Method for bioconversion of chlorogenic acids in plants by adopting aspergillus aculeatus
A technology of Aspergillus aculeatus, biotransformation, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as other uses of strains not mentioned, and achieve short transformation time, strong specificity, and high value. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
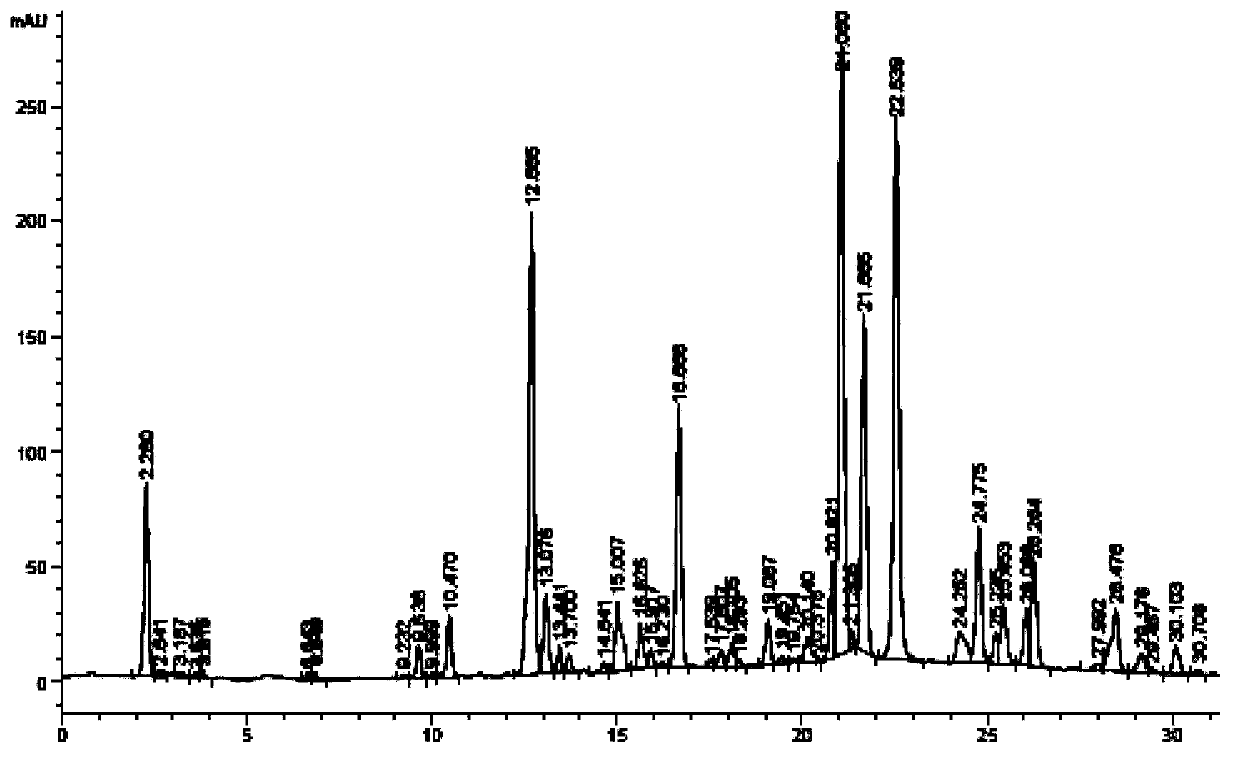
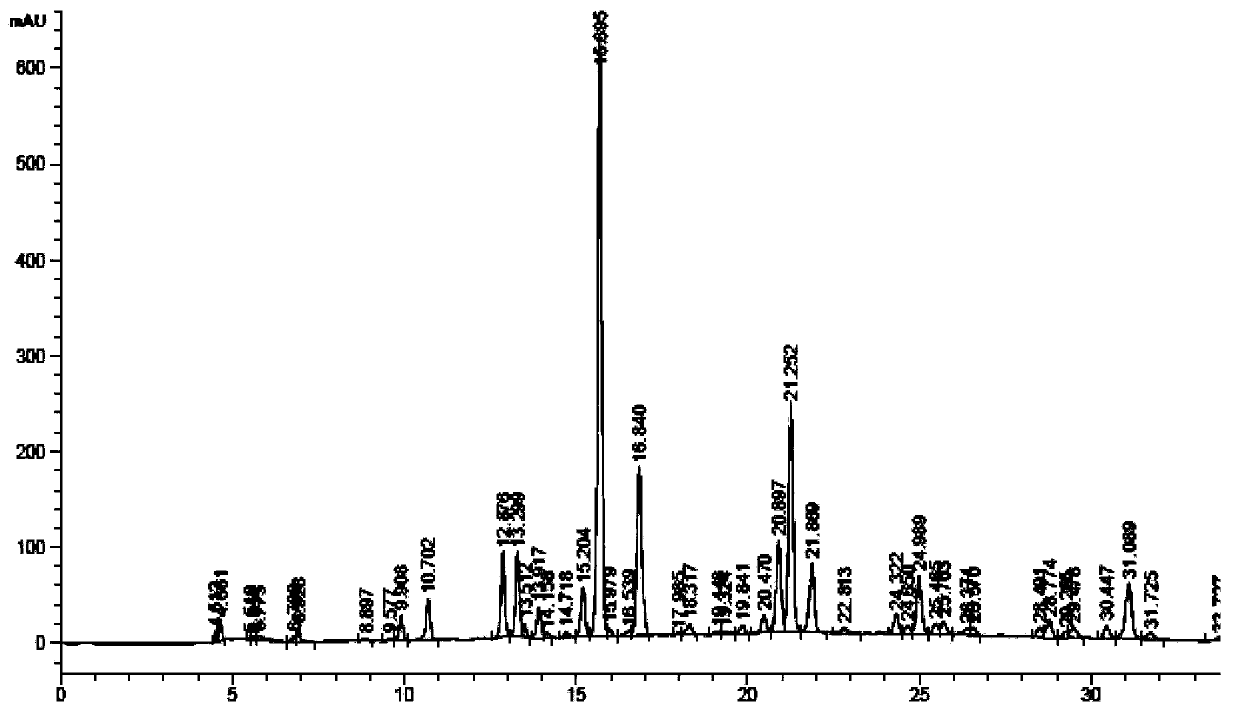
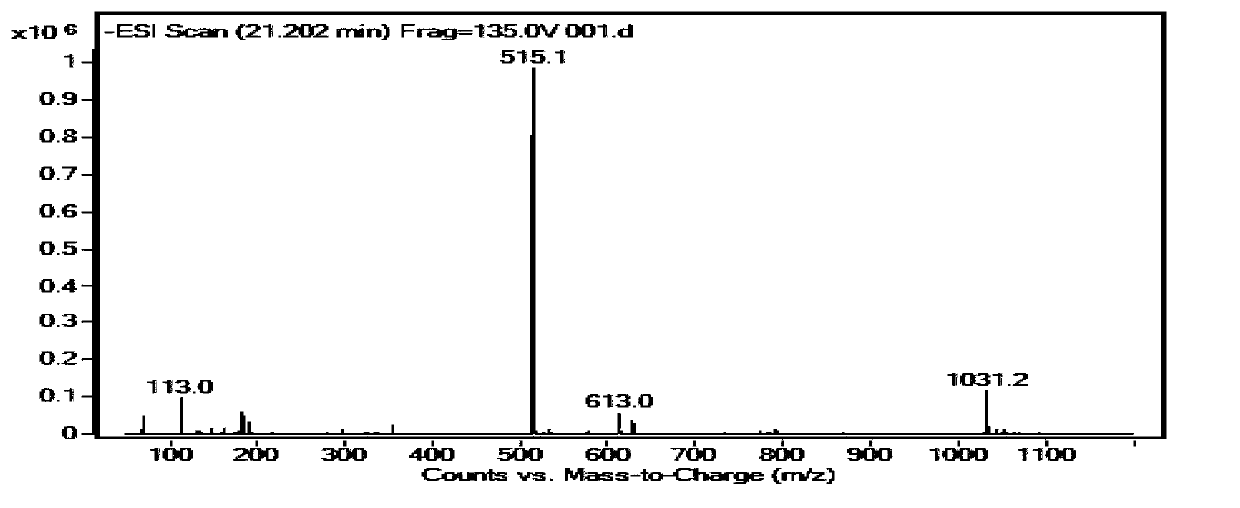
[0032] Use conventional Aspergillus aculeatus solid koji culture medium, add water to extract after fermentation to obtain Aspergillus aculeatus enzyme solution, add Artemisia annua extract containing 1.0% (w / v) chlorogenic acid to 100ml enzyme solution, and analyze the extract by HPLC see results figure 1 As shown, transform in a water bath at 40°C for 1 h, take the supernatant for HPLC analysis, the results are shown in figure 2 As shown, 1-caffeoylquinic acid, 3-caffeoylquinic acid, 4-caffeoylquinic acid, 4-feruloylquinic acid, 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid were obtained by conventional extraction methods, 1-caffeoyl-5-feruloylquinic acid, 1-feruloyl-5-caffeoylquinic acid, 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid and other products (see Figure 4 shown).
Embodiment 2
[0034] Aspergillus aculeatus solid koji culture medium was fermented and extracted with water to obtain Aspergillus aculeatus enzyme solution, 100ml of enzyme solution was added with 15% (w / v) chlorogenic acid wild mugwort extract, transformed in a water bath at 70°C for 60 hours, and then used conventional High-purity 3-caffeoylquinic acid, 4-caffeoylquinic acid, 4-feruloylquinic acid, 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid and other products were obtained by chromatography and other methods.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Use conventional Aspergillus aculeatus solid koji culture medium, after fermentation, add water to extract Aspergillus aculeatus enzyme solution, add 8% (w / v) chlorogenic acid Inula inula extract to 100ml enzyme solution, and transform in a water bath at 10°C 30h, high-purity 1-caffeoylquinic acid, 3-caffeoylquinic acid, 4-caffeoylquinic acid, 4-feruloylquinic acid, 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid can be obtained by recrystallization acid products.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com