Method for recycling waste lead-acid cells to directly produce lead oxide
A lead-acid battery, lead oxide technology, applied in the field of hydrometallurgy, can solve the problem of consuming large acid and alkali, and achieve the effect of improving recovery efficiency, significant environmental value, and shortening treatment process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
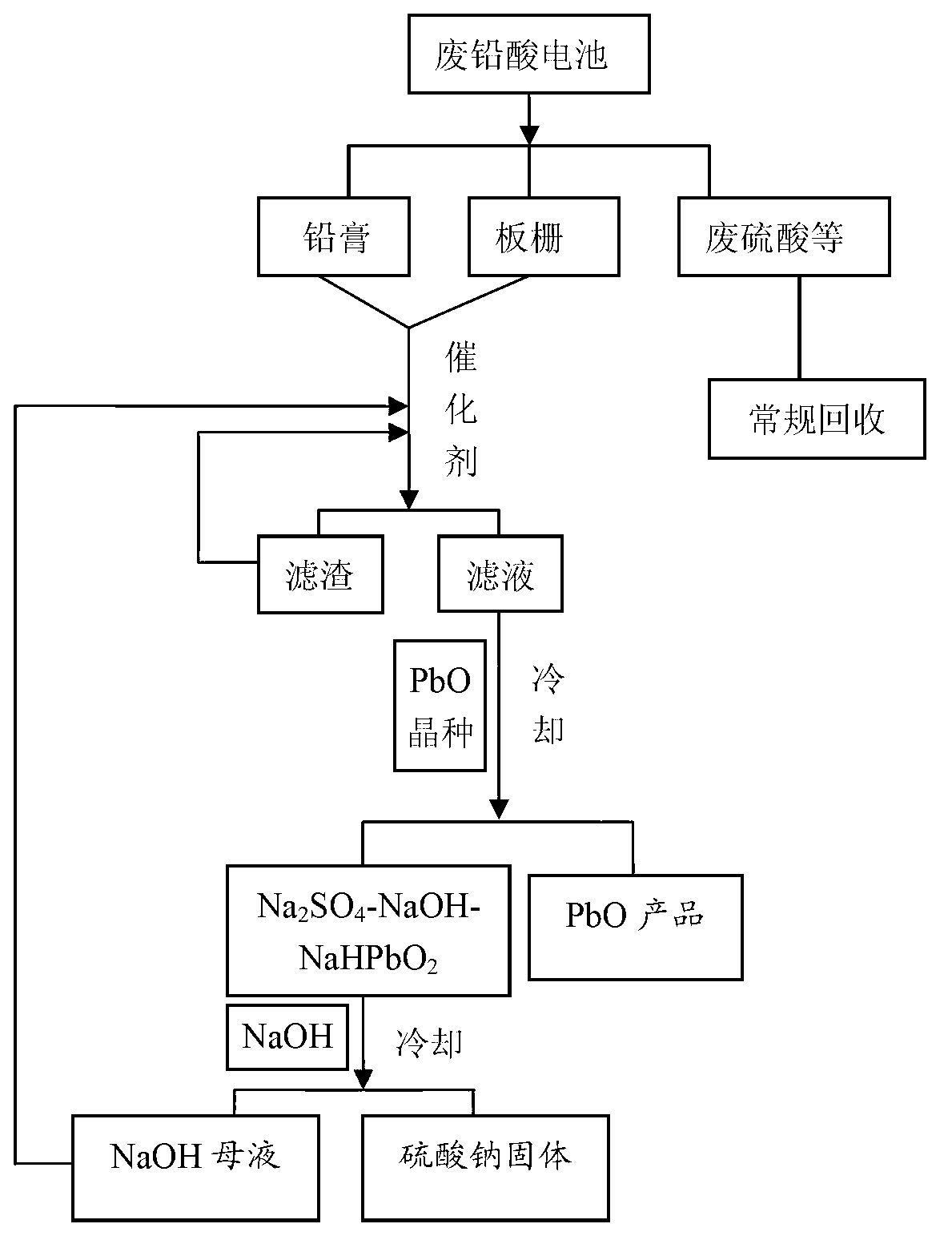
[0059] Get 2 pieces of 12V, 12Ah ordinary electric vehicle waste lead-acid batteries purchased on the market, and the total weight of the battery pack is 9.2 kg. The specific implementation process is as follows:
[0060] 1) After conventional crushing and separation of waste lead-acid batteries, lead paste, grids, waste sulfuric acid, separators and casings are obtained.
[0061] 2) Put the lead paste filtered out into the crusher and ball mill in turn for crushing, and then sieve with a 60-mesh stainless steel screen. The larger lead paste particles continue to be transferred to the grinder for crushing until all the lead paste is completely through a sieve.
[0062] 3) The grids are placed in the crusher and ball mill in turn for crushing, and then sieved with a 20-mesh stainless steel screen, and the larger lead particles continue to be transferred to the crusher for crushing until all the lead particles pass through the screen for later use .
[0063] 4) Prepare 40L of...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Take a 12V, 45Ah waste automobile lead-acid battery, the total weight of the battery pack is 13.2 kg, the specific recycling process is as follows:
[0071] According to (1), (2) and (3) process of embodiment 1, obtain the broken lead paste and grid.
[0072] 4) Prepare 80L of NaOH solution with a concentration of 30% by weight, and at the same time dissolve 300 grams of antimony oxide solid in the NaOH solution as a catalyst, and place the solution for later use.
[0073] 5) Put 5 kg of lead paste in (2) and 3.5 kg of excess lead particles obtained in (3) into the above NaOH solution to make Pb and PbO 2 , and PbSO 4 React with NaOH, so that they are uniformly transformed into PbO, and dissolved in NaOH solution. During the reaction, the reaction temperature was kept at 100° C., and the stirring speed was 100 rpm.
[0074] 4) Filter after 2 hours of reaction to obtain a clear filtrate, a filter residue consisting of a small amount of residual lead powder and insolub...
Embodiment 3
[0079] Take the same waste automobile lead-acid battery as in Example 2, and follow the same (1), (2) and (3) process to obtain the broken lead paste and grid.
[0080] 4) Prepare 75L NaOH solution with a concentration of 28% by weight and place it in a sealed bucket for later use.
[0081] 5) Put 5 kg of lead paste in (2) process, and add 3.3 kg of excess lead pellets obtained in (3), and 200 g of commercially available antimony powder as a catalyst into the above NaOH solution to make Pb and PbO 2 , and PbSO 4 React with NaOH, so that they are uniformly transformed into PbO, and dissolved in NaOH solution. During the reaction, the reaction temperature was kept at 105° C., and the stirring speed was 80 rpm.
[0082] 4) Filter after 2 hours of reaction to obtain a clear filtrate, a filter residue consisting of a small amount of residual lead powder and insoluble impurities.
[0083] 7) The filtrate was placed in a crystallization tank for gradual cooling, and at the same ti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com