiment 2
[0028] This embodiment is a manufacturing process for improving the toughness of non-quenched and tempered steel forgings, including the following steps: blanking → induction heating → pre-forging → final forging → edge trimming → controlled cooling → feeding box stack cooling → shot blasting → magnetic force Flaw detection→machining;
[0029] In the induction heating process, the workpiece heating temperature is usually 1130°C; in the final forging process, the final forging temperature of the workpiece is controlled at 1000°C; in the trimming process, the temperature of the workpiece after edge trimming is 950°C.
[0030] In the controlled cooling process, the workpieces are immediately dispersed and placed on the conveyor belt moving at a speed of 1 m / min after edge trimming, and are cooled to 600 °C at 4.0 °C / s under the cooling condition of spraying water mist and enter the material box for cooling ; In the feeding box stack cooling process, the workpiece is slowly cooled...
Embodiment 3
[0033] This embodiment is a manufacturing process for improving the toughness of non-quenched and tempered steel forgings, including the following steps: blanking → induction heating → pre-forging → final forging → edge trimming → controlled cooling → feeding box stack cooling → shot blasting → magnetic force Flaw detection→machining;
[0034] In the induction heating process, the workpiece heating temperature is usually 1250°C; in the final forging process, the final forging temperature of the workpiece is controlled at 1050°C; in the trimming process, the temperature of the workpiece after edge trimming is 1000°C.
[0035] In the controlled cooling process, the workpieces are immediately dispersed on the conveyor belt moving at a speed of 2 m / min after edge trimming, and are cooled to 650 °C at 16.0 °C / s under the cooling condition of forced air, and then enter the material box for stack cooling ; In the feeding box stack cooling process, the workpiece is slowly cooled to ro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com