Method of removing metal film covering surface of polymer substrate by direct laser etching
A laser direct, polymer technology, applied in the field of metal film, can solve the problems of poor etching accuracy and process repeatability, imperfect pulse energy stability, poor process applicability, etc., to achieve good processing quality and process repeatability, Good applicability and the effect of saving processing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
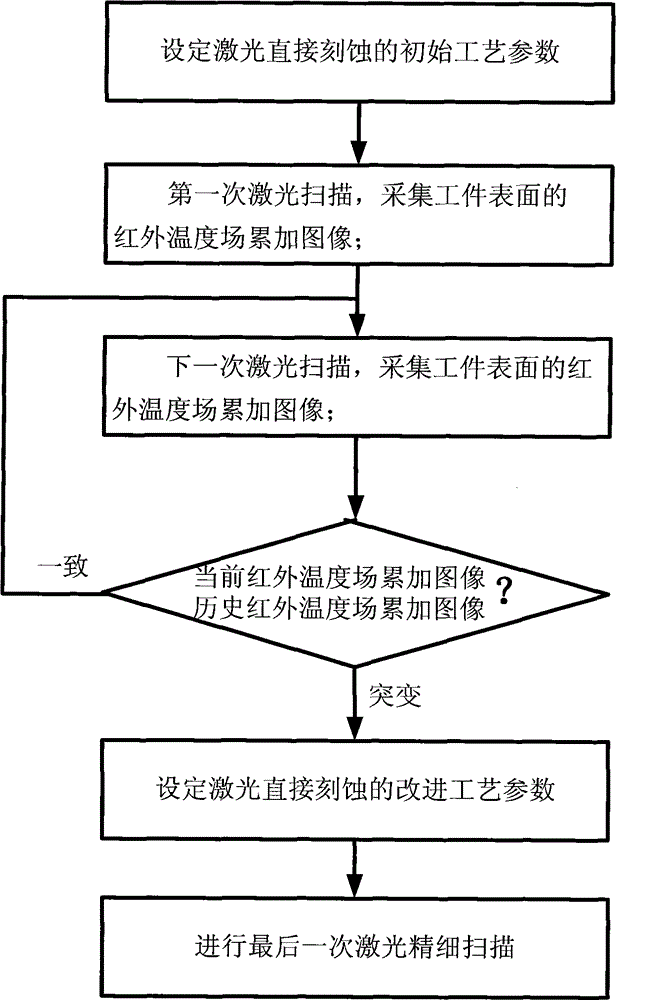
[0043] Ordinary galvanometer scanning ultraviolet laser micromachining equipment is used, and an infrared thermal imager is installed on the galvanometer processing head to form a closed-loop adaptive process control system. The copper clad film on the surface of polyimide is directly etched by laser. The thickness of the polyimide substrate is 100 μm, the thickness of the copper clad film is 40 μm, and the circuit density to be processed is 65%. The steps are as follows:
[0044] First set the initial process parameters of laser direct etching, laser wavelength = 355Nm, beam quality factor M 2 =1.1, pulse repetition frequency 60kHz, laser power 6W, scanning speed 1000mm / s, defocusing amount=0, on / off light delay amount=0, overlapping rate of multi-channel scanning=15%, under the initial process parameters, The test shows that the thickness of the copper clad film that can be removed by a single laser scan is 3.5 μm, which is much smaller than the maximum allowable damage dept...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com