Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for producing 7-dehydrocholesterol and construction method
A technology for dehydrocholesterol and yeast, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of unsatisfactory source and yield, many reaction steps, and complicated by-product removal process and other problems, to achieve the effect of green cleaning and making up for defects in the production process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
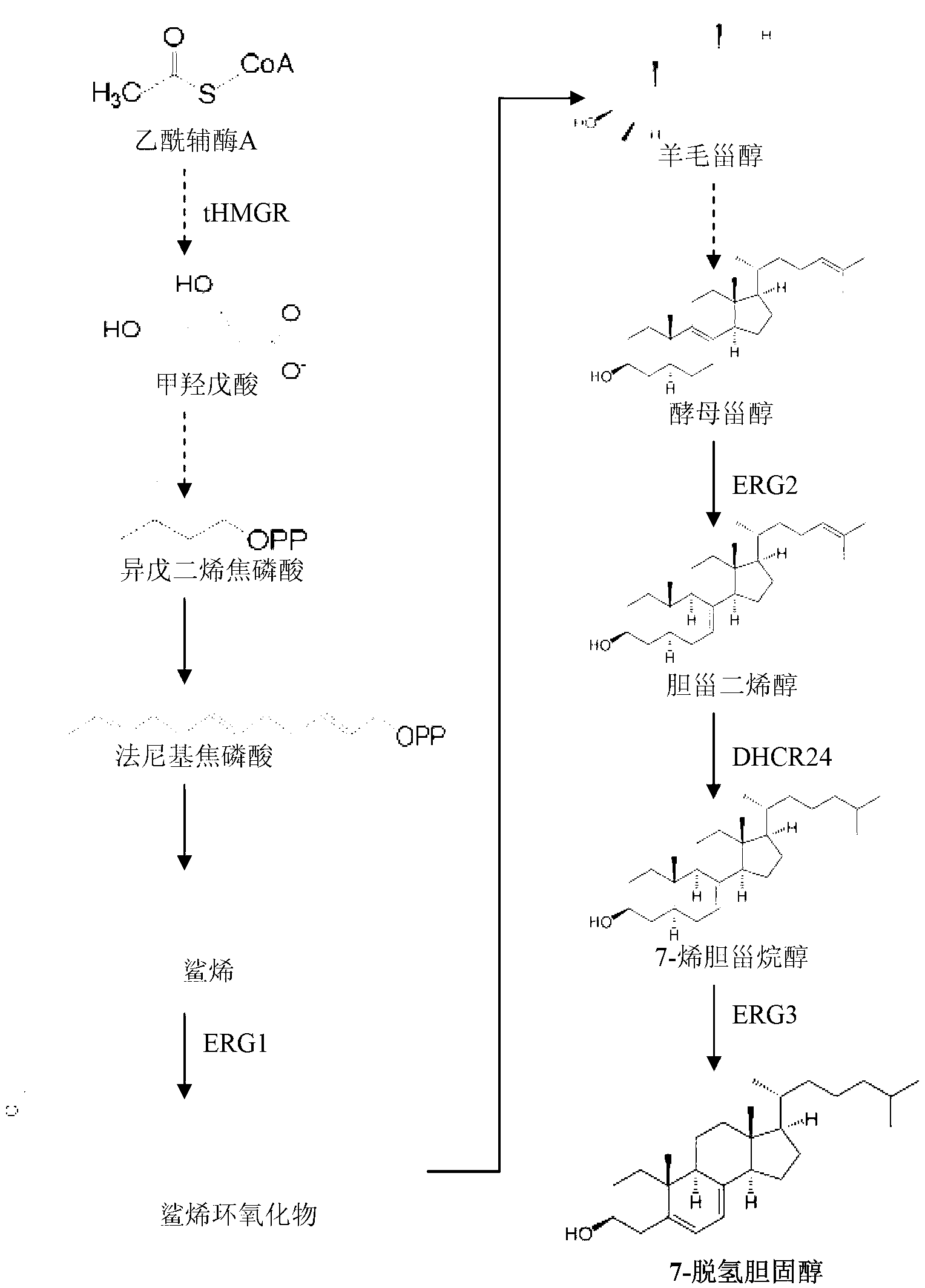
[0040] Example 1: Acquisition of genes related to 7-dehydrocholesterol biosynthesis pathway in yeast
[0041] A, acquisition of tHMGR gene (yeast truncated HMG-CoA reductase gene)
[0042] Primers were designed according to the yeast HMG-CoA reductase gene sequence, SEQ ID NO:1tHMGR-U:5'-GGAATTCGCAGGCACGTCTAGAATGGACCAATTGGT-3' and SEQ ID NO:2tHMGR-D:5'-GCGACTAGTGTTAGGATTTAATGCAGGTGACGG-3', based on the genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742 strain As a template, use fast pfu enzyme for PCR (95°C, 2min; 95°C, 20s, 63°C, 30s, 72°C, 2min, 30cycles; 72°C, 5min; 4°C, +∞) amplification to obtain a 1578bp fragment. Cloned into the pSB1A2 vector and sequenced, it was confirmed that no mutation occurred. The sequence of the 1578bp nucleotide fragment is shown in SEQ ID NO:3, and the encoded amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:4.
[0043] B, the acquisition of ERG1 gene (yeast squalene epoxidase gene)
[0044]Primers were designed according to the yeast ERG1 gene sequence, S...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment 2: the construction of carrier
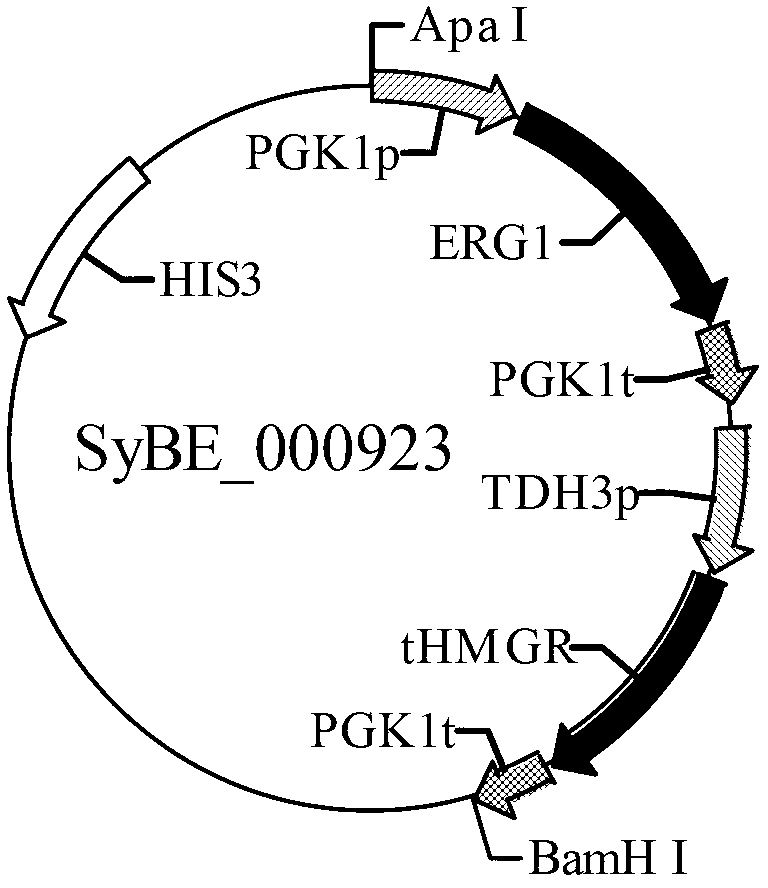
[0048] A, construction of carrier SyBE_000923 (expression vector of truncated HMG-CoA synthase gene and ERG1 gene)
[0049] ①The yeast constitutive promoter TDH3p, tHMGR gene, and terminator PGK1t were spliced together by restriction endonuclease method to obtain a fragment containing XhoⅠ and BamHI restriction sites at both ends, and connected to the integration vector pRS403;
[0050] ②Splice the yeast constitutive promoter PGK1p, ERG1 gene, and terminator PGK1t together using the restriction endonuclease method to obtain a fragment containing two sites of ApaⅠ and SalⅠ at both ends, and connect it to the vector obtained in step ① to obtain the vector SyBE_000923 ,See figure 1 ;
[0051] The tHMGR gene is the nucleotide sequence described in SEQ ID NO:3 of the sequence listing; the ERG1 gene is the nucleotide sequence described in the sequence listing SEQ ID NO:7.
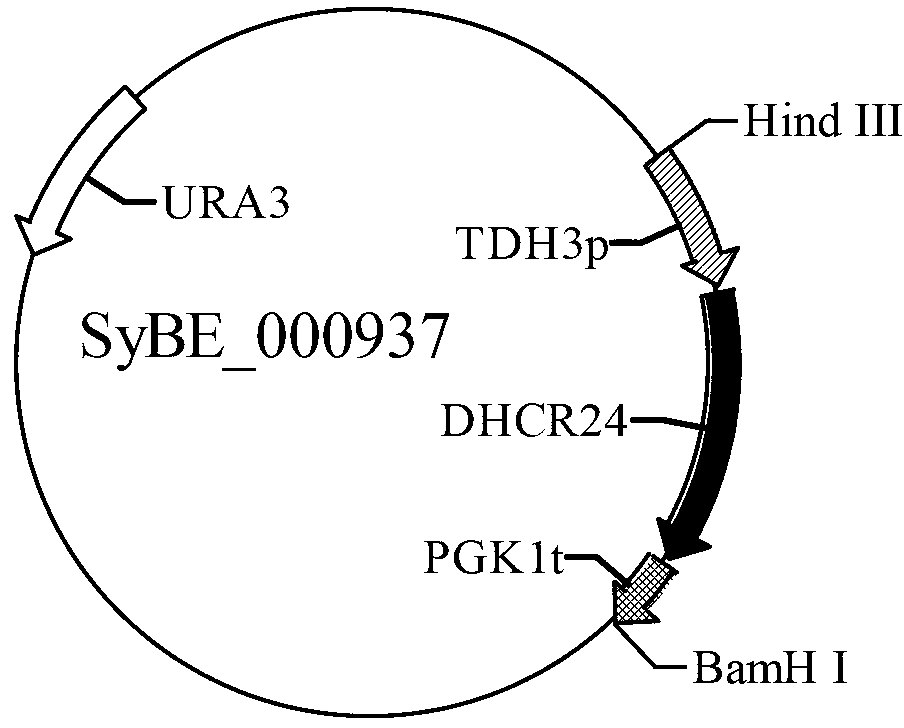
[0052] Experiments have shown that by replacing the ve...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3: the acquisition of yeast strain SyBE_000954
[0059] Primers were designed according to the yeast LEU gene sequence, SEQ ID NO:11LEU-U:5'-TGCTATTCCAATAGACAATAAATACCTTTTTAACATTAAGCAAGGATTTTCTTAACTTC-3'and SEQ ID NO:12LEU-D:5'-TATGATTTATTGTCTGGACAAAAGTTCTGTTTTTCCCCAATGTCTGCCCCTAAGAAGAT-3'to select Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY47 containing the selection marker gene LEU The strain genome was used as a template, and the fast pfu enzyme was used for PCR (95°C, 2min; 95°C, 20s, 62°C, 30s, 72°C, 70s, 30cycles; 72°C, 5min; 4°C, +∞) amplification to obtain 1095bp Fragment (the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 13 in the Sequence Listing). The PCR product was transformed into Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain YML008C by lithium acetate method, using SD-drop solid medium (deaminated yeast nitrogen source, 6.7g / l; glucose, 20g / l; Dropout mix, 0.2%; solid supplemented with 2% agar Powder) for screening, the obtained transformants were transferred to liquid medium an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com