Binding material for filling fine-grain tailings
A technology of cementitious materials and fine-grained tailings, which is applied in the field of mine filling materials, can solve the problems of low cementation and cementation strength of tailings, and achieve the effects of reducing costs, construction investment and maintenance costs, and simple production processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
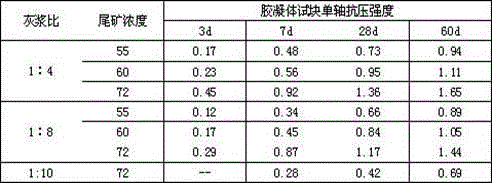
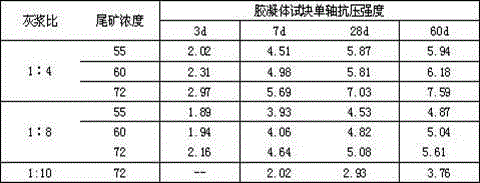
[0032] Belite-sulfoaluminate cement is compounded according to the ratio of 1:3 between sulfoaluminate cement and ordinary Portland cement, and the components in Example 1 are mixed and ground to obtain a cementitious material. The cementitious materials were subjected to cementation tests with the whole tailings of fine ore and the graded tailings of -200 mesh copper ore respectively. The compressive strengths are shown in Table 2 and Table 3.
[0033] Table 2 Full tailings of fine ore (40% mud content), compressive strength of gel (MPa)
[0034]
[0035] The mortar ratio refers to the mass ratio of the cementitious material of the present invention to the tailings slurry, the same below.
[0036] Table 3 -200 mesh copper ore graded tailings, gel compressive strength (MPa)
[0037]
Embodiment 2
[0039] Belite-sulfoaluminate cement is compounded according to the ratio of 1:3 between sulfoaluminate cement and ordinary Portland cement, and the components in Example 1 are mixed and ground to obtain a cementitious material. The cementitious material was subjected to cementation tests with the whole tailings of powder ore and the graded tailings of -200 mesh copper ore respectively. The compressive strengths are shown in Table 4 and Table 5.
[0040] Table 4 Whole tailings of powder ore (40% mud content), compressive strength of gel
[0041]
[0042] Table 5 -200 mesh copper ore graded tailings, gel compressive strength
[0043]
Embodiment 3
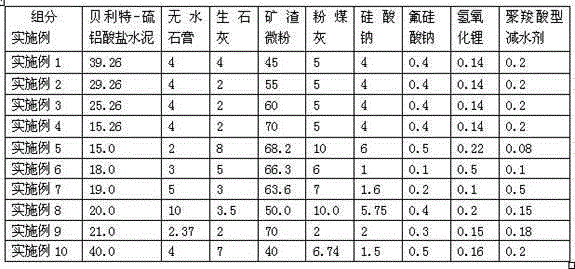
[0045] 25.26% Belite-sulfoaluminate cement (sulfoaluminate cement and ordinary Portland cement are compounded at a ratio of 1:3), 4% anhydrite, 2% quicklime, 60% slag micropowder, 5 % fly ash, 4% sodium silicate, 0.4% sodium fluorosilicate, 0.14% lithium hydroxide, and 0.2% polycarboxylate water reducer are mixed and milled to obtain a gelled material. The cementitious material was subjected to cementation tests with the whole tailings of fine ore and the graded tailings of -200 mesh copper ore respectively. The compressive strengths are shown in Table 6 and Table 7.
[0046] Table 6 Full tailings of fine ore (40% mud content), compressive strength of gel (MPa)
[0047]
[0048] Table 7 -200 mesh copper ore graded tailings, gel compressive strength (MPa)
[0049]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| activation index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com