Method for quickly distinguishing bud mutation of grape
A bud transformation and grape technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as inability to effectively judge plants, low efficiency, and large environmental and experience influences, and achieve easy popularization and operation. , a wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] The extraction of embodiment 1, DNA
[0030] 1. After pre-cooling the mortar, add a small amount of liquid nitrogen and pre-cool it sufficiently;
[0031] 2. Take 3g of fresh, intact and clean leaves pre-cooled at -20°C and put them into a mortar, add half a medicine spoon of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and appropriate amount of liquid nitrogen, grind to fine powder, put into a centrifuge tube, and refrigerate at -20°C 30min;
[0032] 3. Prepare CTAB extraction buffer: weigh CTAB 2g, add distilled water 40ml, 1M Tris-cl (pH8.0) 10ml, 0.5M EDTA (pH 8.0) 4ml and 5M NaCl 28ml, after CTAB is dissolved, dilute to 100ml with distilled water , heat, and then add 2% β-mercaptoethanol to boiling;
[0033] 4. Put the hot CTAB extraction buffer into the centrifuge tube of step 2), 5ml per tube, and evenly disperse the leaf tissue in the buffer, and then put it in a constant temperature water bath at 65°C for 90 minutes, gently light every 5 minutes Gently invert and shake once;
...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2, iPBS-PCR amplification
[0041] Refer to Kalendar et al. for the PCR amplification system and procedures, as shown in Table 2 and Table 3, and the primers were synthesized by Shanghai Bioengineering Technology Co., Ltd., as shown in Table 4.
[0042] Table 2 iPBS-PCR amplification reaction system
[0043] Reagent name
[0044] Table 3 iPBS-PCR amplification reaction program
[0045] program name
[0046] Note: The three steps of denaturation, annealing and extension were cycled 30 times.
[0047] Table 4 iPBS-PCR amplification primers
[0048] serial number
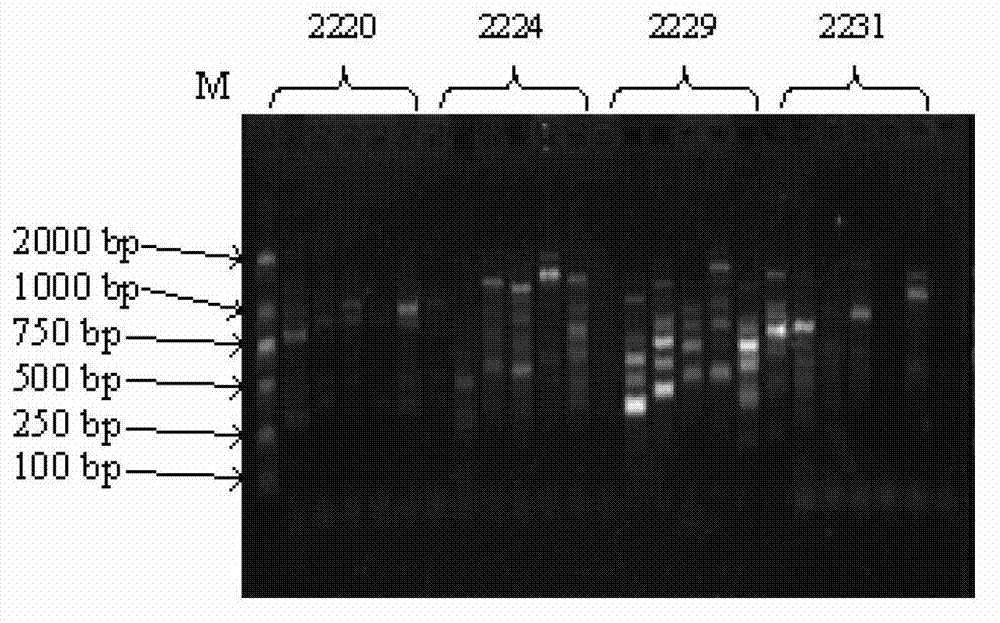
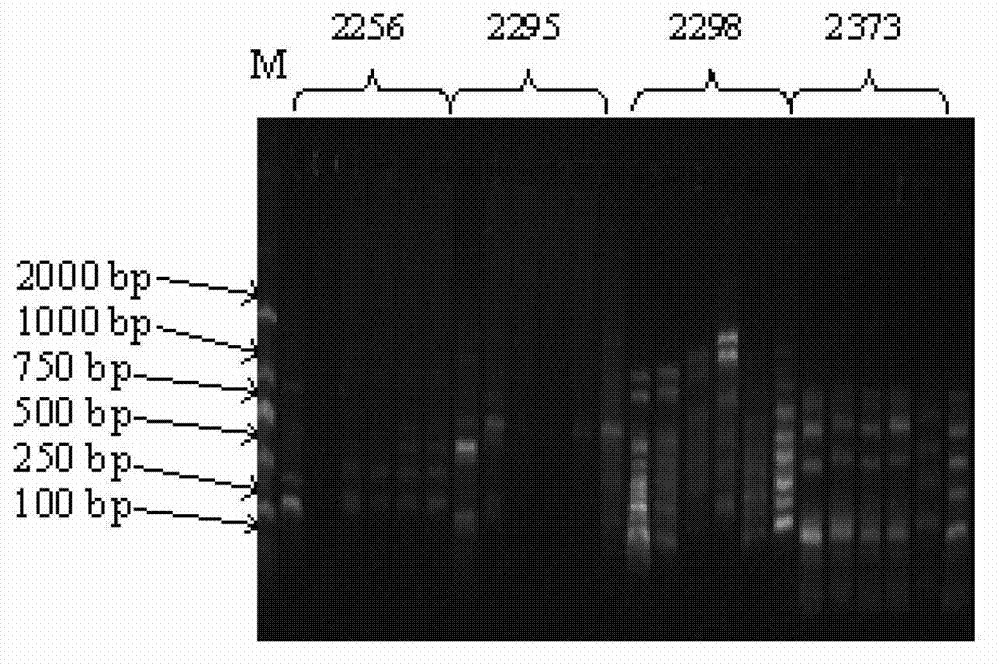
[0049] Wherein, the nucleotide sequence of primer 2224 is the sequence listing SEQ ID NO: 1; the nucleotide sequence of the primer 2229 is the sequence listing SEQ ID NO: 2; the nucleotide sequence of the primer 2298 is the sequence listing SEQ ID NO: 3; The nucleotide sequence of primer 2373 is SEQ ID NO: 4 in the sequence listing.
Embodiment 3
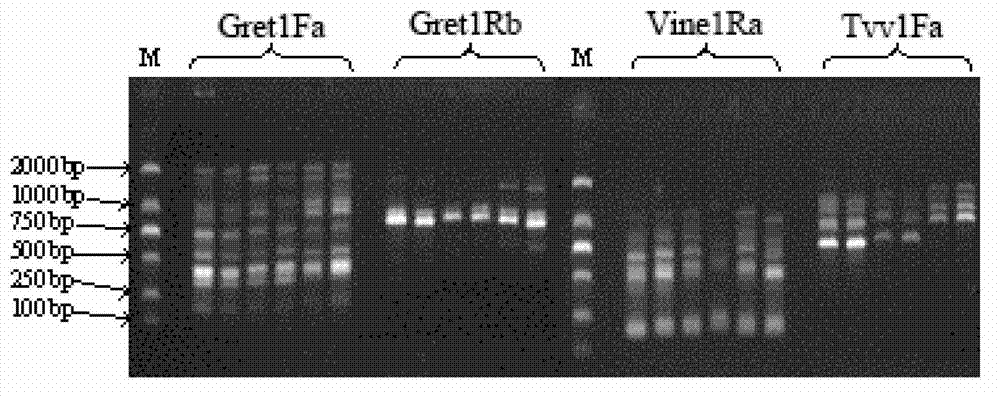
[0050] Embodiment 3, agarose gel electrophoresis detection
[0051] 1) Preparation of buffer solution: Dilute 5×TBE to 0.5×TBE.
[0052] 2) Preparation of glue solution: Weigh 0.70g of agarose, put it in a conical flask, add 70mL of 0.5×TBE dilution buffer, put it in a microwave oven and heat and boil three times until the agarose is completely melted, take it out and shake well, this is 1.0% agarose gel solution.
[0053] 3) Preparation of the gel plate: Cool the boiled agarose gel to 50°C, slowly pour it into the gel tank placed on a horizontal table, let it cool for 60 minutes, and gently pull out the comb.
[0054] 4) Adding samples: Take 5 μL of DNA amplification product, add 1 μL of staining solution, 2.5 μL of bromophenol blue, flick to mix well, and add 5 μL of sample to the well.
[0055] 5) Electrophoresis: After adding the sample, close the cover of the electrophoresis tank, turn on the power immediately, and perform electrophoresis for 40 minutes.
[0056] 6) Ob...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com