Electrode structure on back of solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of solar cells and back electrodes, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of expensive processing technology, reduce production costs, disadvantages, etc., and achieve the effects of improving conversion efficiency, reducing surface recombination rate, and improving infrared spectral response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
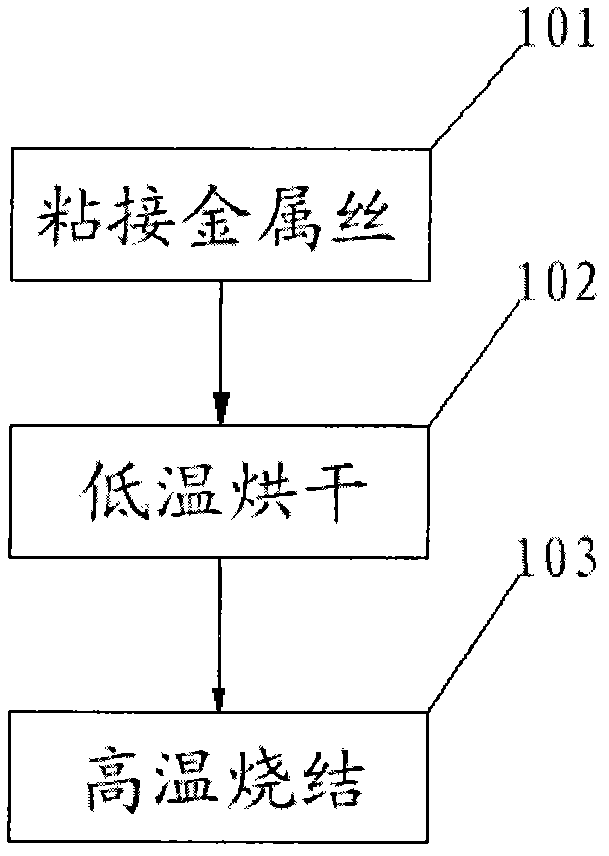
[0035] figure 1 It is a schematic flowchart of a method for fabricating a back electrode of a solar cell provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. see figure 1 As shown, the method mainly includes the following steps:
[0036] Step 101: bonding wires;
[0037] Stick the metal wire with conductive paste and paste it on the surface of the silicon wafer to form an electrode line;
[0038] Step 102: drying at low temperature;
[0039] Dry the silicon wafer bonded with the wire at a temperature of 200°C to 400°C;
[0040] Step 101: high temperature sintering;
[0041] The dried silicon wafer is sintered at a temperature of 500°C to 900°C. At the same time, the silicon wafer and the back electrode are sintered together to form a good ohmic contact between the conductive paste and the silicon wafer. At the same time, the The conductive paste is sintered with the wire to form a complete conductor.
[0042] Ohmic contact refers to the resistive contact between metal and...
Embodiment 2
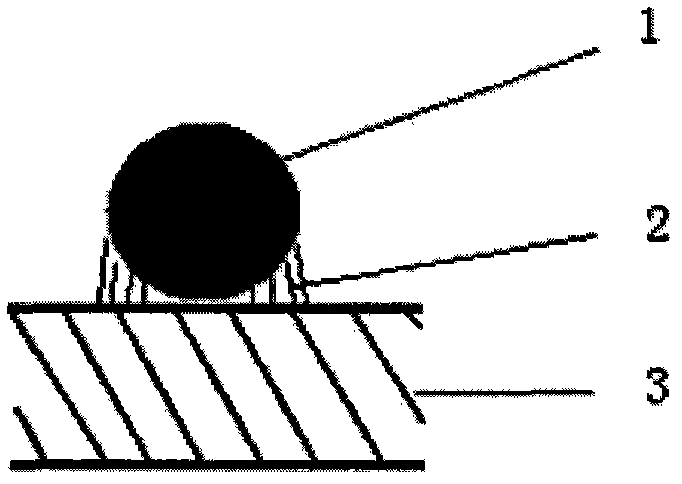
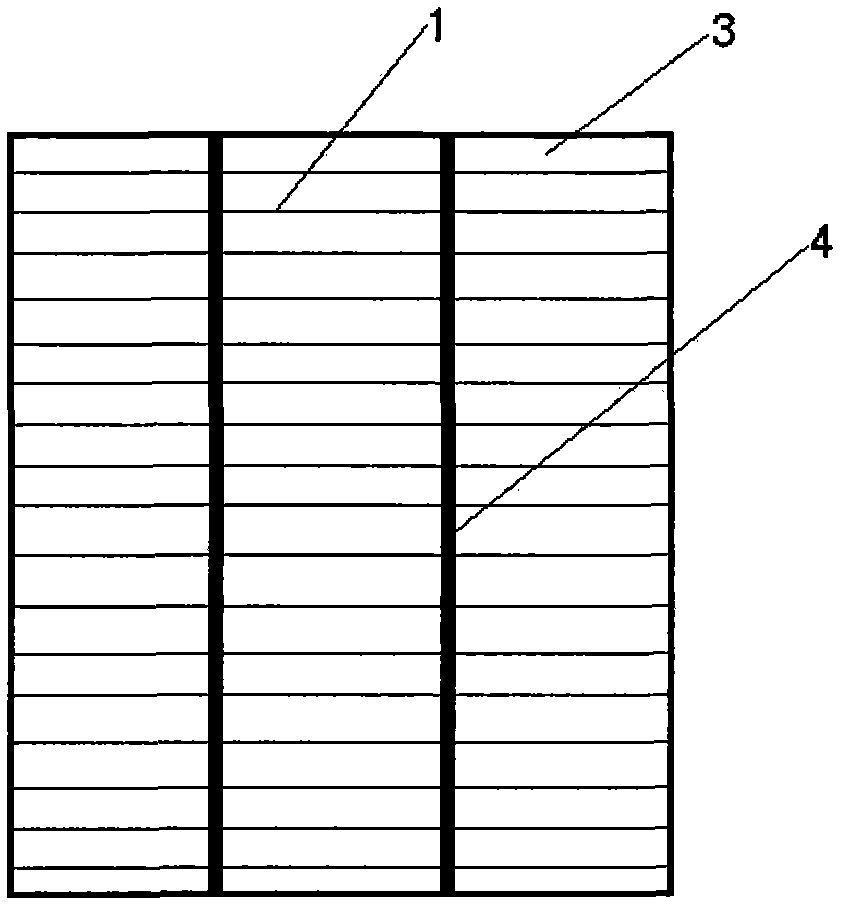
[0045] image 3 A schematic diagram of the back electrode structure of a solar cell provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention; figure 2 It is a partial cross-sectional schematic diagram of a back electrode structure of a solar cell according to the present invention.
[0046] Such as figure 2 As shown, it includes a silicon chip 3 and a metal wire 1, the silicon chip 3 and the metal wire 1 are bonded together by a conductive paste 2, and the diameter of the metal wire 1 is 0.01 mm to 0.15 mm.
[0047] Such as image 3 As shown, the metal wires 1 are equally spaced and parallel bonded on the upper surface of the silicon wafer, and the distance between the metal wires is 0.5 to 3 mm.
[0048] Such as image 3 As shown, on the back surface of the silicon wafer 3, a busbar line is arranged perpendicular to the direction of the metal wire to lead out the back electrode. The busbar line corresponds to the front busbar line one by one, and the position is the same. 1 t...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Figure 4 A schematic diagram of the front electrode structure of a solar cell provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention; figure 2 It is a partial cross-sectional schematic diagram of a front electrode structure of a solar cell according to the present invention.
[0053] Such as figure 2 As shown, it includes a silicon chip 3 and a metal wire 1, the silicon chip 3 and the metal wire 1 are bonded together by a conductive paste 2, and the diameter of the metal wire 1 is 0.01 mm to 0.15 mm.
[0054] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the metal wires 1 are equally spaced and parallel bonded on the upper surface of the silicon wafer, and the distance between the metal wires is 0.5 to 3 mm.
[0055] Such as Figure 4 As shown, one end of the metal wire 1 is provided with an electrode lead-out segment 5, and the electrode lead-out segment 5 protrudes from the surface of the silicon wafer 3 to lead out the back electrode.
[0056] When making this embodiment, first sti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com