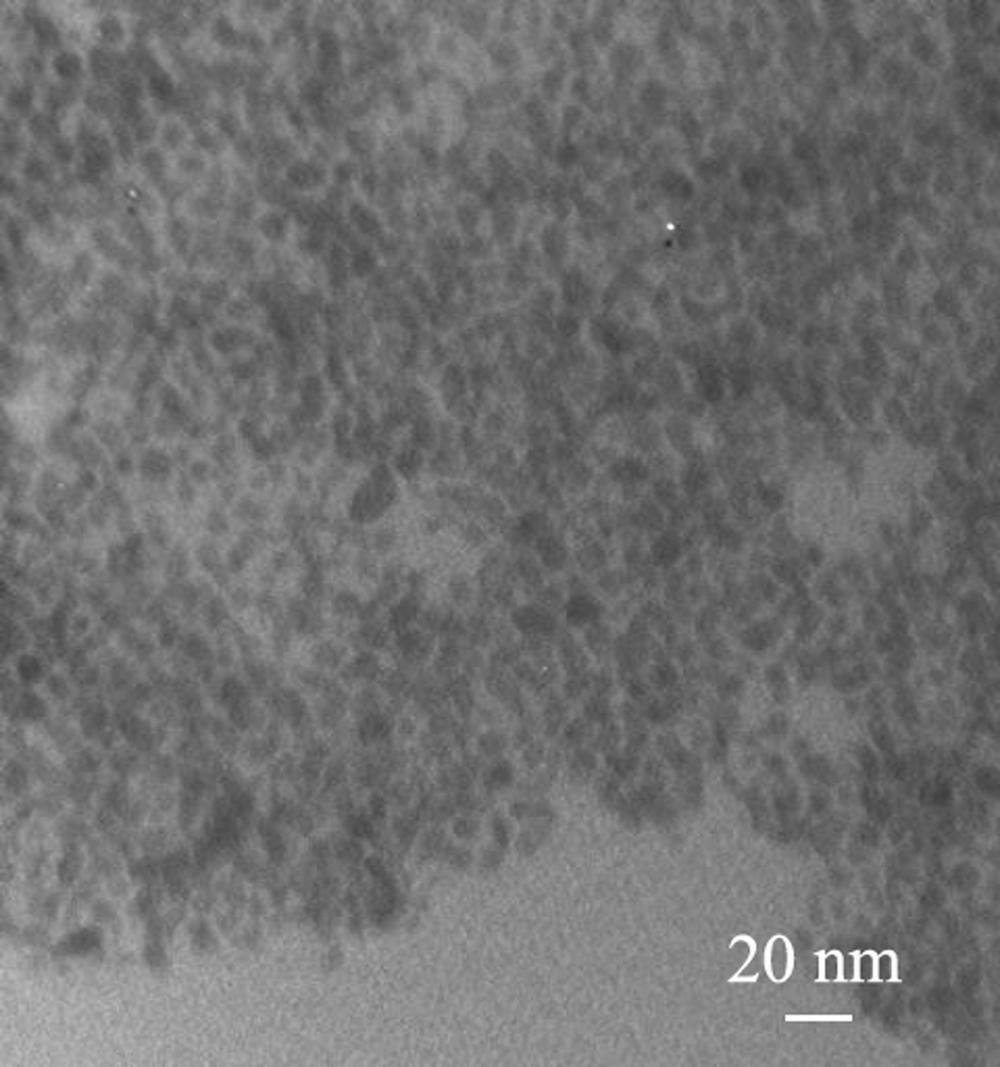
Method for preparing mercuric sulfide (HgS) quantum dots by using mercury-containing wastewater
A technology of quantum dots and mercury sulfide, applied in chemical instruments and methods, mercury compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing processing costs, cheap prices, and less environmental hazards
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Hg in mercury-containing wastewater 2+ Transfer to the organic phase: take 10 ml of 0.1 mol / L mercury-containing wastewater, add 1.2 mmol oleylamine, 20 ml ethanol, and 30 ml n-hexane. Stir the system so that it is at 50 o C for 40 min. After the reaction, the system was cooled to room temperature, and the calculated Hg 2+ The phase transfer rate is 97.9%.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Preparation of HgS quantum dots by conventional solvothermal method: Take 10 ml of 0.02 mol / L mercury-containing wastewater, add 3.0 mmol oleylamine, 20 ml ethanol, and 30 ml n-hexane. Stir the system so that it is at 50 o C for 30 min. After the system was cooled to room temperature, it was transferred to a hydrothermal reaction kettle, 2 mmol thiourea was added, and then the reaction kettle was sealed and heated to 180°C in a heating box. o C, constant temperature for 24 h. After the reaction, the reaction system was separated, the lower aqueous phase was removed, the upper organic phase containing HgS quantum dots was centrifuged, and the obtained black solid particles were dispersed with n-hexane.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Preparation of HgS quantum dots by microwave solvothermal method: Take 10 ml of 0.02 mol / L mercury-containing wastewater, add 3.0 mmol oleylamine, 20 ml ethanol, and 30 ml n-hexane. Stir the system so that it is at 50 o C for 30 min. Then add 3 mmol sulfur powder and continue to stir until the sulfur powder dissolves. Afterwards, the solution system was transferred to the microwave reactor, and at 150 o C microwave reaction for 20 min. After the reaction, the reaction system was separated into liquids, the lower aqueous phase was removed, and the upper organic phase containing HgS quantum dots was centrifuged to obtain black solid particles dispersed with n-hexane.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quantum dot | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com