Scheelite beneficiation wastewater treatment technique
A technology for wastewater treatment and scheelite beneficiation, applied in mining wastewater treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of stable discharge, incomplete removal, and high operating costs. Achieve the effect of accelerating decomposition and sedimentation speed, stable treatment effect, and small footprint
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
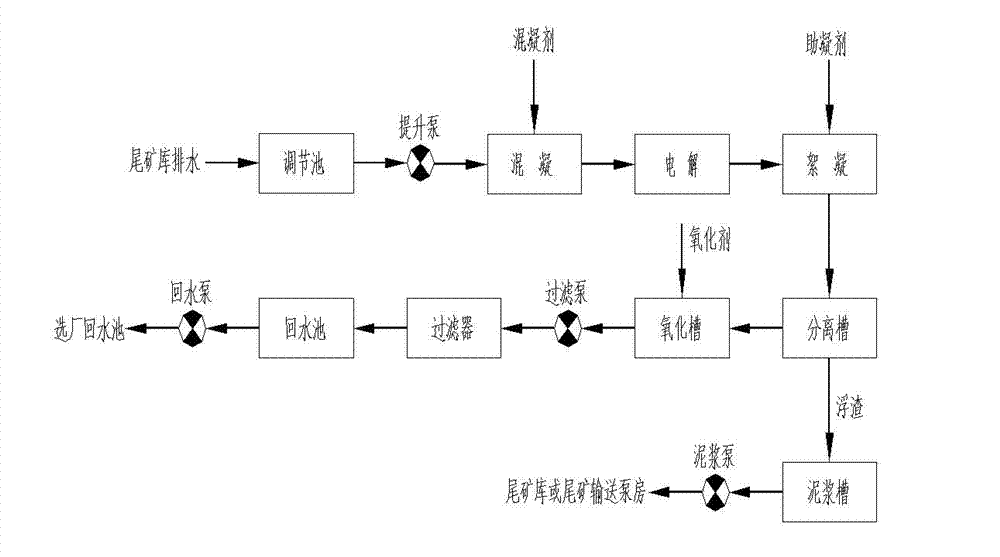
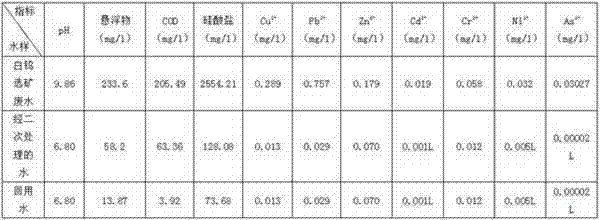
[0015] Example 1 10,000 liters of scheelite beneficiation wastewater, the test data are shown in Table 1, the wastewater was directly electrolyzed to decompose water glass and organic chemicals, and the wastewater after primary treatment was obtained; coagulant aid (PAM) was added to the wastewater after primary treatment 150g, sedimentation removes water glass, obtains the waste water through secondary treatment; The detection data of the waste water through secondary treatment is shown in Table 1; Then in the waste water through secondary treatment, add oxygenant (H 2 o 2 ) 2.1kg, to fully oxidize the remaining organic matter in the water, and filter to obtain water return. The measured data of reused water is shown in Table 1, which exceeds the requirements of the first-level discharge standard of GB 8978-1996 "Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard". The reclaimed water is used in the beneficiation process, which has the same effect as the use of fresh water for benefic...
Embodiment 2
[0018] Example 2 With the scheelite mineral processing wastewater in Example 1, 26 kg of coagulant (PAC) was added to the wastewater, and electrolysis was performed to decompose water glass and organic agents to obtain once-treated wastewater; in the once-treated wastewater Add 200g of coagulation aid (PAM), settle to remove water glass, and obtain secondary treated wastewater; the test data of the secondary treated wastewater is shown in Table 2; then add oxidant (H 2 o 2 ) 2.2kg, fully oxidize the remaining organic matter in the water, and filter to get back water (see process flow chart figure 1 ). The measured data of reused water is shown in Table 2, which exceeds the requirements of the first-level discharge standard of GB 8978-1996 "Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard". The reclaimed water is used in the beneficiation process, which has the same effect as the use of fresh water for beneficiation, and does not affect the beneficiation index.
[0019]
[0020] ...
Embodiment 3
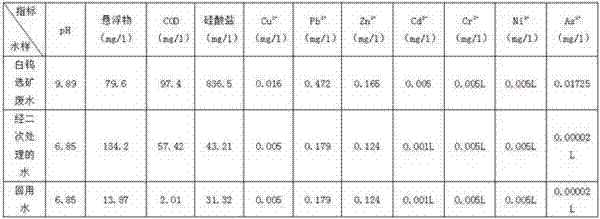
[0021] Example 3 10,000 liters of scheelite beneficiation waste water, 16.5 kg of coagulant (PAC) was added to the waste water, and electrolysis was carried out to decompose water glass and organic agents to obtain once-treated waste water; Add coagulant aid (PAM) 180g, settle to remove water glass, and obtain secondary treated wastewater; the test data of the secondary treated wastewater is shown in Table 2; then add oxidant (H 2 o 2 ) 2.3kg, to fully oxidize the remaining organic matter in the water, and filter to obtain water. The measured data of recycled water is shown in Table 3, exceeding the requirements of the first-level discharge standard of GB 8978-1996 "Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard". The reclaimed water is used in the beneficiation process, which has the same effect as the use of fresh water for beneficiation, and does not affect the beneficiation index.
[0022]
[0023] Table 3 Detection data of scheelite beneficiation wastewater, secondary trea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com