Compound serving as PPAR gamma ligand and application thereof
A technology of ligands and uses, applied to PPARγ ligands, ionomycin (ionomycin) and its derivatives, in the field of treatment of PPARγ-mediated diseases, can solve the problems of side effects restricting use, increasing heart attack rates, weight gain, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] Example 1, proves that ionomycin is a ligand of PPARγ with high specificity and low transcription activity.
[0131] To prove that ionomycin can specifically bind to PPARγ, we co-transfected Cos7 cells with a Gal-4 driven reporter gene and a plasmid containing the target gene of different nuclear receptor LBD fragments. It is obvious that after 10μMionomycin treatment, only cells transfected with PPARγLBD have increased reporter gene activity, which reflects the high specificity of ionomycin as a PPARγ ligand (attached figure 1 A). In addition, ionomycin-mediated transcriptional activity of PPARγ can be inhibited by the PPARγ antagonist 1μM GW9662, which once again confirmed that ionomycin is a ligand of PPARγ (attached figure 1 B).
[0132] The 3T3-L1 preadipocyte oil red staining experiment showed that the ability of 10μM ionomycin to induce adipocyte differentiation was significantly lower than that of 1μM rosiglitazone, that is, the ability of ionomycin to activate PPA...
Embodiment 2
[0134] Example 2, The molecular structure verification experiment of the complex of PPARγ ligand binding region fragment and ionomycin
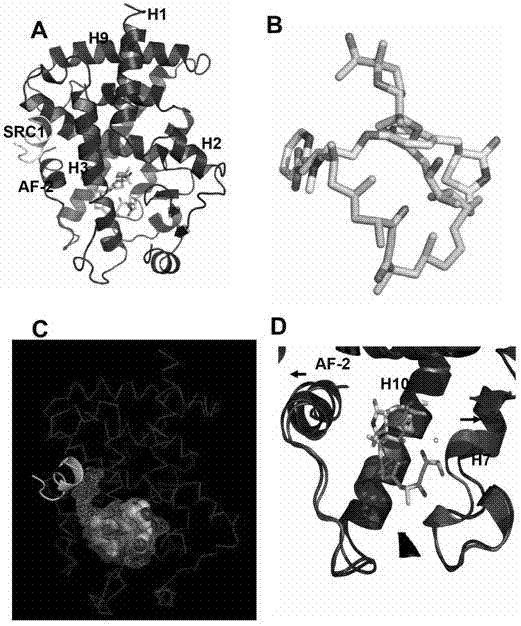
[0135] In order to detect the high affinity of ionmycin and PPARγ at the molecular level, we solved the Protein crystal structure of the PPARγ / ionomcyin complex with the co-activator SRC1-2 LXXLL motif. The structure shows that the combination of ionomycin and PPARγ ligand binding domain conforms to the classical conformation, and the overall structure of the complex is strongly conserved with most regions of PPARγ / rosiglitazone (attached figure 2 A). However, due to the huge difference in molecular weight and structure of ionomycin and rosiglitazone, the difference in the spatial position of the two in the ligand binding pocket and the resulting change in the relative position of the surrounding peptides (attached) figure 2 D). The molecular weight of Ionomycin is about twice that of rosiglitazone, and the structure diagrams of the two overl...
Embodiment 3
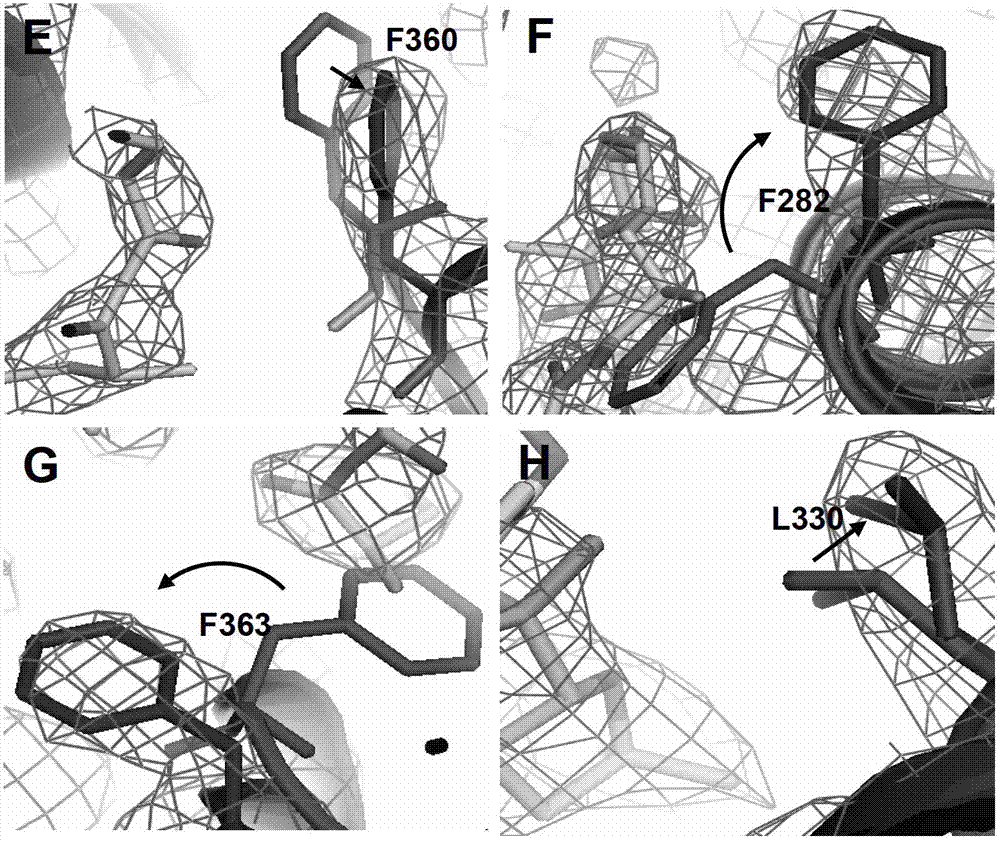
[0136] Example 3. Ionomcyin unique binding site in the PPARγ ligand binding pocket
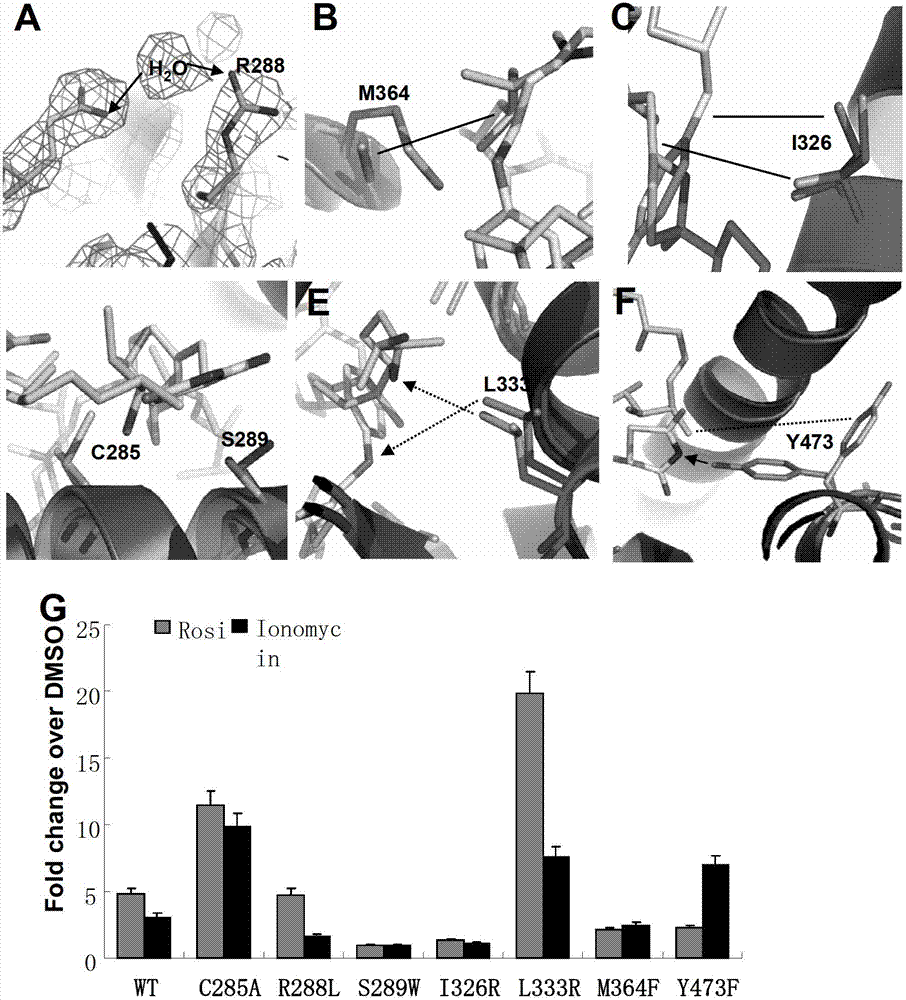
[0137] In order to verify that the ligand pocket residues are binding to ionomycin, we mutated some of the key residues in contact with ionomycin, and then tested the transcriptional activity of these mutant PPARγ to determine the importance of the mutant residues.
[0138] Y473 has been confirmed to play a key role in the formation of stable hydrogen bonds between the complete activator and PPARγH12 and rosiglitazone, while ionomycin and Y473 have only weak hydrophobic effects. Y473F disrupts the formation of hydrogen bonds. Transient transfection experiments have confirmed that Y473F reduces the transcriptional activity of rosiglitazone on PPARγ and promotes the transcriptional activity of ionomycin on PPARγ. This indicates that the structural difference between ionomycin and rosiglitazone leads to its regulation. PPARγ activity produced corresponding changes. (Attached image 3 F)
[0139] R288 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com