Nickel-copper alloy with high strength and high corrosion resistance and manufacturing method thereof
A high corrosion resistance, nickel-copper alloy technology, applied in the field of copper-nickel alloys, can solve problems such as failure to see, and achieve the effects of easy production in processing links, simple processing links and lower production costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
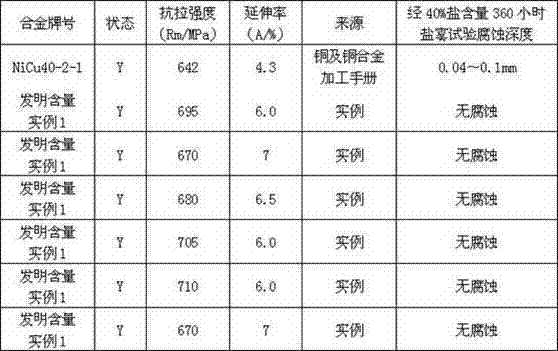
[0016] (1) Prepare alloy materials with electrolytic nickel, electrolytic copper, manganese, iron, silicon, metal magnesium, and metal titanium. The design masses of each group are: electrolytic nickel 14.275 kg, electrolytic copper 10.25 kg, manganese 0.325 kg, iron 0.075 kg, 0.025 kg of silicon, 0.02 kg of magnesium, 0.035 kg of titanium metal (loaded into a 25kg smelting furnace step by step) The operating procedure is as follows: nickel + copper + iron + glass → melting → adding manganese, silicon → stirring to remove slag → adding Glass→stirring→sampling before furnace analysis→temperature measurement→adding titanium and magnesium→sampling→casting;
[0017] (2) Formed by casting, heated to 950-1050°C after casting ingots, billet-rolled and billeted, manually repaired by multiple stretching blade dies, stripped and skinned, annealed at 800-850°C, and then drawn into finished alloys. The total processing rate is controlled between 60-70%, and the finished product processing...
Embodiment 2
[0029] (1) Electrolytic nickel, electrolytic copper, manganese, iron, metal magnesium, and metal titanium are used as raw materials to prepare alloy materials. The design masses of each group are electrolytic nickel 14.458 kg, electrolytic copper 10 kg, manganese 0.35 kg, iron 0.1 kg, and silicon powder 0.03 kg, 0.0175 kg of magnesium, 0.0325 kg of titanium (into a 25 kg melting furnace step by step); the operation procedure is as follows: nickel + copper + iron + glass → melting → adding manganese, silicon → stirring to remove slag → adding glass → stirring → Sampling before furnace analysis→temperature measurement→adding titanium and magnesium→sampling→casting;
[0030] (2) After the ingot is processed, it is heated to 950℃~1050℃ to open the billet and roll the billet. After several times of stretching and peeling, it is manually repaired and then annealed at 800~850℃ to draw the finished alloy; the total processing rate is controlled within 60-70%. During the period, the fi...
Embodiment 3
[0033] (1) Prepare alloy materials with electrolytic nickel, electrolytic copper, manganese, iron, metal magnesium, and metal titanium as raw materials. The design masses of each group are electrolytic nickel 14.598 kg, electrolytic copper 9.78 kg, manganese 0.4 kg, iron 0.15 kg, silicon 0.0325 kg of powder, 0.015 kg of magnesium, and 0.03 kg of titanium (loaded into a 25kg melting furnace step by step); the operating procedure is as follows: nickel + copper + iron + glass → melting → adding manganese, silicon → stirring to remove slag → adding glass → stirring →Sampling before furnace analysis→temperature measurement→adding titanium and magnesium→sampling→casting;
[0034] (2) After the ingot is processed, it is heated to 950℃~1050℃ to open the billet and roll the billet. After several times of stretching and peeling, it is manually repaired and then annealed at 800~850℃ to draw the finished alloy; the total processing rate is controlled within 60-70%. During the period, the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com