Production of calcium carbonate from waste sludge
A technology of calcium carbonate and sludge, applied in the direction of calcium carbonate/strontium/barium, combustion methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as not giving product quality, and achieve excellent rheological effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
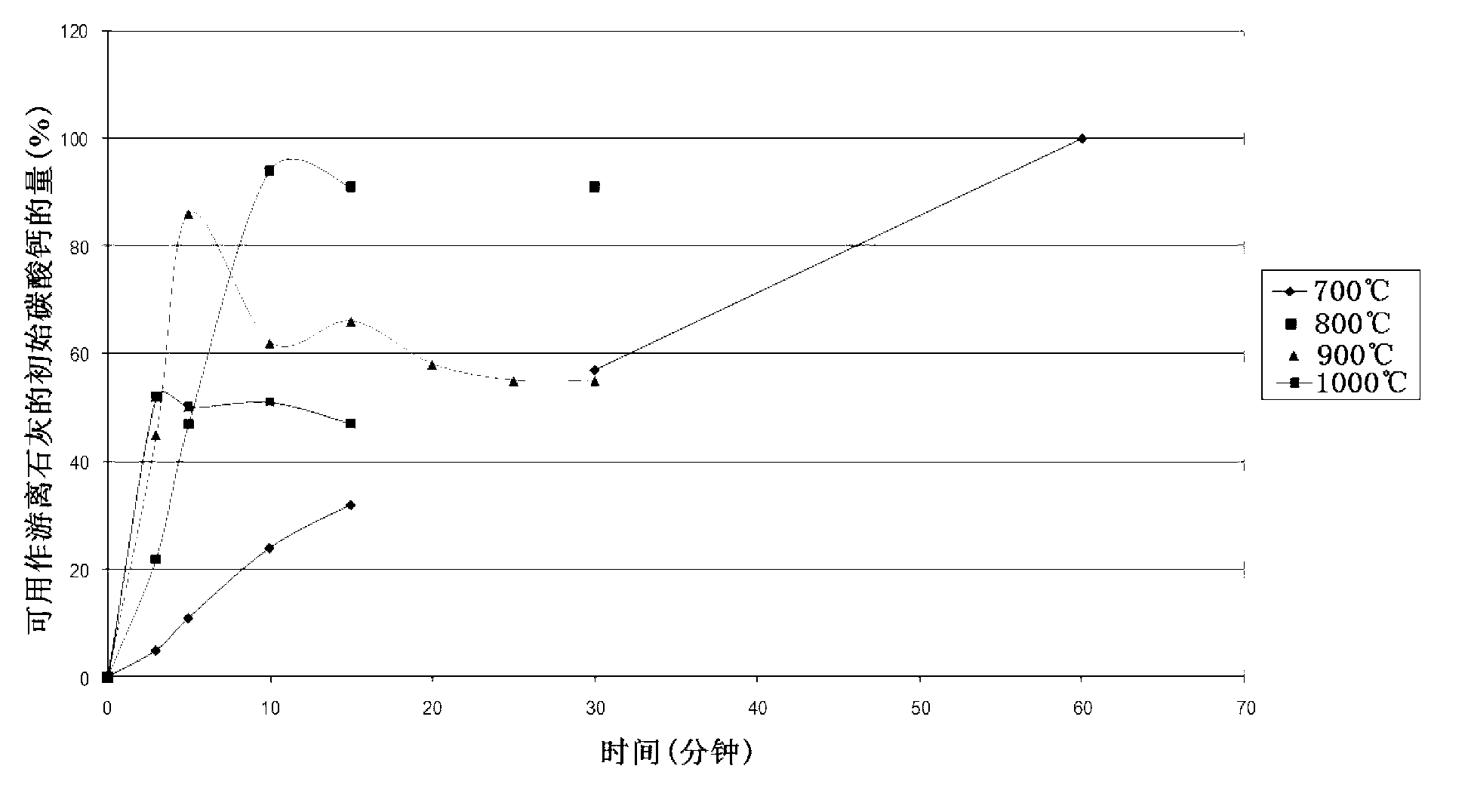
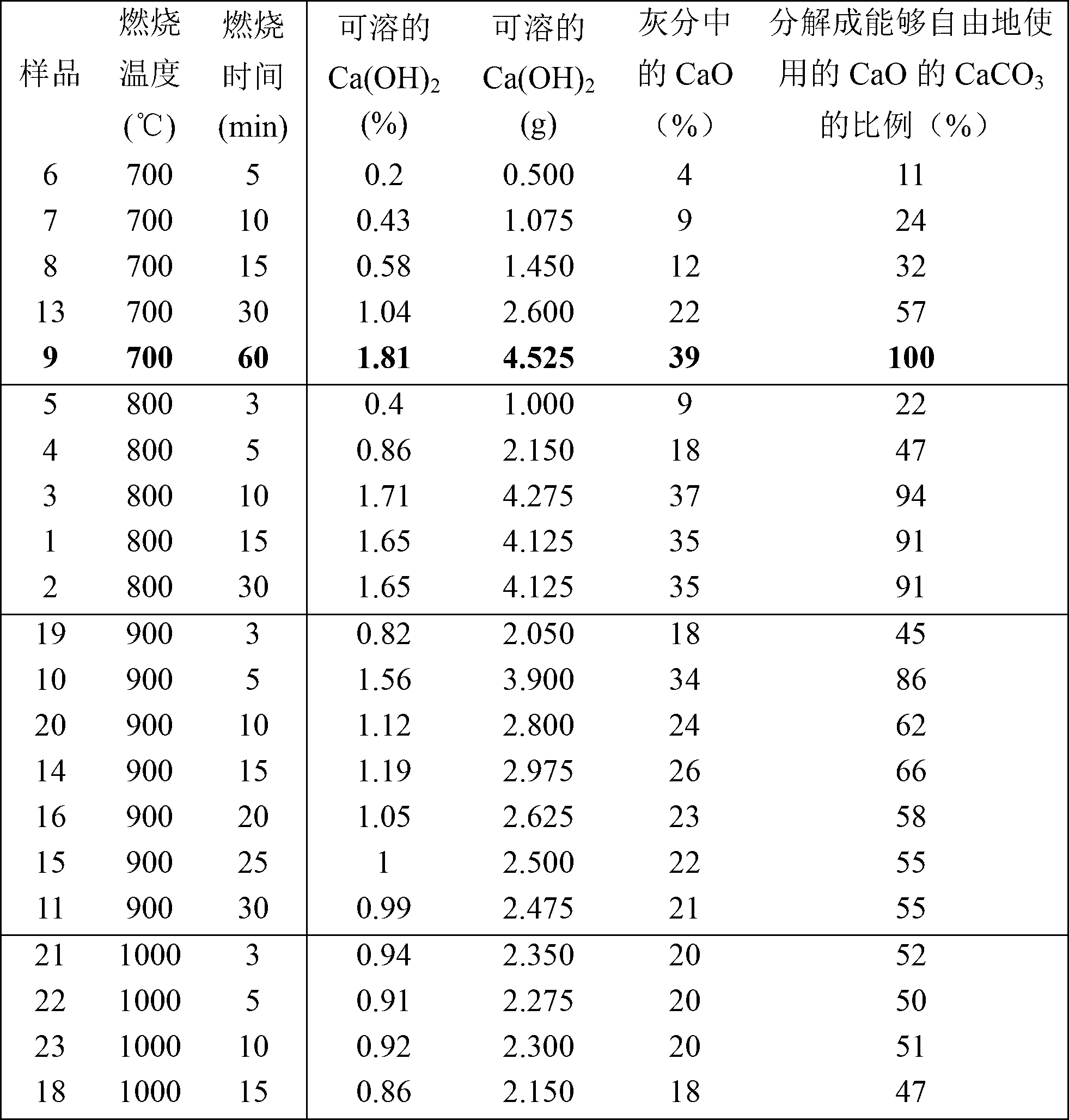
[0126] This example demonstrates how temperature and time affect the composition of the ash obtained from paper sludge in terms of the amount of freely available calcium oxide present in the sludge.
[0127] For paper sludge using deinked fibers from a German paper mill, 50 g of the sample was burned in an experimental electric furnace at temperatures of 700 °C, 800 °C, 900 °C and 1000 °C for different times. In order to reduce material layer thickness and increase heat flow, small samples are evenly distributed over large trays.
[0128] The effect of these combustion conditions on the amount of freely available calcium oxide in the PSA was determined by adding 8.799 g of ash to 250 g of an aqueous solution containing 25% sorbitol. The mixture was then stirred in a 1 L laboratory beaker for 30 minutes, and insolubles were removed by filtration using a Buchner funnel. The remaining clear filtrate was titrated with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid to determine the concentration of calc...
Embodiment 2
[0136] 150 g of deinked sludge from Aylesford Newsprint were heated under atmospheric conditions in a laboratory furnace. The initial heating was at 600°C for 15 minutes to dry and burn the organic components of the sludge. This is followed by a second heating stage at 800° C. for 2 hours to ensure that all calcium carbonate contained in the sludge is decomposed into calcium oxide. The resulting ash was then cooled and then ground in a Janke & Kunkel mill for 1 minute.
[0137] XRD analysis of this PSA confirmed that all calcium carbonate was decomposed and no glassy complex silicate was formed. PSA has the following composition:
[0138] 0% calcium carbonate
[0139] 60% lime (CaO&Ca(OH) 2 )*
[0140] 1% Quartz
[0141] 39% amorphous metakaolin
[0142] *Some hydration reactions occur when the hot ash cools in the humid atmosphere.
[0143]30 g of the ground powder were added directly to 505 g of an aqueous solution containing 25% by weight sorbitol.
[0144] The mix...
Embodiment 3
[0156] Embodiment 3 (comparative)
[0157] Paper sludge (PSA) from Ayersford Newsprint was characterized as having a brightness of 68% (R457) and a very wide range of particle sizes between 1-200 microns. This PSA has an approximate composition as determined by XRD.
[0158]
[0159] The equivalents of CaO (expressed as mass percent of ash) provided by each of the above components is illustrated in Table 2 below.
[0160] Table 2
[0161] components Equivalent of CaO (%) Lime (expressed as CaO) 23.4 Ca(OH) 2 1.6 calcium carbonate 9.7 Calceolite 3.6 Alpha wollastonite 10.8 calcium aluminate 1.3 quartz - Metakaolin -
[0162] Thus, an ash comprising 50.4% by weight equivalent of lime relative to 100 g of ash represents 90 g of calcium carbonate in the initial sludge (i.e. (50.4 / 56*100, where 56 is the molecular weight of calcium oxide and 100 is the molecular weight of calcium carbonate). molecular weight). ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| whiteness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com