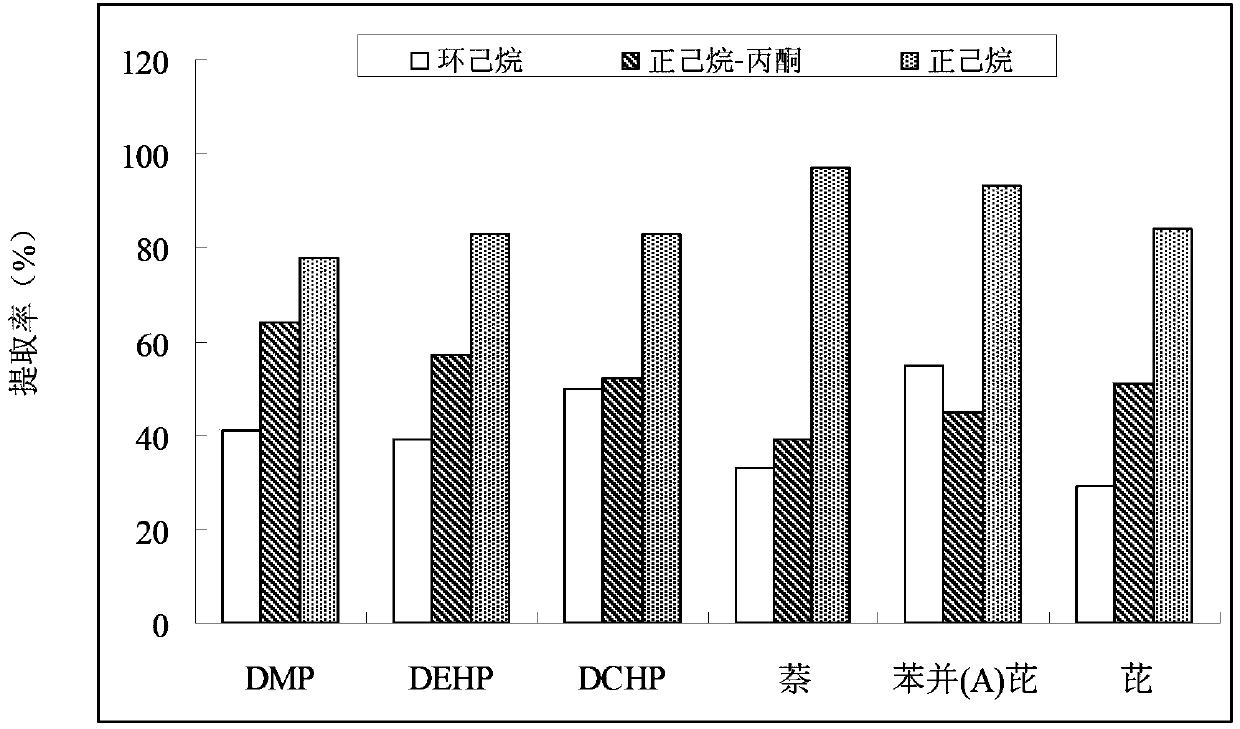
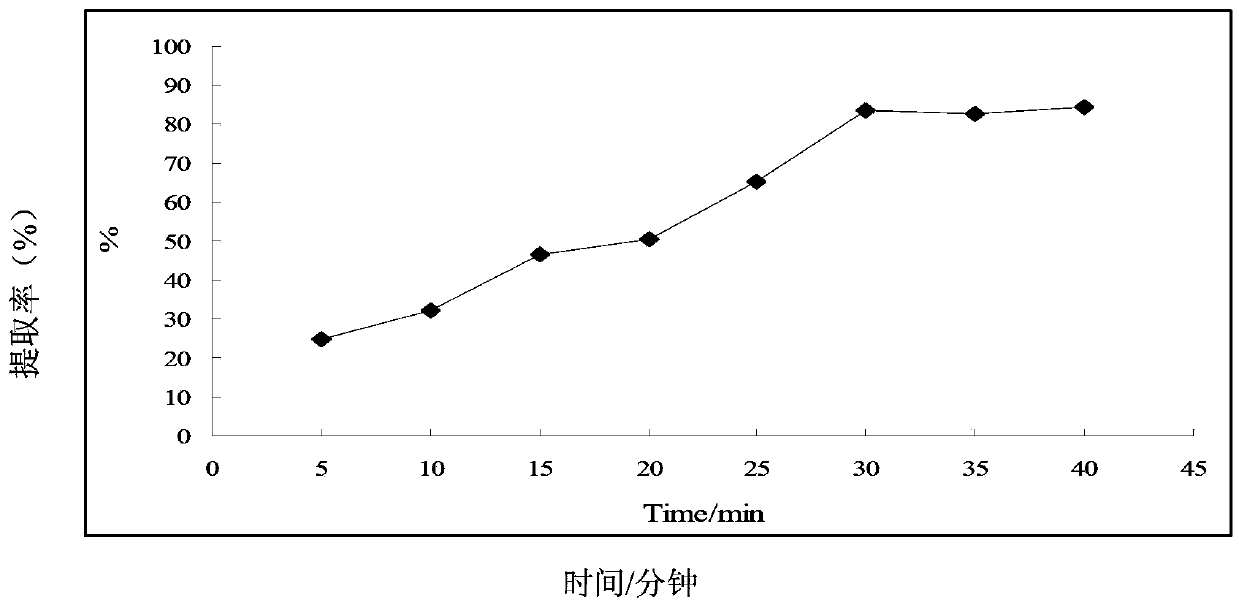
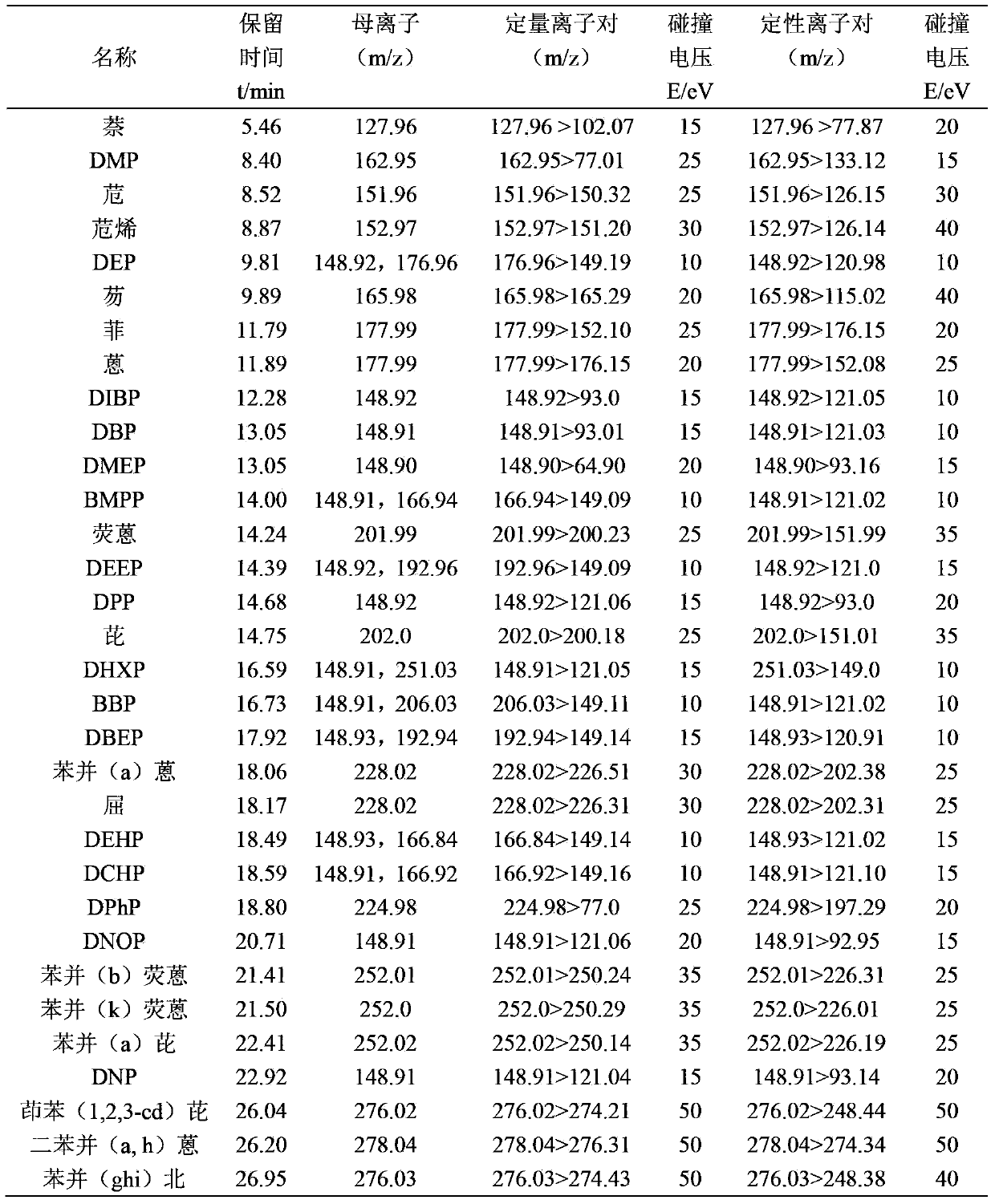
Method for detecting polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and phthalic acid esters (PAEs) in plant extract
A technology of phthalates and plant extracts, applied in the field of detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalates, can solve the problem of inability to simultaneously detect toxic and harmful substances of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalates low detection limit, easy operation and good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Weigh 1.000g of commercially available green tea extract into a 50mL glass centrifuge tube, add 4mL of water and 4mL of organic solvent in sequence, the organic solvent is n-hexane, vortex and mix well, ultrasonically extract for 25 minutes, and centrifuge at 2000 for 3 minutes. Take the supernatant, add it to a glass centrifuge tube containing 0.1 g of ethylenediamine-N-propylsilane (PSA), vortex for 1 min, and centrifuge at 2000 rpm for 3 min.
[0043] Chromatographic conditions: DB-5MS (30m×0.25mm×0.25μm), carrier gas: helium (purity ≥99.999%), flow rate 1.0mL / min, inlet temperature 280°C, mass spectrometer transfer line temperature 290°C, injection volume 1.0 μL, sampling method: splitless injection, open the split valve after 1.0 min. Programmed temperature rise: the initial temperature is 80°C, keep for 1min, rise to 225°C at 12°C / min, then rise to 265°C at 6°C / min, and finally rise to 290°C at 5°C / min, keep for 8min. Mass spectrometry conditions: electron bombar...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Still taking the above-mentioned commercially available green tea extract as the object, weigh 1.000g into a 50mL glass centrifuge tube, add 5mL of water and 5mL of organic solvent in sequence. Centrifuge for 3 minutes. Take the supernatant, add it to a glass centrifuge tube containing 0.1 g of ethylenediamine-N-propylsilane (PSA), vortex for 2 minutes, and centrifuge at 2500 rpm for 5 minutes.
[0047] Chromatographic conditions: DB-5MS (30m×0.25mm×0.25μm), carrier gas: helium (purity ≥99.999%), flow rate 1.0mL / min, inlet temperature 280°C, mass spectrometer transfer line temperature 290°C, injection volume 1.0 μL, sampling method: splitless injection, open the split valve after 1.0 min. Programmed temperature rise: the initial temperature is 80°C, keep for 1min, rise to 225°C at 12°C / min, then rise to 265°C at 6°C / min, and finally rise to 290°C at 5°C / min, keep for 8min. Mass spectrometry conditions: electron bombardment ion source (EI); ionization energy 70eV; ion ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Still taking the above-mentioned commercially available green tea extract as the object, weigh 1.000g into a 50mL glass centrifuge tube, add 6mL of water and 6mL of organic solvent in sequence. Centrifuge for 3 minutes. Take the supernatant, add it to a glass centrifuge tube containing 0.1 g of ethylenediamine-N-propylsilane (PSA), vortex for 2 minutes, and centrifuge at 2500 rpm for 5 minutes.
[0051] Chromatographic conditions: DB-5MS (30m×0.25mm×0.25μm), carrier gas: helium (purity ≥99.999%), flow rate 1.0mL / min, inlet temperature 280°C, mass spectrometer transfer line temperature 290°C, injection volume 1.0 μL, sampling method: splitless injection, open the split valve after 1.0 min. Programmed temperature rise: the initial temperature is 80°C, keep for 1min, rise to 225°C at 12°C / min, then rise to 265°C at 6°C / min, and finally rise to 290°C at 5°C / min, keep for 8min. Mass spectrometry conditions: electron bombardment ion source (EI); ionization energy 70eV; ion ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com