Lipase made of aspergillus niger strains, and producing method and utilization thereof
A technology of Aspergillus niger strain and lipase, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as restricting industrial applications, and achieve the effects of low fermentation production cost, good commercial prospects, and stable temperature.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Aspergillus niger strain (Aspergillus niger) AN0512
[0038] 1. Identification of strain AN0512
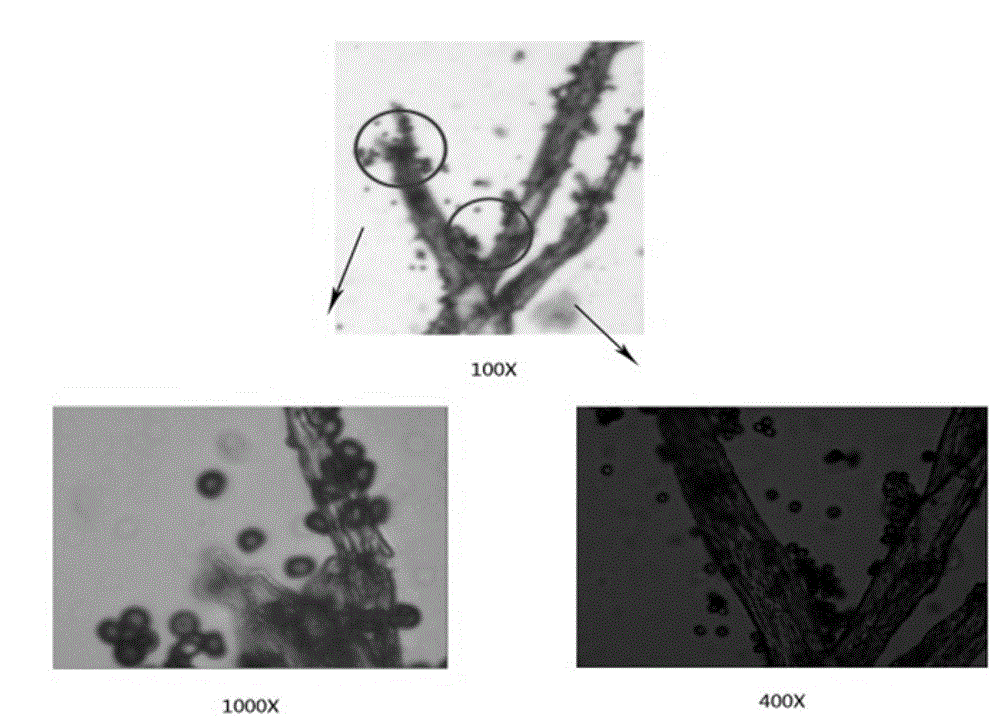
[0039] The lipase-producing strain 0512 isolated from Tibetan milk dregs was cultured on a PDA slant medium at 28°C for 48 hours. It was observed that the colonies spread rapidly, and the slant was covered with white hyphae. After 72 hours of cultivation, the bacteria turned light yellow until dark brown velvet ( figure 1 ). Microscopic observation of the mycelia showed that figure 2 As shown, the hyphae and spores under different magnifications are clearly visible, some have dichotomous branches, more or less transverse, and the spores are oval or round. According to the above morphology, it was preliminarily determined that strain 0512 belonged to the genus Mold.
[0040] In order to further confirm the species attribute of strain 0512, the 18s rRNA of 0512 was amplified by PCR, and the amplification primers used fungal universal primers: F: 5'-CCA GTA GTC ATA TGC TC...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Method for producing lipase from Aspergillus niger AN0512
[0047] 1. Preparation of crude enzyme solution
[0048] Prepare a medium containing 0.8% (v / w) of olive oil, 2% (w / w, the same below) of yeast extract, 0.2% of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.05% of magnesium sulfate, and 0.05% of potassium chloride, and adjust the pH to 7.0, after sterilization at 121°C, inoculate first-grade seeds at 1.5% (v / v), culture at 29°C and 250r / m for 90h, and centrifuge at 4°C and 10,000r / m for 20min. Remove the bacterial cells and take the supernatant as a crude enzyme solution, and take the crude enzyme solution for enzymatic property experiments.
[0049] (1) Optimum reaction temperature: the change of enzyme activity in the temperature range of 25-70°C was investigated, and the results are as follows: Figure 4 As shown, the results show that the optimum reaction temperature of the crude enzyme is 30°C, and the crude enzyme still retains more than 60% of the enzyme activity a...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Lipase produced by Aspergillus niger AN0512
[0061] Properties of Electrophoretic Pure Lipase
[0062] The electrophoretic pure lipase collected by molecular exclusion chromatography in Example 2 was used for lipase property experiment.
[0063] (1) Optimum reaction temperature: Use disodium hydrogen phosphate-citric acid with pH 7.0 as the buffer solution to prepare the lipase activity assay reaction system, preheat the reaction system at 20-70°C for 30 minutes, and then measure the enzyme live, the result is as Figure 7 , it can be seen from the figure that the optimum reaction temperature of the lipase is 50°C, and it still has 50% of the enzyme activity at 60°C.
[0064] (2) Optimum reaction pH: The lipase catalytic reaction system was prepared by disodium hydrogen phosphate-citric acid buffer solution in different pH ranges, and the reaction system was reacted at 37°C for 30 minutes to measure the enzyme activity. The results were as follows: Figure 8 , it ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com