Water treatment method of microbial fuel cell
A fuel cell water and treatment method technology, which is applied in the fields of magnetic field/electric field water/sewage treatment, energy wastewater treatment, light water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of refractory wastewater treatment difficulties, save treatment costs, and improve biochemical The effect of low performance and selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
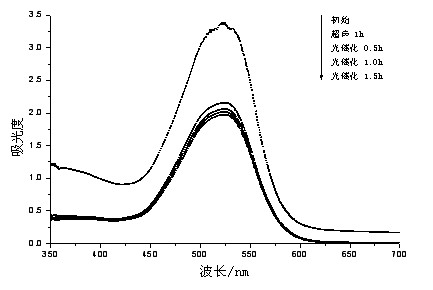
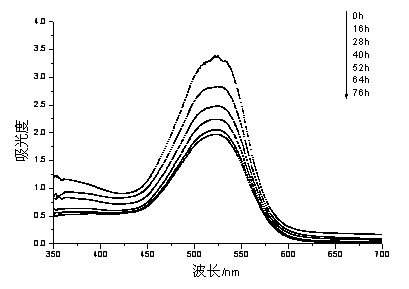
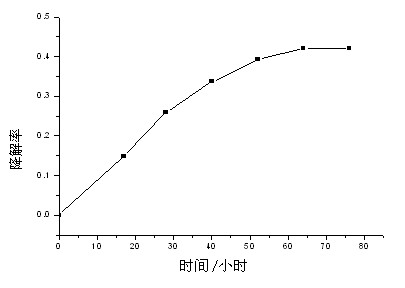
[0025] Example 1: Anatase-type titanium dioxide TiO doped with elements whose mass ratio of element fluorine to titanium is 1:200 2 Photocatalyst added to azo dye solution, element-doped anatase TiO 2 The mass ratio of photocatalyst to azo-type dye is 15:1, ultrasonically oscillate for 0.5 hours to reach adsorption equilibrium, and then perform photocatalysis: use a light source to irradiate the solution while stirring for 2 hours, and circulate the photocatalyzed solution Type vacuum pump decompression filtration; then according to the ratio of easy biochemical organic matter and the organic matter mass ratio in the photocatalyzed solution to be 6:1, add it as microbial carbon source to the fully activated microbial fuel cell water treatment device, wherein the battery temperature is controlled at 30°C±1°C, the anode chamber of the battery is sealed and the pH value of the solution is controlled at about 7.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2: Anatase-type titanium dioxide TiO doped with an element with a mass ratio of elemental silver to titanium of 1:100 2 Photocatalyst added to azo dye solution, element-doped anatase TiO 2 The mass ratio of photocatalyst to azo-type dye is 1:1, ultrasonically oscillate for 1 hour to reach adsorption equilibrium, and then perform photocatalysis: use a light source to irradiate the solution while stirring for 1 hour, and pass the photocatalyzed solution through micro Pore membrane filtration; then mixed according to the mass ratio of easy biochemical organic matter and organic matter in the solution after photocatalysis as 2:1 as microbial carbon source and added to the fully activated microbial fuel cell water treatment device, wherein the battery temperature was controlled at 30 ℃±1℃, the anode chamber of the battery is sealed and the pH value of the solution is controlled at about 7.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: Anatase-type titanium dioxide TiO doped with an element with a ratio of element nitrogen to titanium mass of 1:150 2 Photocatalyst added to azo dye solution, element-doped anatase TiO 2 The mass ratio of the photocatalyst to the azo dye is 5:1, ultrasonically oscillate for 40 minutes to reach adsorption equilibrium, and then perform photocatalysis: use a light source to irradiate the solution while stirring for 1.5 hours, and pass the photocatalyzed solution through micro Pore filter membrane filtration; then mixed according to the mass ratio of easy biochemical organic matter and organic matter in the solution after photocatalysis is 10:1 as microbial carbon source and added to the fully activated microbial fuel cell water treatment device, wherein the battery temperature is controlled at 30 ℃±1℃, the anode chamber of the battery is sealed and the pH value of the solution is controlled at about 7.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com