Multiplex-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) kit for rapidly detecting deer product and preparation method thereof
A technology of deer products and kits, applied in the field of multiplex PCR kits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] Embodiment 1: Composition and preparation of kit
[0098] 1) Preparation of DNA extraction solution
[0099] (1) Low-salt buffer (pH 7.6): Dissolve 1.21g Tris base (trishydroxymethylaminomethane) and 3.38g Na in 800ml distilled water 2 EDTA (disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid), 0.76g MgCl 2 , 0.47gNaCl. Add concentrated hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH to the desired value, add distilled water to make up to 1L.
[0100] (2) Cell lysate: Add 1g SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) and 1ml Triton X-100 (polyethylene glycol p-isooctylphenyl ether) to 200ml low-salt buffer.
[0101] (3) Proteinase K: Dissolve 100 mg proteinase K in 5 ml sterile deionized water and store at -20°C.
[0102] Extraction method: Add 200ul anticoagulant blood and 400ul low-salt buffer solution into a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, mix well, centrifuge at 1000RPM for 10min, discard the supernatant; add 500ul low-salt buffer solution, mix well, and centrifuge at 1000RPM for 5min at room temperature...
Embodiment 2
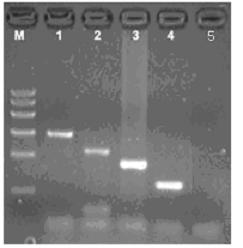
[0139] Embodiment 2: the specificity test of kit
[0140] 1. The interspecies specificity and intraspecies generality of each primer pair in deer-derived multiplex PCR reaction.
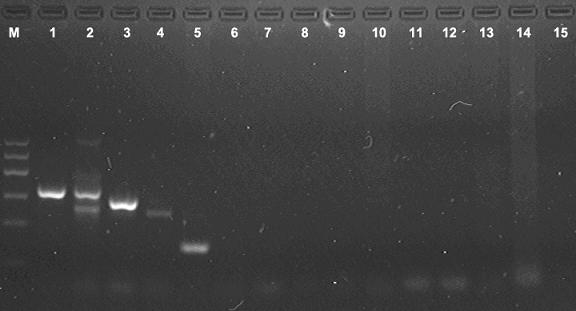
[0141] (1) To prove that each primer pair in the deer-derived multiplex PCR reaction has cross-species specificity.
[0142] ① Genomic DNA of sika deer, red deer, Tarim red deer, red deer, reindeer, sambar, eld deer, white-lipped deer, elk, fallow deer, pig, cattle, sheep and chicken were extracted from the blood according to the method in Example 1. The extracted DNA was used to prepare the following reaction systems, and sterile water was used as a negative control.
[0143] ②Preparation of the reaction system: step ① Add 1.0ul of the extracted DNA to the deer-derived multiplex PCR reaction solution in Example 1.
[0144] ③According to the program: 94°C for 5 minutes; 94°C for 30s, 56°C for 30s, 67°C for 1min; 67°C for 5min, amplify for 30 cycles. Perform PCR amplification.
[0145] ④ Results...
Embodiment 3
[0156] Example 3: Sensitivity of multiplex PCR.
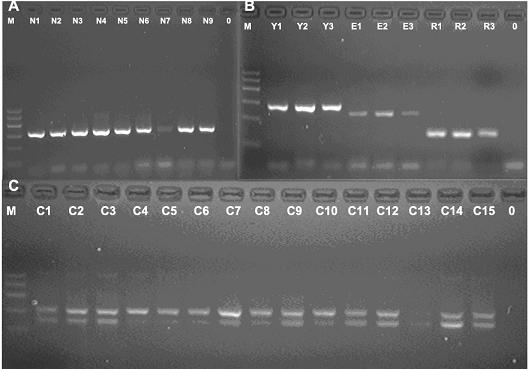
[0157] 1. To evaluate the sensitivity of deer-derived multiplex PCR reaction.
[0158] (1) According to the extraction method in Example 1, blood genome DNA of sika deer, red deer, Tarim red deer, red deer and reindeer were extracted respectively. Carry out serial dilution respectively, and the dilution conditions are as follows: 10, 5, 1, 0.5, 0.2, 0.1, 0.05, 0.02 ng.
[0159] (2) Preparation of reaction systems: Step (1) 1.0 ul of extracted DNA was added to the deer-derived multiplex PCR reaction solution in Example 1.
[0160] (3) According to the program: 94°C for 5 minutes; 94°C for 30s, 56°C for 30s, 67°C for 1min, 67°C for 5min, amplify for 30 cycles. Perform PCR amplification.
[0161] (4) Results: The minimum detection limits of genomic DNA samples of sika deer, red deer, Tarim red deer, red deer and reindeer were 0.05, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5 and 0.02 ng, respectively.
[0162] 2. Evaluate the sensitivity of multiple PCR...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com