Continuous ion exchange device and method for removing boron from salt lake magnesium chloride brine
A technology of continuous ion and exchange device, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, to achieve the effect of high degree of automation, stable product concentration and saving consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
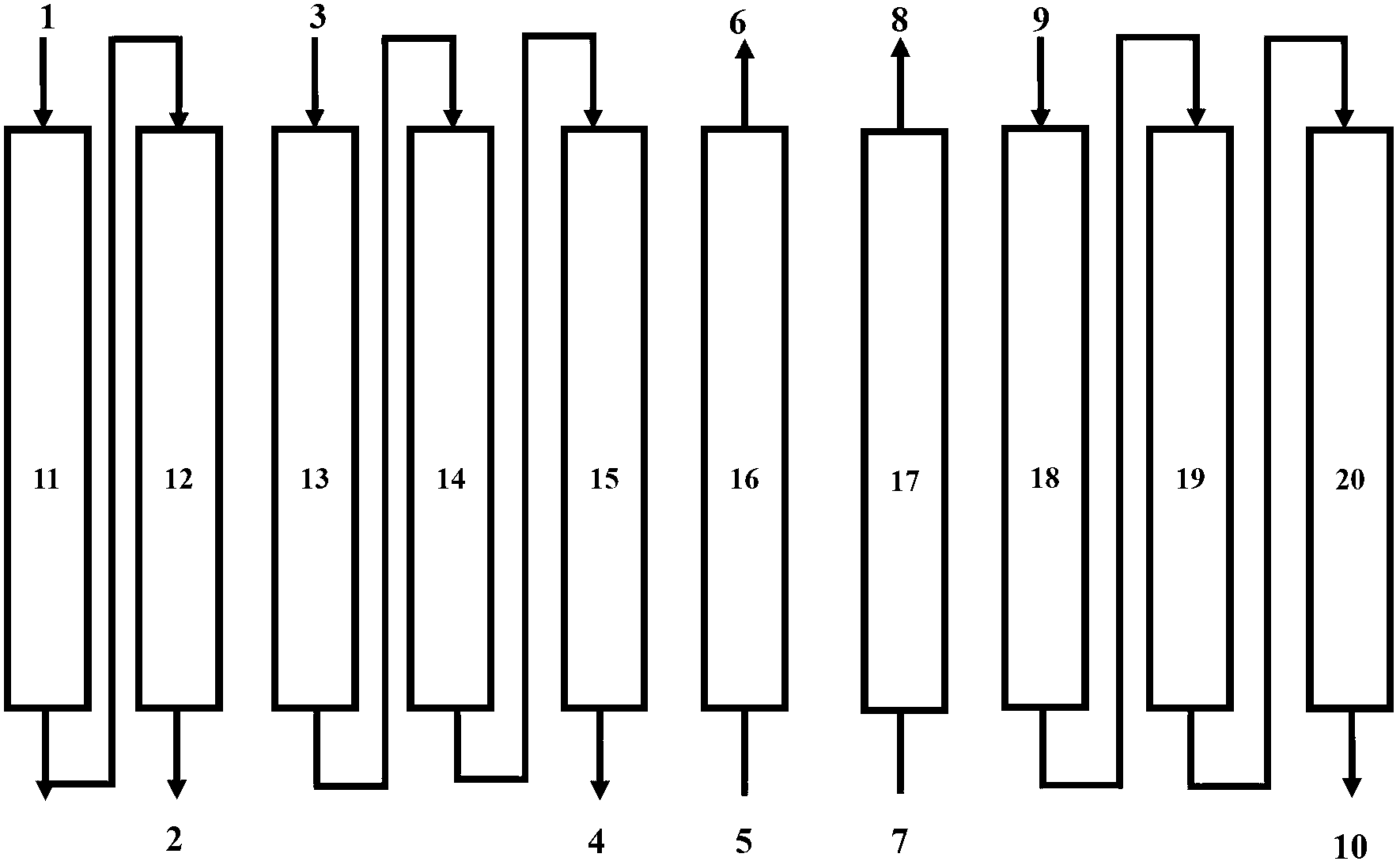
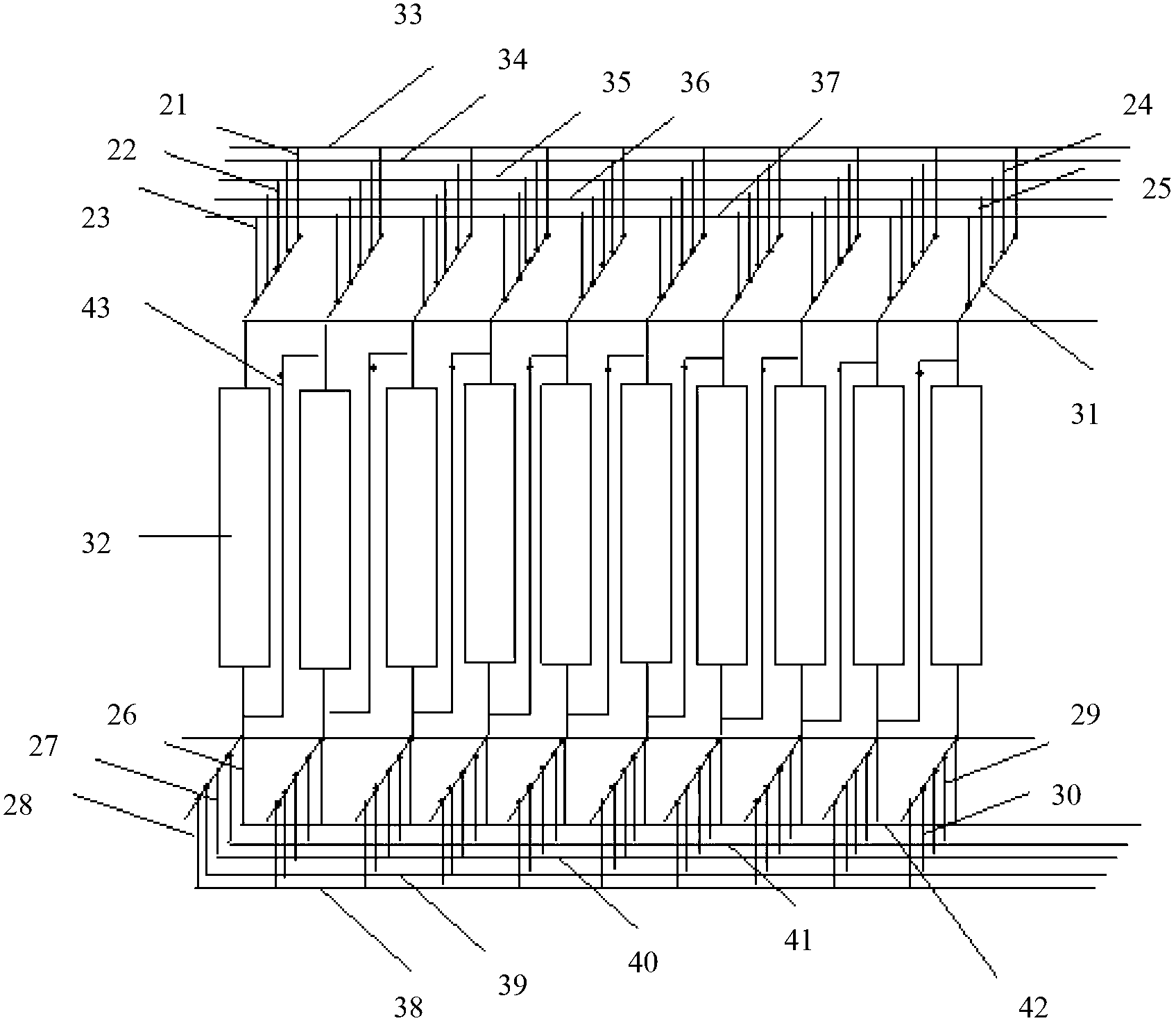
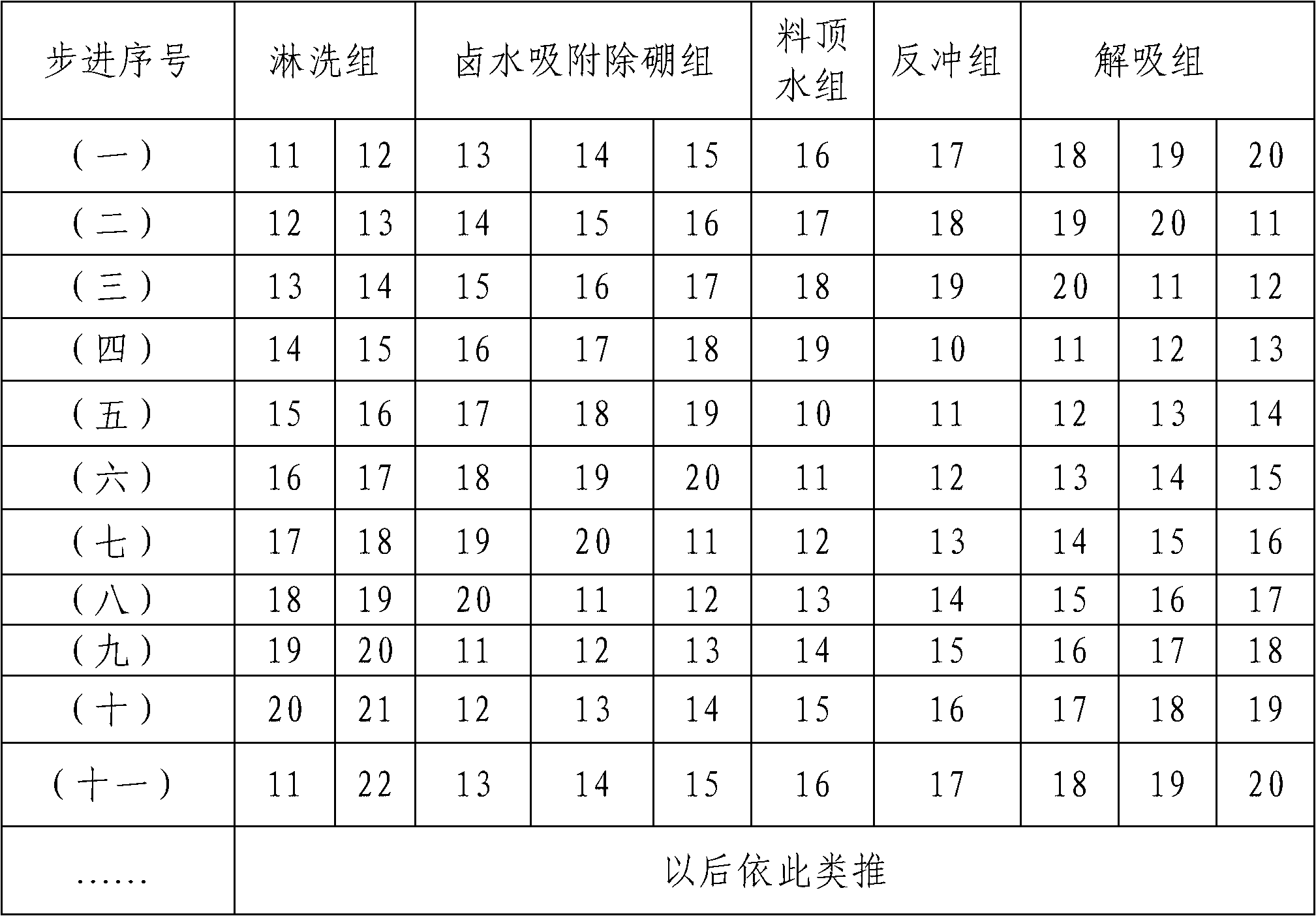
[0106] As shown in Table 1, the continuous ion exchange extraction process of the present invention for removing boron from salt lake magnesium chloride brine adopts continuous ion exchange equipment to remove boron from salt lake magnesium chloride brine, and adopts a series continuous operation mode. (Numbers represent different resin columns)
[0107] Table 1: Functional step-by-step operation table of different regions of the resin column
[0108]
[0109] The method described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0110] The resin of the resin column is seplite LSC-100 (Xi'an Lanxiao Technology New Material Co., Ltd.), and the boron content in the brine is 294ppm.
[0111] As shown in Table 1, each resin column is in the following different resin column groups, taking step number (1) as an example:
[0112] 1#, 2# column: desorption group 3# column: eluting group
[0113] 4#, 5#, 6# columns: brine adsorption boron removal group 7#, 8# columns: material t...
Embodiment 2
[0123] The method described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0124] The resin of the resin column is seplite LSC-800 (Xi'an Lanxiao Technology New Material Co., Ltd.), and the boron content in the brine is 60ppm.
[0125] As shown in Table 1, each resin column is in the following different resin column groups, taking step number (3) as an example:
[0126] 3#, 4# column: desorption group 5# column: eluting group
[0127] 6#, 7#, 8# column: brine adsorption boron removal group 9#, 10# column: material top water group
[0128] 1#, 2# column: recoil group
[0129] 6#, 7#, 8# columns: brine adsorption boron removal group. 6#, 7#, and 8# columns operate in series in forward flow, and the salt lake brine enters the brine feed branch pipe at the top of the 6# column from the brine feed main pipe, passes through the 7# column and 8# column in turn through the series pipeline, and finally The brine discharge branch pipe from the lower port of the 8# column enters ...
Embodiment 3-16
[0137] The difference with embodiment 1 is:
[0138] Carry out comparative experiments under different speed and temperature conditions of the brine adsorption boron removal group:
[0139] The resin of the resin column is sepliteLSC-500 (Xi'an Lanxiao Technology New Materials Co., Ltd.).
[0140] name
[0141] name
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com