In-situ repair method for polluted sediment nitrogen nutritive salt and in-situ repairing pile applied to in-situ repair method
An in-situ restoration and sedimentation technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, sludge treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of poor long-term restoration effect, improve the activity of indigenous microorganisms, and reduce costs , easy-to-operate effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
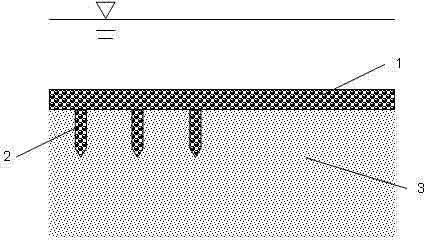
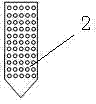
[0033] like figure 1 , the in-situ repair method of the present embodiment, the steps are:
[0034] 1) Preparation of nitrogen-immobilized materials
[0035] According to the patent "A Groundwater Nitrogen Immobilization Restoration Filter Material and Its Preparation Method" (patent application number: 201110001391.5), select clinoptilolite, palygorskite, and diatomaceous earth and mix them according to the mass ratio of 70:25:5. h 2 O as a bonding material, made into 5mm pellets in a granulator, calcined in a rotary furnace at 450°C for 4 hours, and sintered into a nitrogen-immobilized material with a particle strength >30N.
[0036] 2) Preparation of slow-release oxygen material
[0037]According to the patent "A Slow-release Oxygen Material for Groundwater Restoration and Its Preparation Method" (patent application number: 201110426869.9), calcium peroxide was selected as the oxygen-releasing agent, cement was used as the plastic binder, fly ash was used as the pH buff...
Embodiment 2
[0046] combine figure 1 , the steps of the in-situ repair method in this embodiment are as follows:
[0047] 1) Preparation of nitrogen-immobilized materials
[0048] According to the patent "A groundwater nitrogen immobilization repair filter material and its preparation method" (patent application number: 201110001391.5), select clinoptilolite, palygorskite, diatomite, mix according to the ratio of 70:25:5, and use H 2 O as a bonding material, made into 5mm pellets in a granulator, calcined in a rotary furnace at 450°C for 4 hours, and sintered into a nitrogen-immobilized material with a particle strength >30N.
[0049] 2) Preparation of slow-release oxygen materials
[0050] According to the patent "A Slow-release Oxygen Material for Groundwater Restoration and Its Preparation Method" (patent application number: 201110426869.9), calcium peroxide was selected as the oxygen-releasing agent, cement was used as the plastic binder, fly ash was used as the pH buffer, and quart...
Embodiment 3
[0056] During the test, samples were taken regularly to determine the changes in the static release of total nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen in the sediment. The results showed that after 6 months of operation, the concentration of total nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen and the content of organic matter in the sediments of the control river reach were 24.7-72.5 mg·L-1, 11.02-48.83 mg·L-1, 15.40%-20.00% respectively , the concentration of total nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen and the content of organic matter in the restored river section sediments were 5.20-7.15 mg·L-1, 2.75-3.78 mg·L-1, 9.24%-12.55%, and the restoration effect was 79%-80.1 %, 75%~92%, 37.5%~39.5%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Grain strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com