Method for preparing efficient adsorbent through in-situ reaction
An in-situ reaction and adsorbent technology, applied in the directions of alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, inorganic chemistry, alkali metal compounds, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to meet continuous operation, unable to reach drinking water, low adsorption efficiency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
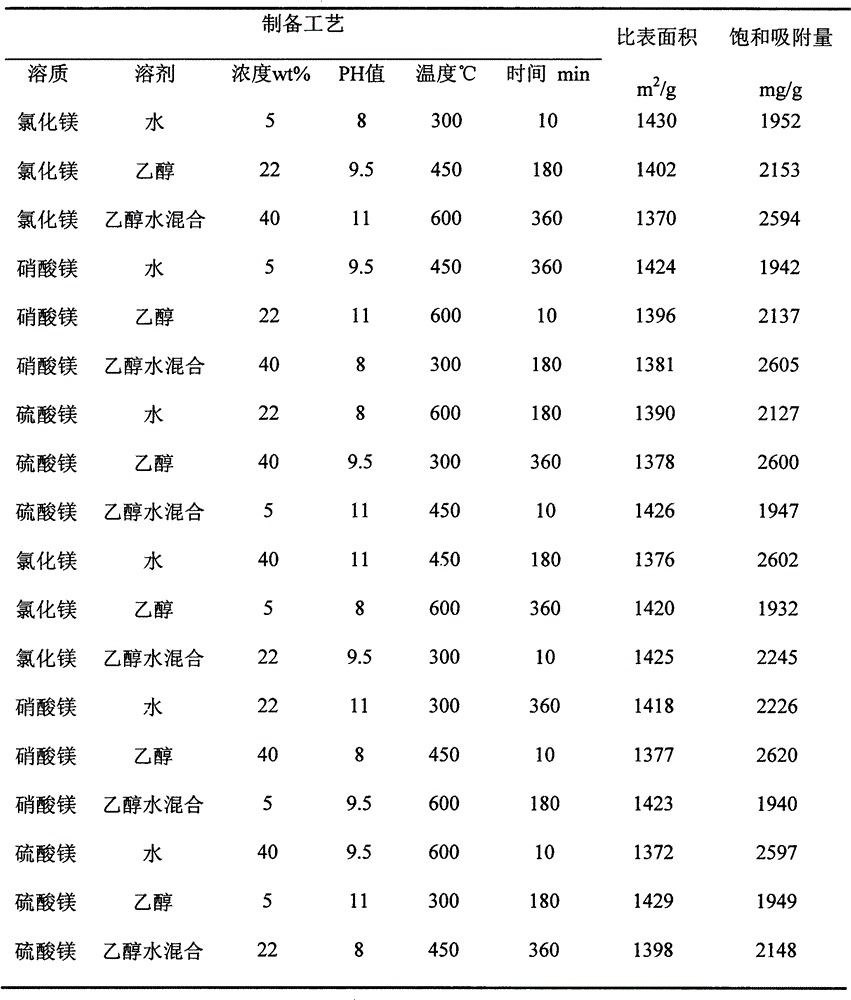
[0014] Soak activated carbon in water, ethanol or ethanol-water mixed solutions with a concentration of 5wt%, 22wt%, and 40wt% magnesium chloride, magnesium nitrate, and magnesium sulfate, stir for 5 hours, and add 10wt% NaOH solution dropwise to adjust the pH value to 8, 9.5, 11 , stirred for 1 hour, filtered, dried, and calcined in a protective atmosphere, the calcining temperatures were 300°C, 450°C, and 600°C, and the calcining times were 10min, 180min, and 360min, respectively. The specific surface area and saturated adsorption capacity for lead ions of the samples obtained from the orthogonal experiments of each process are tested, as shown in Table 1.
[0015] Table 1 Specific surface area of porous magnesium oxide and saturated adsorption capacity for lead ions
[0016]
[0017] The above experiments show that the most important factor affecting the specific surface area is the concentration of the solution, and other factors have less influence, so the following ...
Embodiment 2
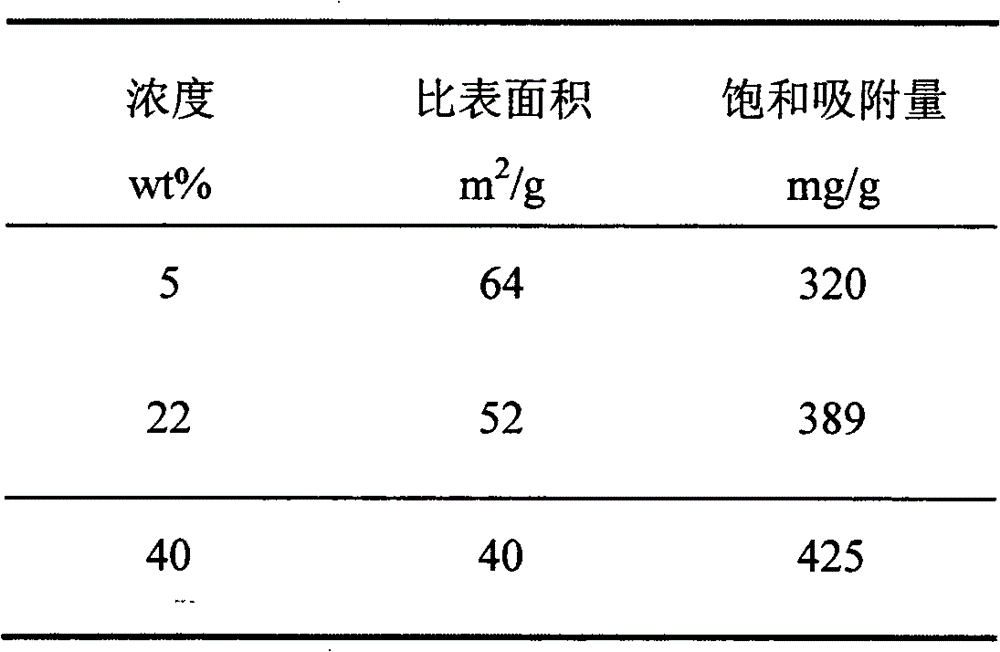
[0019] Soak the diatomite in aqueous solutions of 5wt%, 22wt%, and 40wt% magnesium chloride respectively, stir for 5 hours, add 10wt% ammonia solution dropwise to adjust the pH value to 10, filter after stirring for 1 hour, dry, and calcinate in a protective atmosphere. 600°C and 180min calcination time respectively. The specific surface area and the saturated adsorption capacity of the samples obtained by each process were tested, as shown in Table 2.
[0020] Table 2 Specific surface area of porous magnesium oxide and saturated adsorption capacity for lead ions
[0021]
Embodiment 3
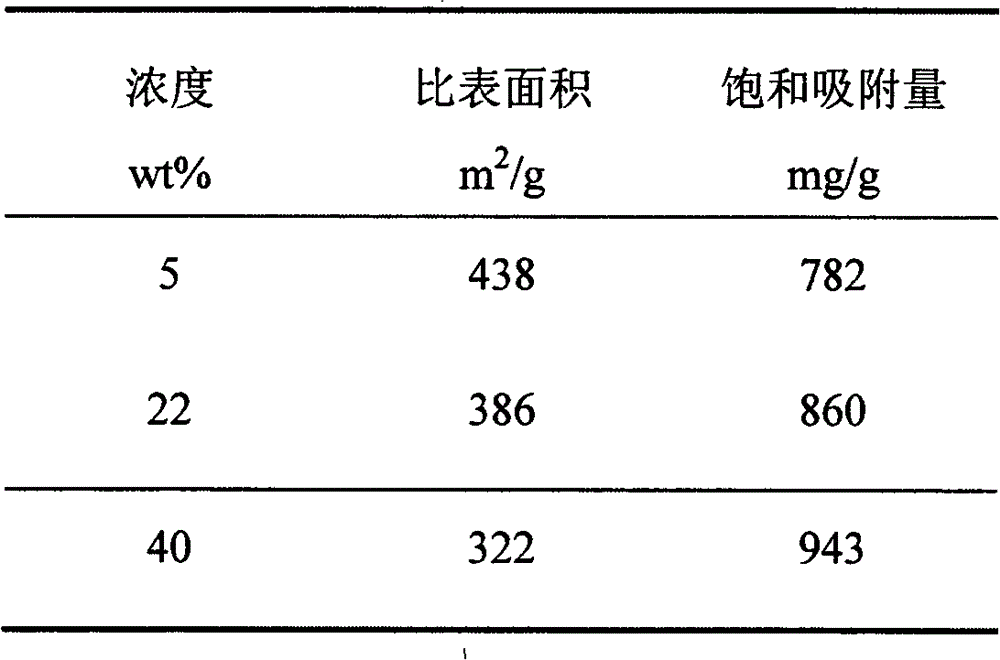
[0023] Soak the silica gel in an aqueous solution of 5wt%, 22wt%, and 40wt% magnesium chloride, stir for 5 hours, add 10wt% ammonia solution dropwise to adjust the pH value to 10, stir for 1 hour, filter, dry, and calcinate in a protective atmosphere at a temperature of 600°C, the calcination time is 180min respectively. The specific surface area and saturated adsorption capacity of the samples obtained by each process were tested, as shown in Table 3.
[0024] Table 3 Specific surface area of porous magnesium oxide and saturated adsorption capacity for lead ions
[0025]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com