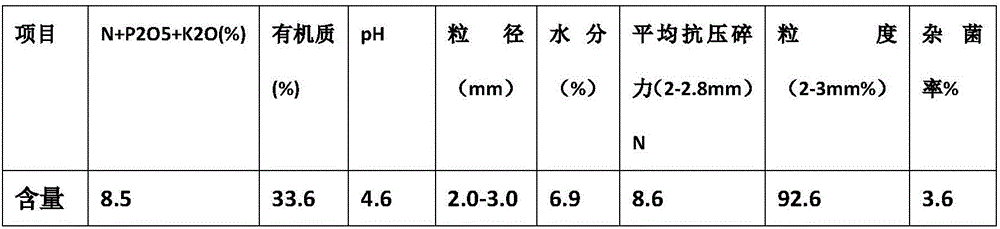
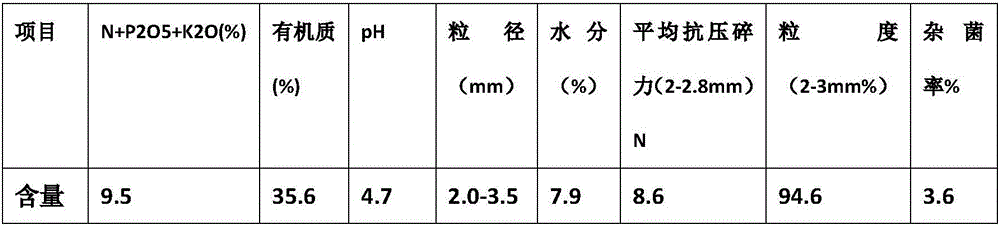
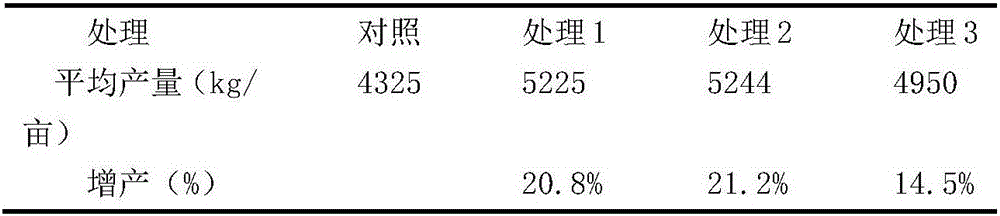
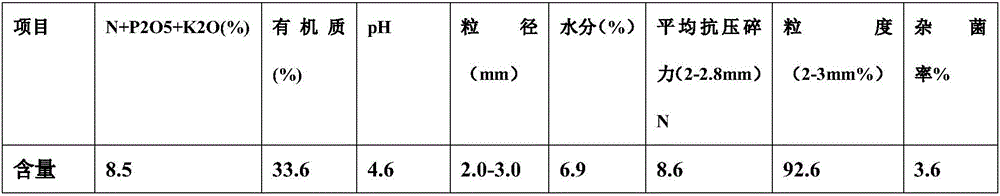
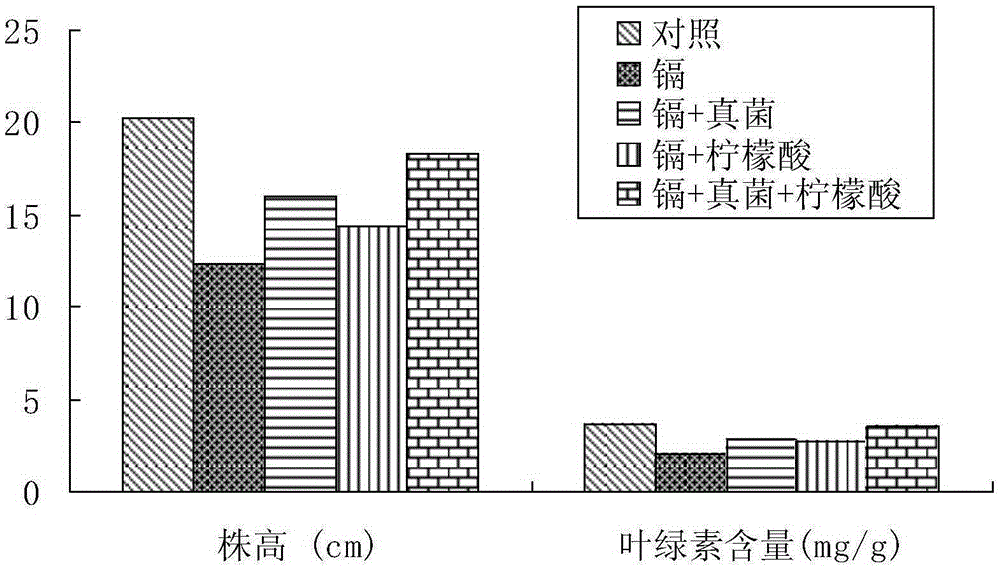
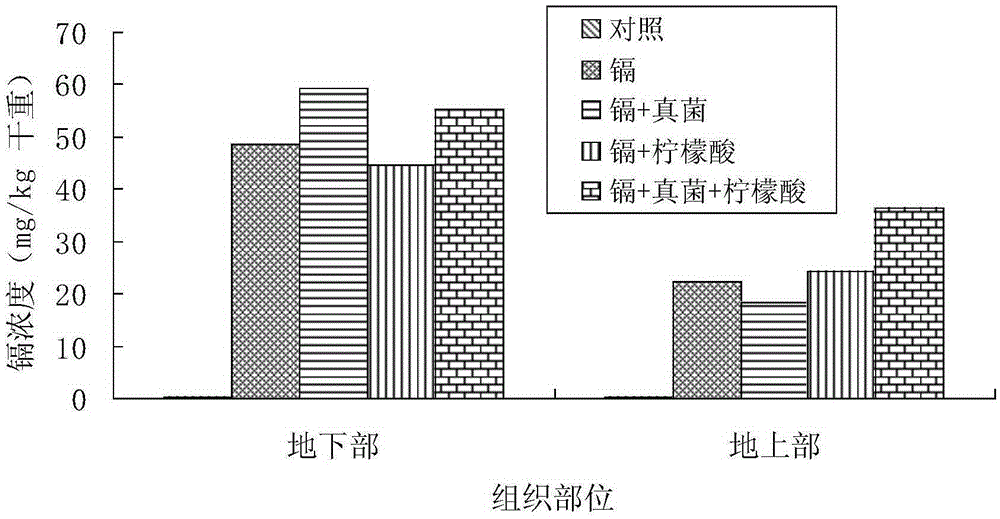
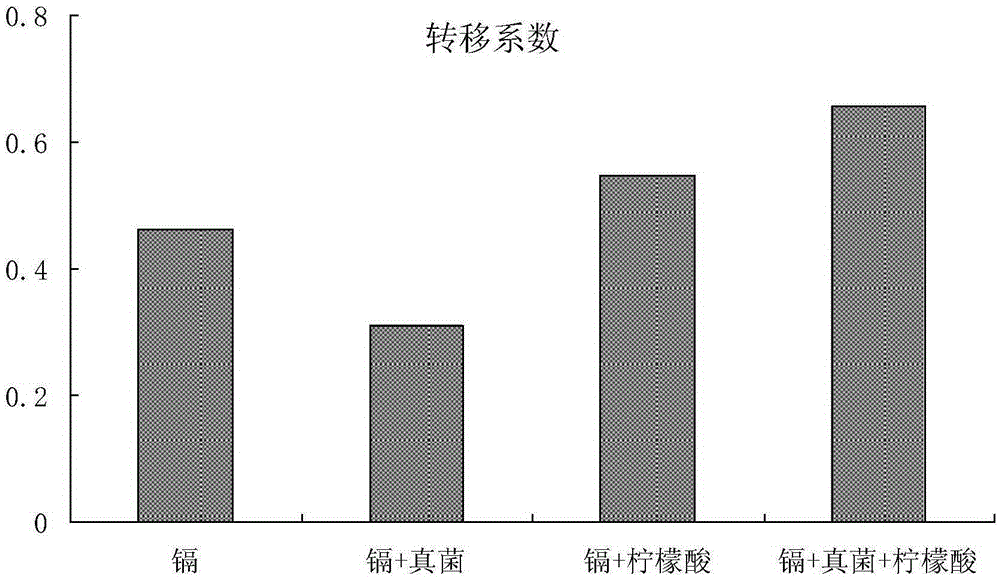
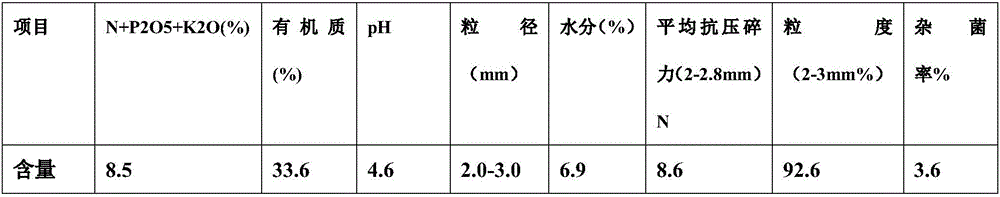
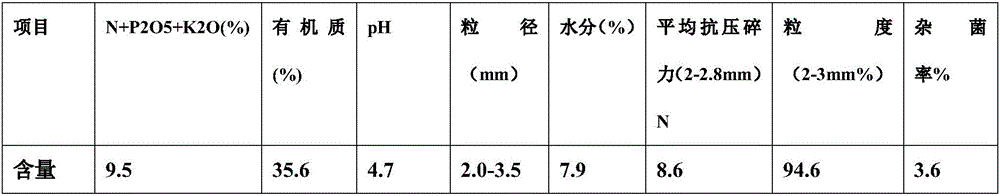
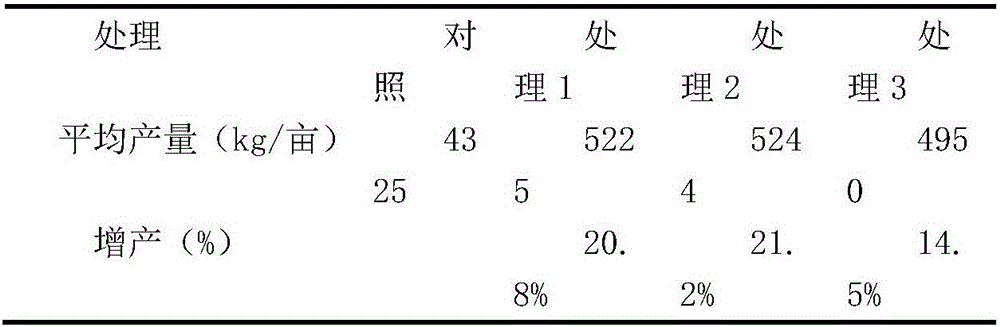
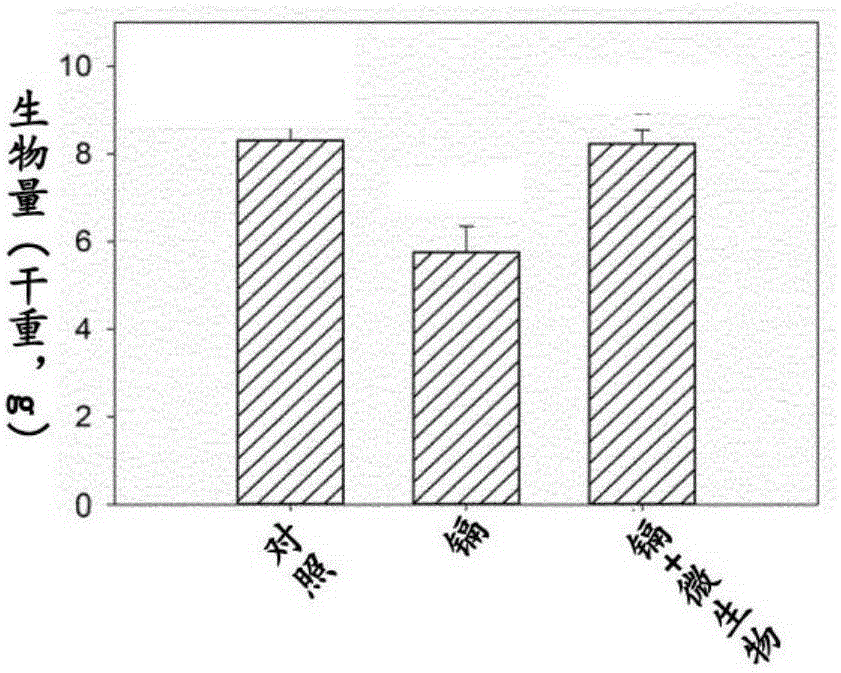
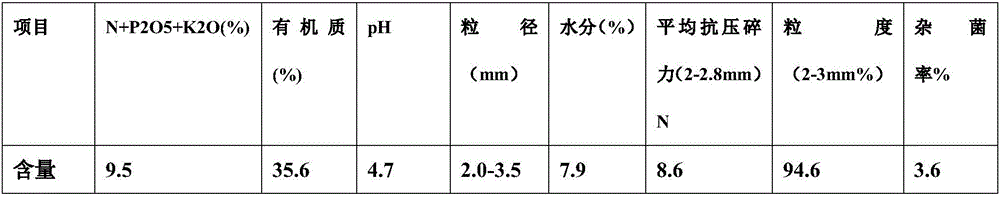
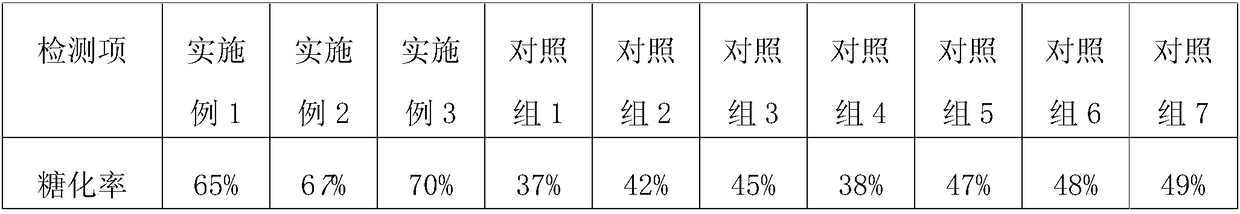
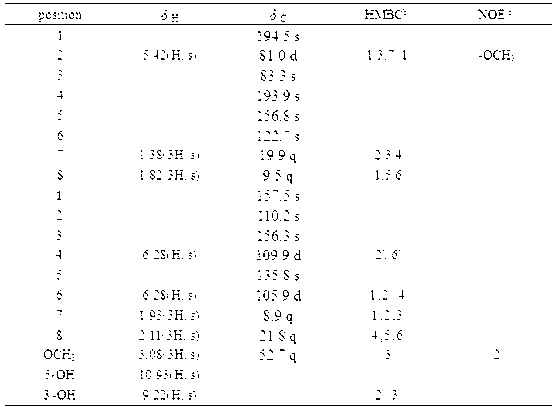
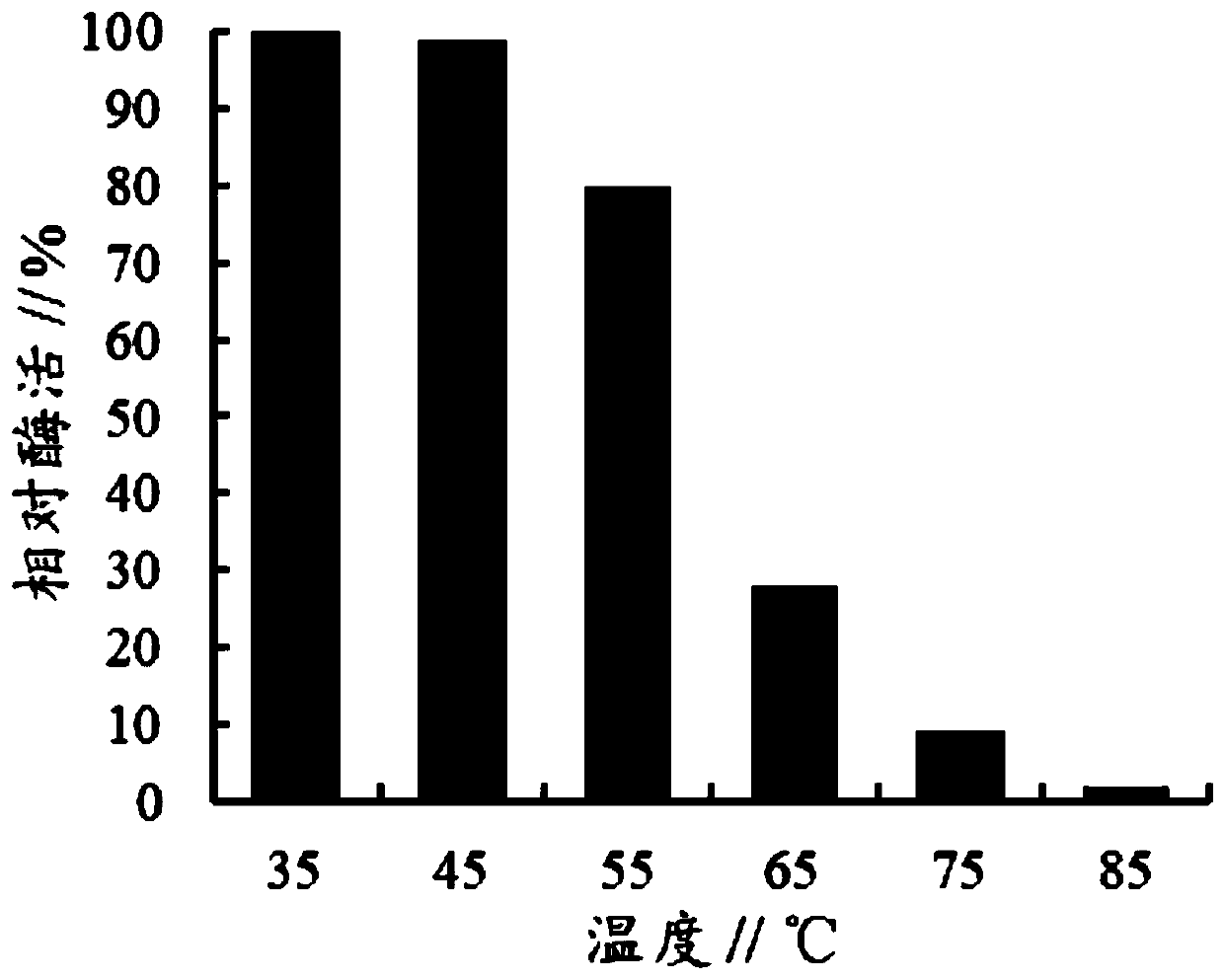
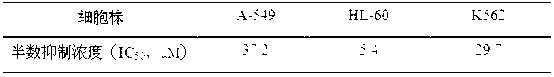
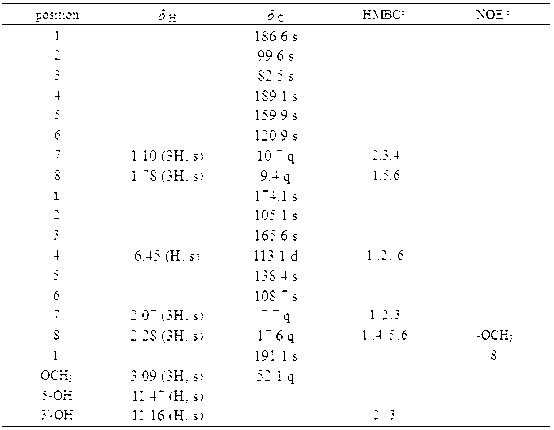
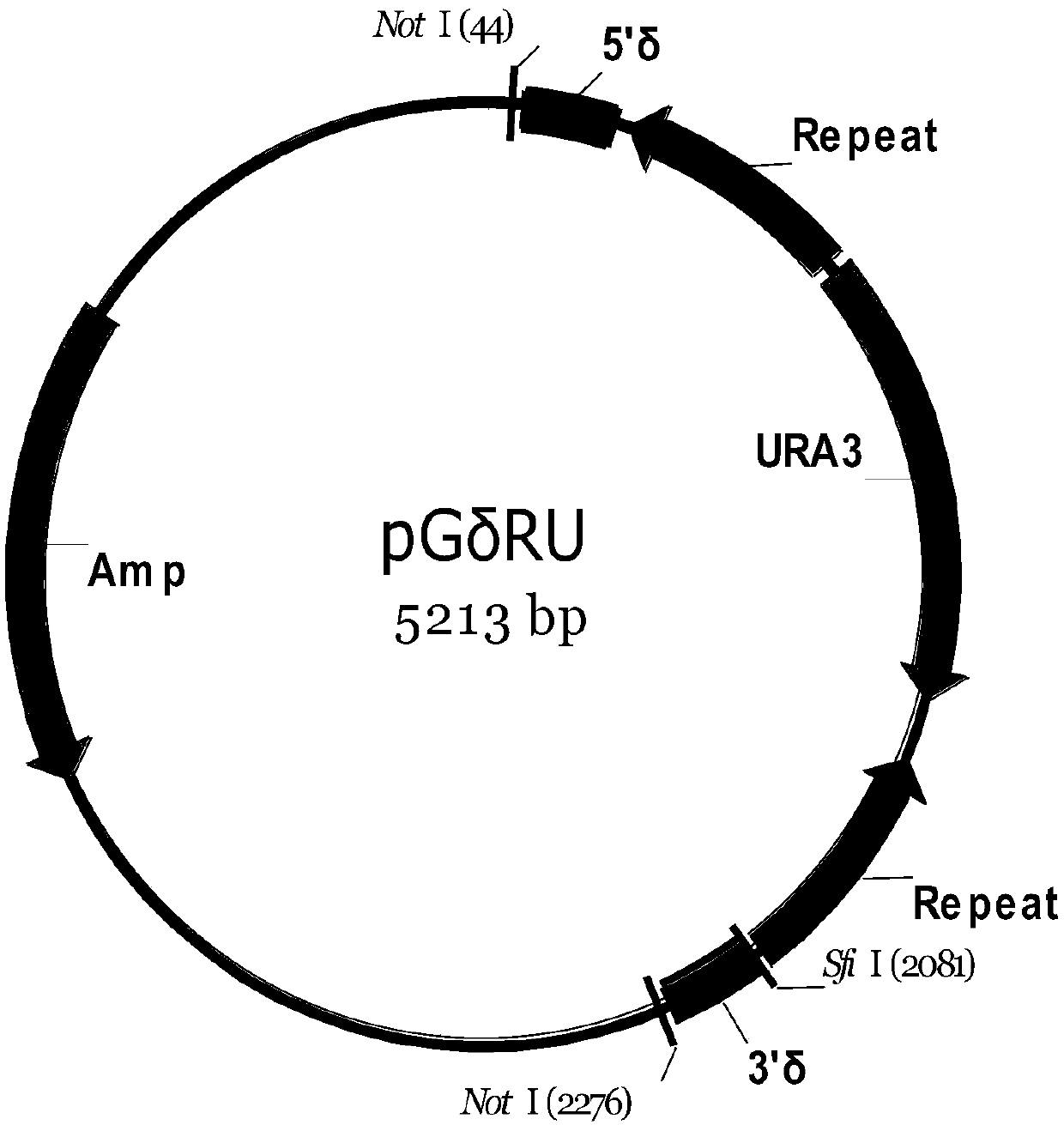
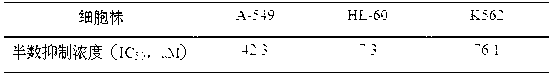Patents
Literature
80 results about "Aspergillus aculeatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aspergillus aculeatus is a fungus species in the genus Aspergillus. It has been implicated as the causative agent in plant disease. A. aculeatus belongs to the group of black Aspergilli which are important industrial workhorses. A. aculeatus belongs to the Nigri section.
Compound microbial fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101891509AHigh effective bacteria countSimple production processBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationDiseaseGrowth promoting
The invention relates to a compound microbial fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The compound microbial fertilizer is characterized by being prepared from the following materials in percentage by weight: 40.0-50.0 % of rape seed cakes, 10.0-20.0% of crops straws, 1.5-3.0% of mycothallus, 0.5-1.0% of bacterium thallus and 35.0-40.0% of water. By using the solid fermentation method twice, the invention organically combines the fungi (Trichoderma harzianum and Aspergillus aculeatus for biological control effect) and the bacteria (Bacillus subtillis and Bacillus megatherium for growth-promoting effect), and realizes a simple preparation method. The compound microbial fertilizer has the advantages of environmental condition resistance, high count of active viable bacteria, less influence by the environment after application, slow release of thallus and long-term effective colonization at rhizosphere of plants, promotes plant growth and simultaneously has a certain biological control effect on soil-borne diseases.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Composite microbe fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106083313AProlong survival timeFree from influenceSuperphosphatesCalcareous fertilisersBacillus megateriumPeat
The invention relates to a composite microbe fertilizer. The composite microbe fertilizer is prepared by 25-35 wt% of vegetable garden soil, 5-10 wt% of active functional bacteria, 5-15 wt% of mineral powder, 25-30 wt% of an organic fertilizer, 15-20 wt% of an inorganic composite fertilizer, and water; wherein the sum of the components is 100%. The active functional bacteria comprise lactic acid bacteria, bacillus subtilis, Bacillus megaterium, trichoderma, aspergillus niger, monascus, Trichoderma harzianum, aspergillus aculeatus and yeast, the mineral powder is a mixture of one or more of peat, zeolite, vermiculite, montmorillonite, calcium carbonate and expanded perlite, fineness of the mineral powder is less than or equal to 200 meshes, the organic fertilizer contains decomposed manure, a rapeseed cake fertilizer, and straw, and the weight ratio of the manure to the rapeseed cake fertilizer to straw is 5.5-7.5:2.5-3.5:0.5-1.5.
Owner:杨子正
Controlled release fertilizer special for saline alkali soil improvement
InactiveCN106588424AHigh effective bacteria countSimple production processCalcareous fertilisersSuperphosphatesAlkali soilPotassium
The invention provides a controlled release fertilizer special for saline alkali soil improvement. The controlled release fertilizer is characterized by being prepared from 25-35 wt% of medical stone, 5-10 wt% of potassium chloride, 5-15 wt% of mineral powder, 25-30 wt% of organic fertilizer and water, and the sum of the all components is 100%; the active solid strains include lactic acid bacteria, bacillus subtilis, bacillus megatherium, trichoderma, aspergillus niger, monascus, trichoderma harzianum, aspergillus aculeatus and yeast; the mineral powder is one or a mixture of peat, zeolite, vermiculite, montmorillonite, calcium carbonate and expanded perlite, the fineness of the mineral powder is less than or equal to 200 meshes, the organic fertilizer contains a fermented manure fertilizer, a rape seed cake fertilizer and straw, and the weight ratio of the fermented manure fertilizer to the rape seed cake fertilizer to the straw is (5-7.5):(2.5-3.5):(0.5-1.5).
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
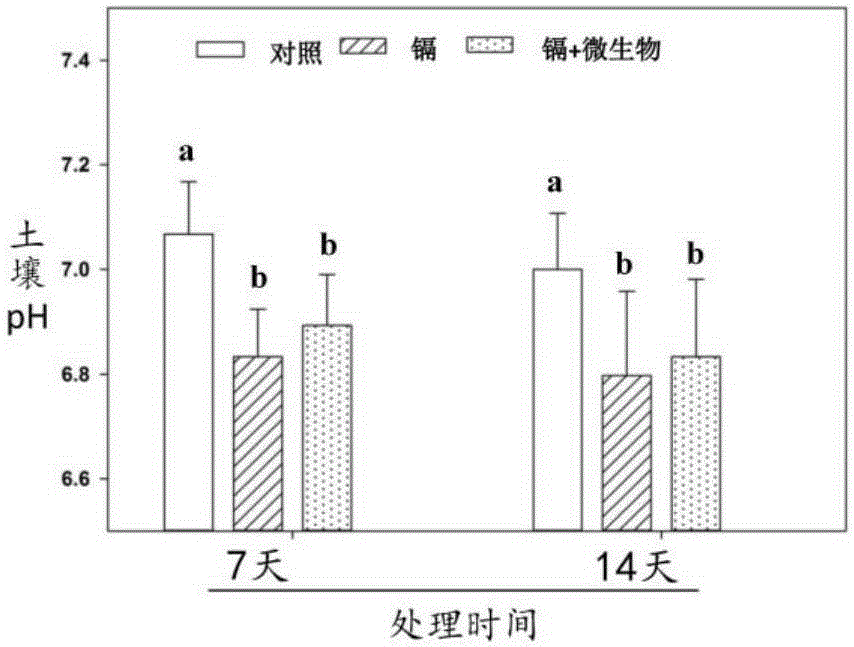
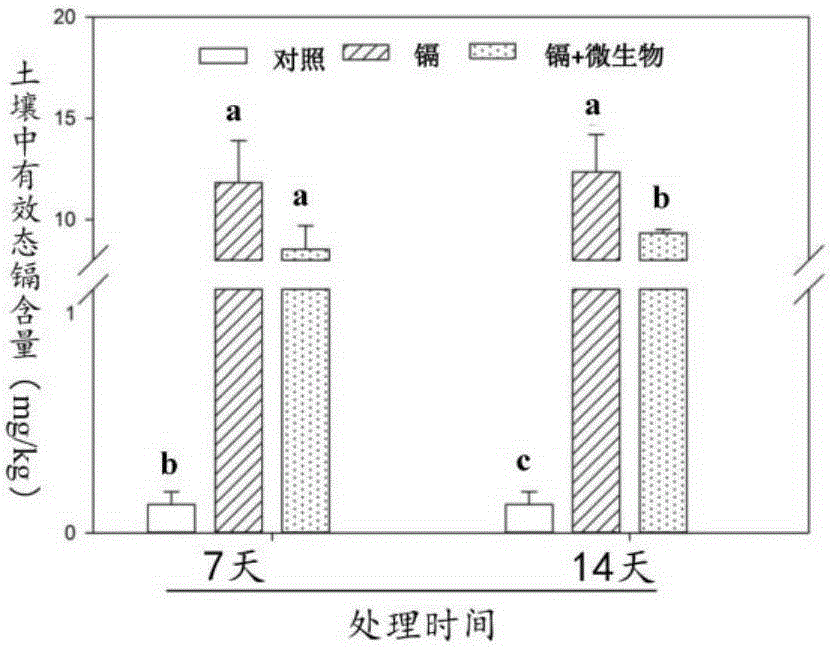
Method for utilizing cadmium-resisting fungus aspergillus aculeatus for promoting festuca arundinacea to remedy cadmium contaminated soil
InactiveCN105290103AAddressing Adaptive IssuesGuaranteed nutrient supplyContaminated soil reclamationCadmium CationBiology
The invention discloses a method for utilizing cadmium-resisting fungus aspergillus aculeatus for promoting festuca arundinacea to remedy cadmium contaminated soil, and relates to the technical field of plant-microorganism combined ecological remediation. The method mainly comprises the steps that firstly, cadmium-resisting fungus aspergillus aculeatus separated, purified and identified out of rhizosphere soil of dominant species in heavy metal contaminated soil is bred and inoculated into crushed crop straw to be prepared into a microbial remediation matrix, and the microbial remediation matrix is applied into cadmium contaminated soil; secondly, a festuca arundinacea lawn is planted in a sowing manner; thirdly, watering of a citric acid aqueous solution of a proper concentration and a proper quantity is carried out in batches; and fourthly, the rhizosphere microenvironment of festuca arundinacea is adjusted and controlled through citric acid to promote the interaction of cadmium-resisting fungus aspergillus aculeatus and a root system of festuca arundinacea so as to improve cadmium remediation efficiency. The problem of adaptability of screened-out microorganisms to the soil environment is solved; transferring of cadmium towards ground parts of plants is promoted, and the cadmium remediation efficiency is improved; and good environmental benefits, economic benefits and social benefits are achieved.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for converting polydatin to resveratrol by microbial enzyme method
InactiveCN102408999APromote the application of production practiceFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyGlycoside hydrolase
The invention provides a microbial strain aspergillus.aculeatus (CGMCCNo.3876) used for efficiently extracting polydatin and analogues thereof from plant materials such as polygonum cuspidatum, peanut shells, grape skins and the like, and a complex enzyme prepared by fermenting the microbial strain. The complex enzyme of the strain is used for extracting polydatin and analogues thereof by an enzyme method, and the extraction ratio is 2.3%. The extraction ratio of the complex enzyme is improved by 91.7% through treatment compared with the exoenzyme (control) to which the strain aspergillus.aculeatus is not added. The ratio of conversion from polydatin to resveratrol by using the complex enzyme of the strain is above 99.5%. The polygonum cuspidatum glycoside hydrolase purified from the complex enzyme of the strain is used for converting 98% of polydatin to resveratrol, and the conversion ratio is 99.7%. The purity of resveratrol is 98.5%. By the invention, a novel complex enzyme preparation is actually provided for production, the problems of low catalytic activity of enzymes, low conversion ratio, overlong time and high cost in current production upgrading are fundamentally solved, and the production practice application is promoted.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for remedying cadmium-contaminated soil through turfgrass and microorganism combination
InactiveCN103551371AImprove environmental adaptabilityIncrease runoffContaminated soil reclamationSoil treatmentCadmium Cation
The invention discloses a method for remedying cadmium-contaminated soil through turfgrass and microorganism combination, and relates to a heavy metal-contaminated soil treatment technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) screening cadmium-resistant bermuda grasses so as to obtain the bermuda grasses with strong cadmium resistance; (2) collecting rhizosphere soil of the bermuda grasses in a contaminated area; (3) screening cadmium-resistant microorganisms so as to obtain the microorganisms with the strongest cadmium resistance, which are fungi-aspergillus aculeatus; (4) preparing microorganism remedying matrixes; and (5) carrying out turfgrass and microorganism combined remediation. The method has the advantages that the dominant plants, namely the bermuda grasses in the cadmium-contaminated area are used as cadmium-resistant plant screening sources and have strong adaptability to the soil environments in the contaminated area; the cadmium-resistant fungi-aspergillus aculeatus is derived from the rhizosphere soil of the bermuda grasses in the cadmium-contaminated area, is well compatible with the cadmium-resistant bermuda grasses and has strong adaptability to the soil environments in the contaminated area; the microorganism remedying matrixes can be used for ensuring the nutrient supply of microorganism growth, enhancing the operability of applying the microorganisms in soil and improving soil environments, and the waste is effectively utilized; the method is low in cost and simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Saline alkali soil improver and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106520131ASimple structureReduce salt contentAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesAlkali soilInorganic compound
A saline soil improver is characterized by comprising 25%-35wt% of vegetable soil, 5%-10wt% of active functional bacteria, 5%-15wt% of mineral powder, 25%-30wt% of an organic fertilizer, 15%-20wt% of an inorganic compound fertilizer and balance of water, the active functional bacteria includes lactic acid bacteria, bacillus subtilis, bacillus megatherium, trichoderma, aspergillus niger, Monascus, Trichoderma harzianum, Aspergillus aculeatus and yeast, the mineral powder is one of or a mixture of more than one of peat, zeolite, vermiculite, montmorillonite, calcium carbonate and expansion perlite, the mineral powder fineness is less than or equal to 200 meshes. The organic fertilizer contains composted manure, a rapeseed cake fertilizer and straws, and the weight ratio of composted manure to rapeseed cake fertilizer to straws is 5.5-7.5: 2.5-3.5: 0.5-1.5.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
Method for reducing cadmium content of rice grains in cadmium-polluted rice field by using cadmium-resisting microorganisms
InactiveCN105191715AImprove environmental adaptabilityGood effectRice cultivationBiotechnologyBacillus cereus
The invention discloses a method for reducing the cadmium content of rice grains in a cadmium-polluted rice field by using cadmium-resisting microorganisms, belonging to the technical field of biological remediation of heavy metal polluted soil. The method comprises the following steps: (1) screening and purifying the cadmium-resisting microorganisms to obtain two microorganism strains capable of resisting 300mg / L of cadmium; (2) identifying the cadmium-resisting microorganisms, wherein the cadmium-resisting microorganisms are identified to be aspergillus aculeatus and bacillus cereus; (3) preparing a cadmium-resisting microorganism culture substrate; and (4) applying the cadmium-resisting microorganism culture substrate in the rice field. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the screened cadmium-resisting microorganism strains come from rhizosphere soil of dominant plants of a cadmium polluted mine area, and have very good environment adaptability; the effect of the mixed strains of the aspergillus aculeatus and the bacillus cereus is remarkably better than the single application of the aspergillus aculeatus or the bacillus cereus, so that the repairing efficiency is improved; and the cost is low, the operation is simple and convenient and the effect is remarkable. The method is applicable to the biological remediation of the rice field oil with relatively light cadmium pollution.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Slow-release fertilizer for preventing soil salinization and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107915555AHigh effective bacteria countSimple production processCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingBacillus megateriumPeat
The invention relates to a slow-release fertilizer for preventing soil salinization, which is prepared from 25%-35% by weight of vegetable garden soil, 5%-10% by weight of active solid bacterial strains, 5%-15% by weight of mineral powder material, 25%-30% by weight of organic fertilizer and water, and the sum of the components is 100%, wherein the active solid bacterial strains includes lactic acid bacteria, bacillus subtilis, bacillus megaterium, trichoderma, aspergillus niger, monascus, trichoderma harzianum, aspergillus aculeatus and yeast, the mineral powder material is one or a mixture of more than one of peat, zeolite, vermiculite, montmorillonite, calcium carbonate and expanded perlite, the fineness of the mineral powder material is not more than 200 mesh, the organic fertilizer contains decomposed manure, rapeseed cake fertilizer and straw, and the weight ratio of the manure to the rapeseed cake fertilizer to the straw is 5.5-7.5:2.5-3.5:0.5-1.5.
Owner:SHANDONG SHENGJING TOURISM DEV CO LTD
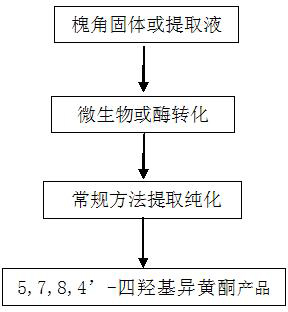
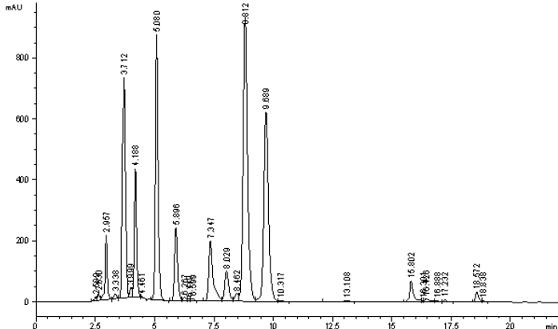
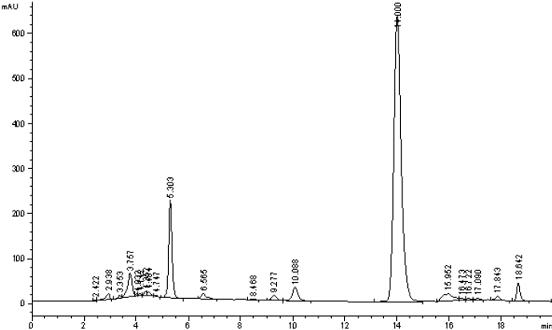
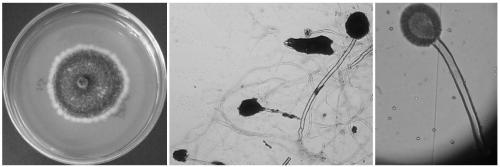
A strain of Aspergillus aculeatus and method for preparing 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxyisoflavones using the strain
ActiveCN102277304AStrong transformation specificityImprove conversion efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGlycoside
The invention relates to an Aspergillus aculeatus ZJ bacterial strain and an application thereof. The collection number of the Aspergillus aculeatus ZJ is CCTCC NO.M2011264. The bacterial strain is mainly used for converting effective components of the pod of Chinese scholartree to produce 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxyisoflavone. The specific method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: acting the Aspergillus aculeatus ZJ with strong specificity or the produced enzyme on the pod of Chinese scholartree or extracting solution thereof; converting glucosides compounds including sophoricoside and the like, genistein and the like to produce the 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxyisoflavone. The invention provides the method for producing the 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxyisoflavone through utilizing the Aspergillus aculeatus with high specificity and high conversion efficiency to convert the sophoricoside; and the method provided by the invention has moderate conditions, green process and simple requirements on the process and the device, and has a very good application value.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Aspergillus aculeatus strain and application thereof
InactiveCN104893985AIncrease enzyme activityEasy to separate and purifyFungiMicroorganism based processesAlgluceraseMicroorganism
The invention relates to an aspergillus aculeatus strain and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of fermentation engineering and biology. The preservation name of the aspergillus aculeatus strain is (Aspergillus sp.) BG30, the preservation department is China microorganism culture preservation management committee common microorganism center, the preservation data is June 28th, 2013, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.7799. During fermentation of the aspergillus aculeatus strain, the enzymatic activity of ectoenzyme beta-glucosidase is high, by-products are few, the beta-glucosidase is prone to separation and purification, the separation and purification cost is low, and therefore the fact that the aspergillus aculeatus strain serves as original strain to ferment and produce beta-glucosidase facilitates industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Aspergillus and application of aspergillus in fructosyltransferase preparing
The invention discloses aspergillus and an application of aspergillus in fructosyltransferase preparing. The preservation number of the aspergillus is CGMCC No.8912. The aspergillus aculeatus bacterial strain is a bacterial strain for producing the high-activity and ectoenzyme fructosyltransferase, the bacterial strain can be applied to producing fructo-oligosaccharide with saccharose or molasses as raw materials, and the aspergillus plays a significant role in promoting deep processing of saccharose and effective utilizing of waste.
Owner:广西多得乐生物科技有限公司
Aspergillus echinosporus strain and application thereof
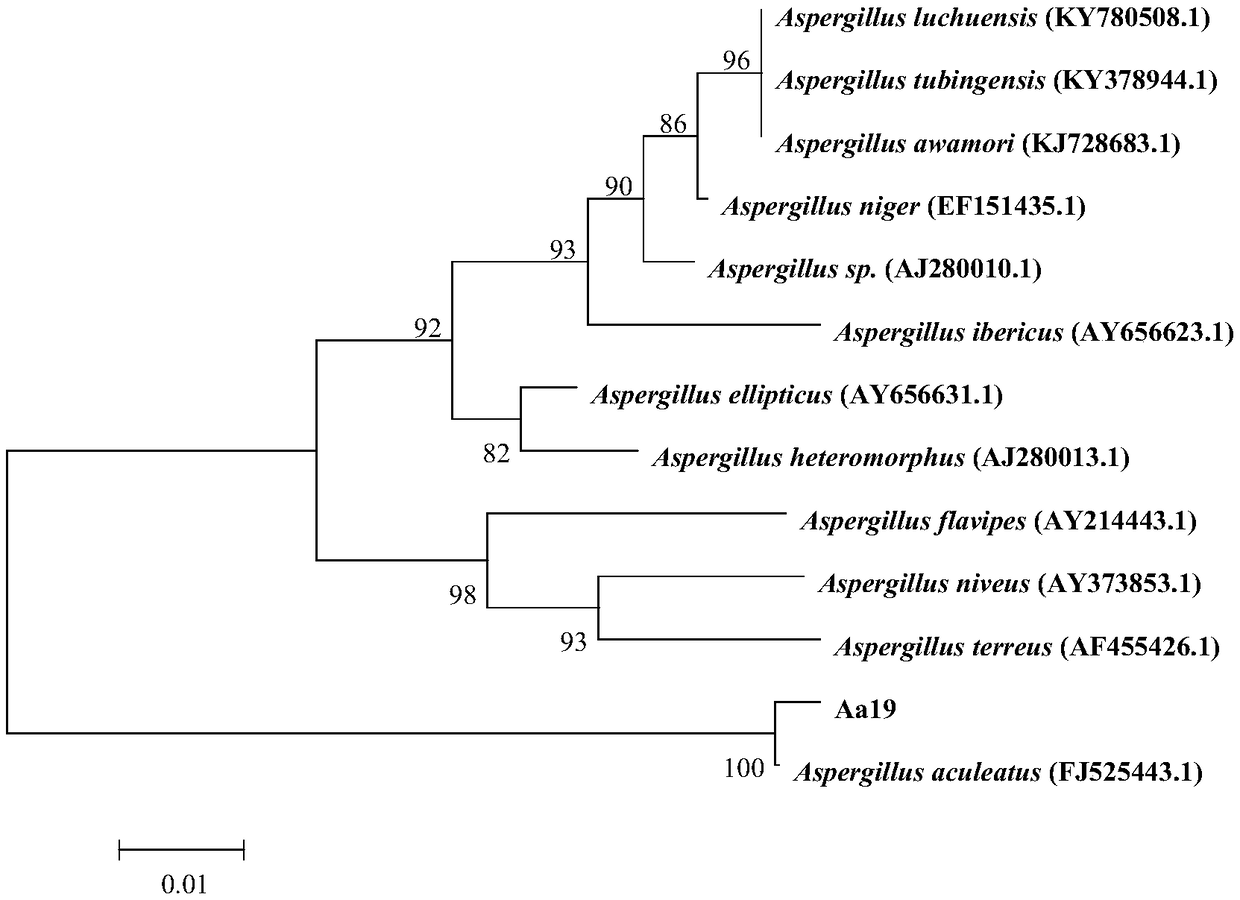
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant protection, in particular to an Aspergillus echinosporus strain and application thereof, and relates to biological control of soil-borne diseasesof vegetables. Aspergillus aculeatus (Aspergillus aculeatus) Aa19 is isolated from rhizosphere soil collected from vegetable plots where soil-borne diseases are serious. The strain is deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection under the accession number CCTCC NO: M 2018648. Aspergillus aculeatus (Aspergillus aculeatus) Aa19 is isolated from the rhizosphere soil of vegetable plots wheresoil-borne diseases occurred. The stability of the strain of Aspergillus aculeatus, the activity of the spore suspension and the activity of the fermentation filtrate were tested by the reference number CWSC NO:M 2014314 for the Fusarium oxysporum JWS-1. The biological function verification proves that the isolate of the invention has good control effect on soil-borne diseases of vegetables. Aspergillus acanthosporus Aa 19 is safe to vegetables, has good stability and high bacteriostatic activity, and can be used for biological control of soil-borne diseases-cowpea wilt.
Owner:WUHAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Aspergillus aculeatus strain and application thereof
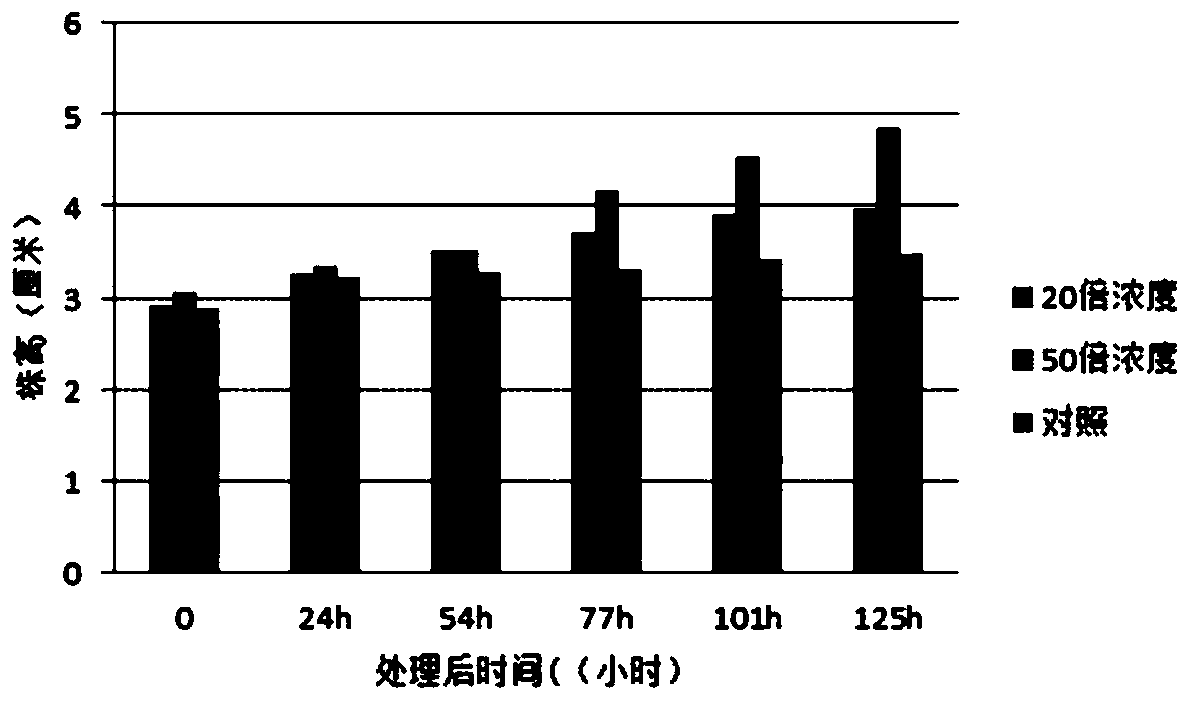
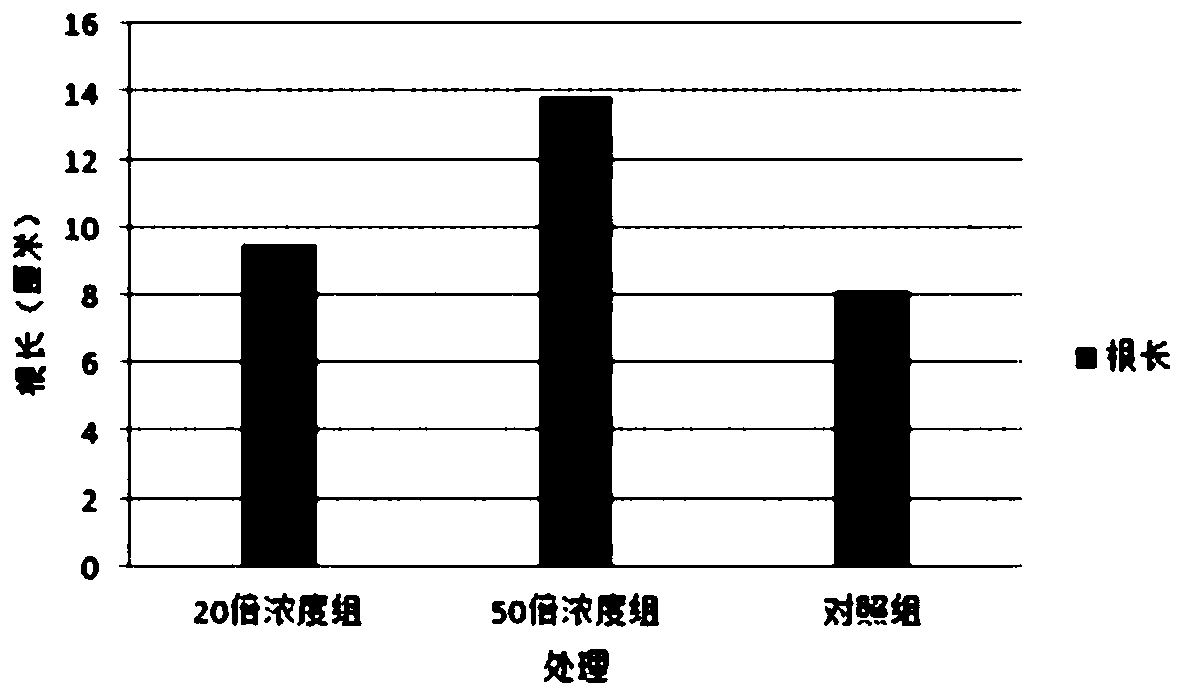
ActiveCN110129210APromote growthPromotes the prevention and control of Fusarium wiltPlant growth regulatorsBiocideGrowth plantMicroorganism
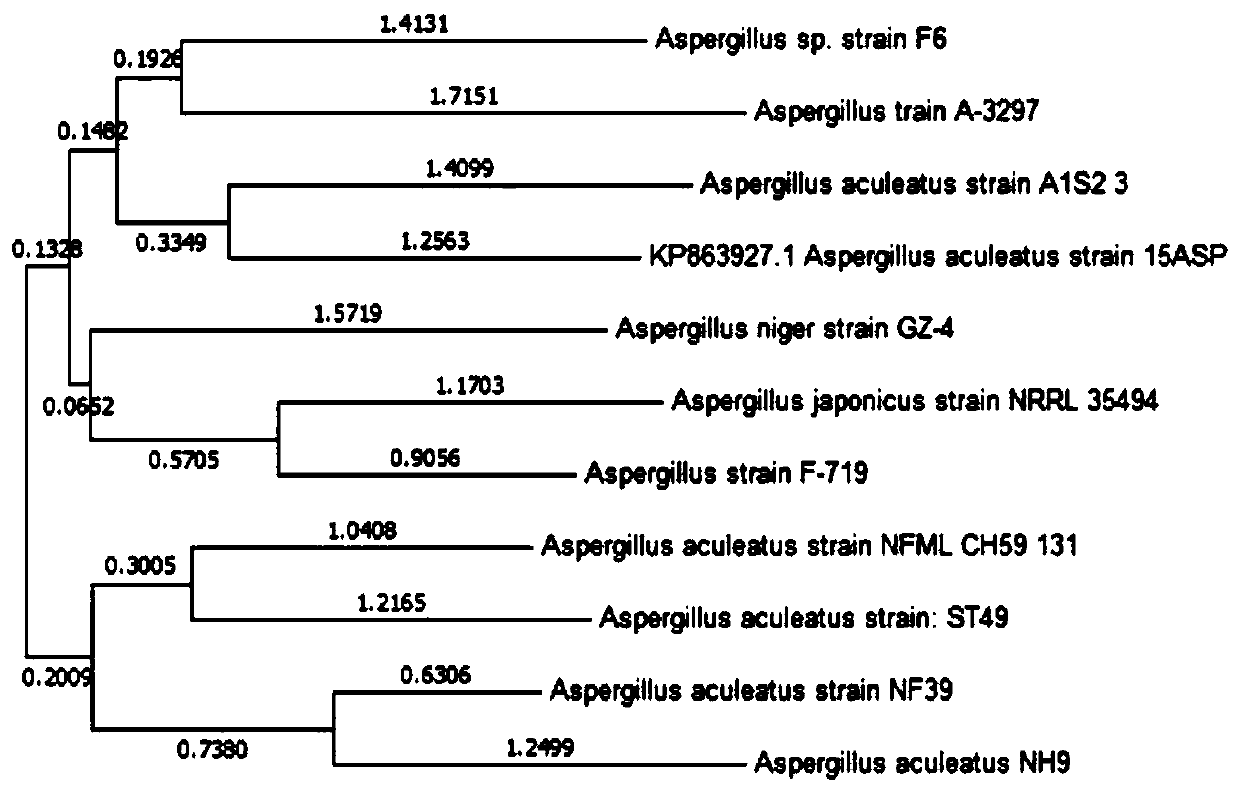
The invention discloses an aspergillus aculeatus strain and an application thereof. The aspergillus aculeatus strain NH9 is collected in a CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) on April 1, 2019, and the collection number of the strain is CGMCC No. 17191. Cucumber plant growth can be effectively promoted, the strain can be used as a biological pesticide and is low in cost,simple to operate and free from pollution, and environmental harm is avoided.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
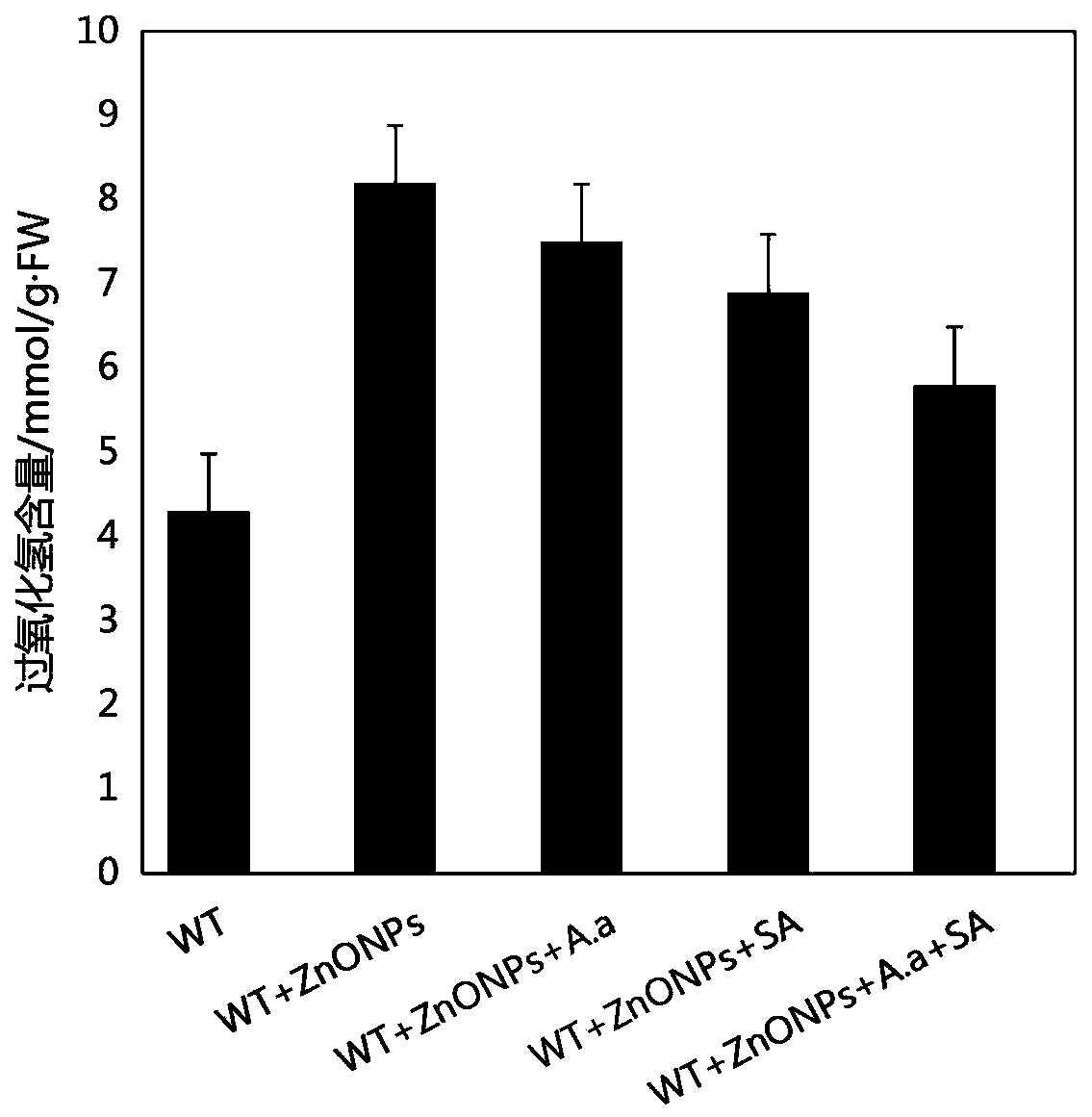
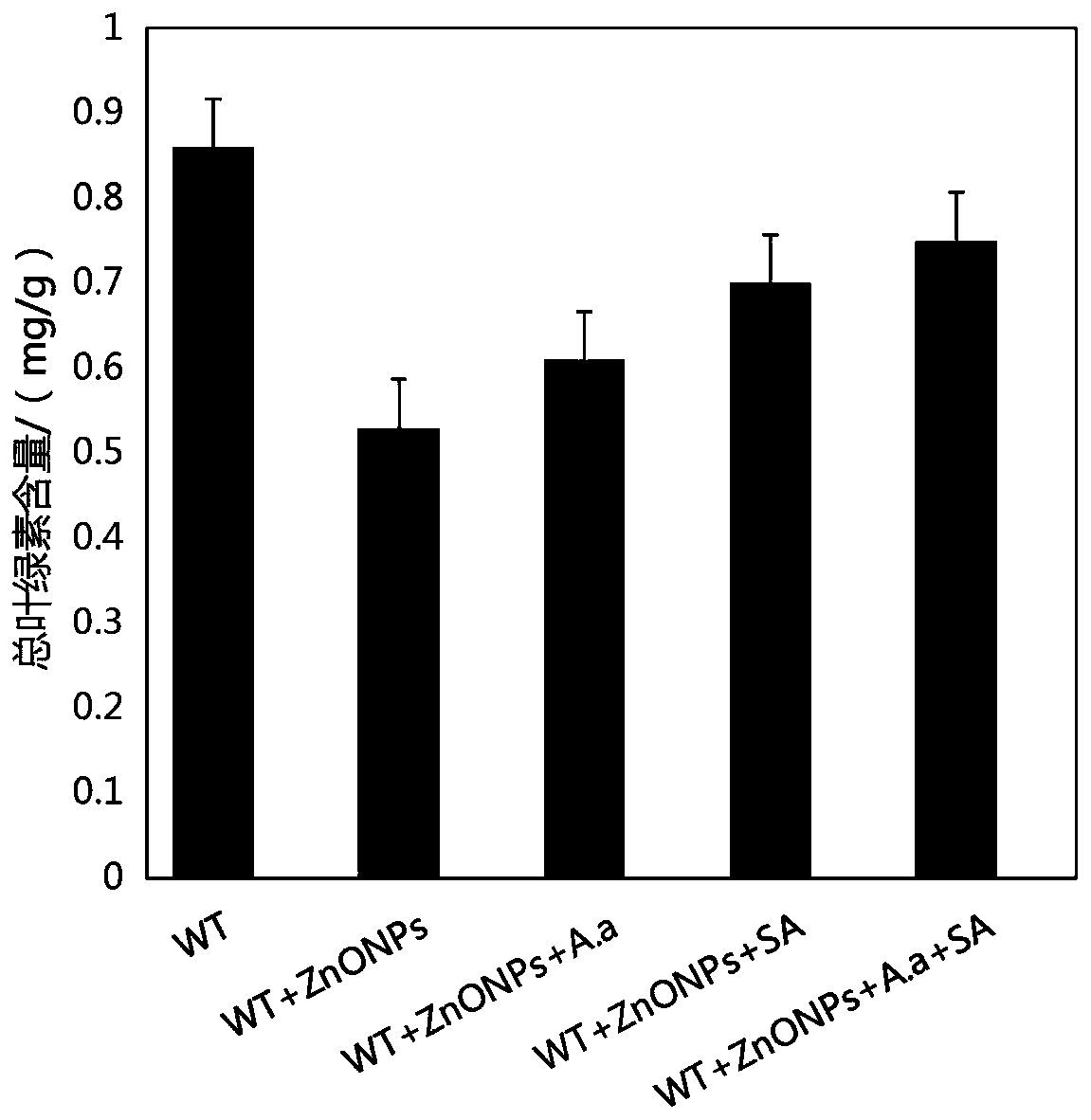
Joint relieving method for stress damage of nanometer zinc oxide to plants by utilizing aspergillus aculeatus fungus and salicylic acid
InactiveCN110338000ACoercion damage mitigationRaw materials are easy to getTobacco cultivationCultivating equipmentsSalicylic acidZinc
The invention discloses a joint relieving method for the stress damage of nanometer zinc oxide to plants by utilizing aspergillus aculeatus fungus and salicylic acid. The method comprises the steps that plant seedlings growing robustly are selected and transplanted into soil containing nanometer zinc oxide, aspergillus aculeatus fungus liquid and a salicylic acid solution are added to the rhizosphere of plants, and growth is achieved through culture. According to the method, the raw materials are easy to obtain, and the method is simple, easy to implement and low in cost and has a good application prospect. It is proved through an experiment that the aspergillus aculeatus fungus and the salicylic acid are utilized for jointly relieving the stress damage of the nanometer zinc oxide to the plants.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
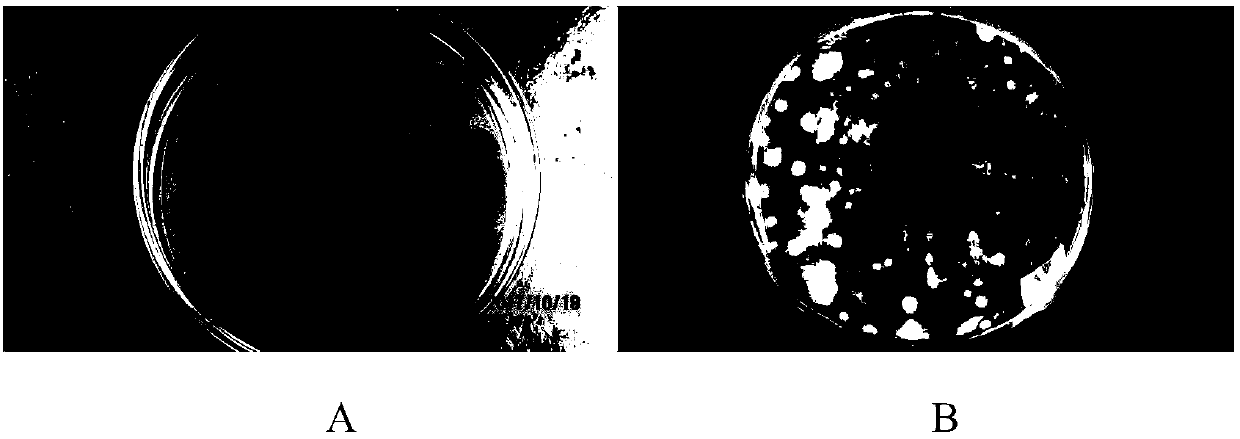
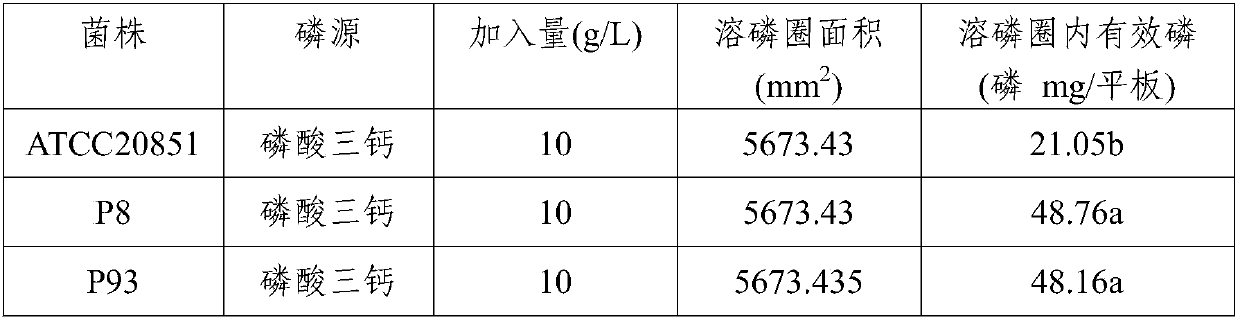
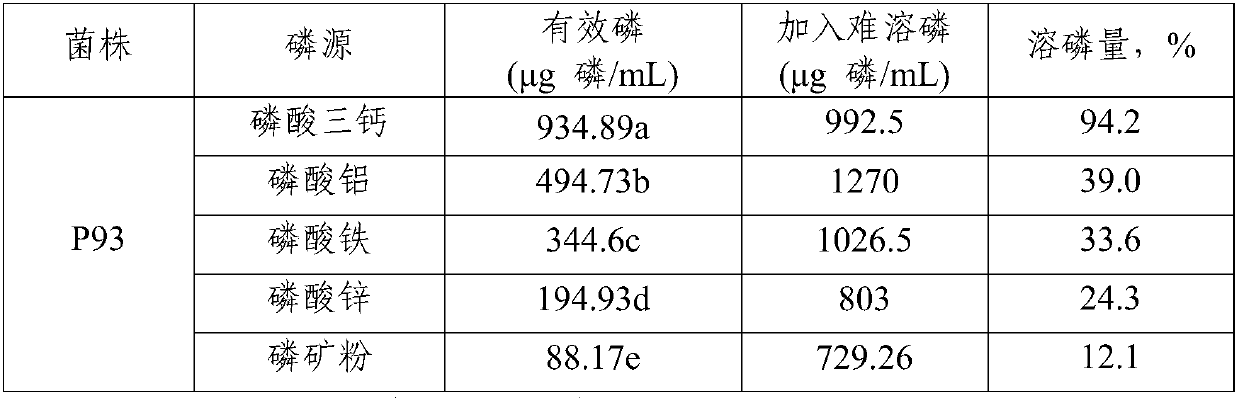
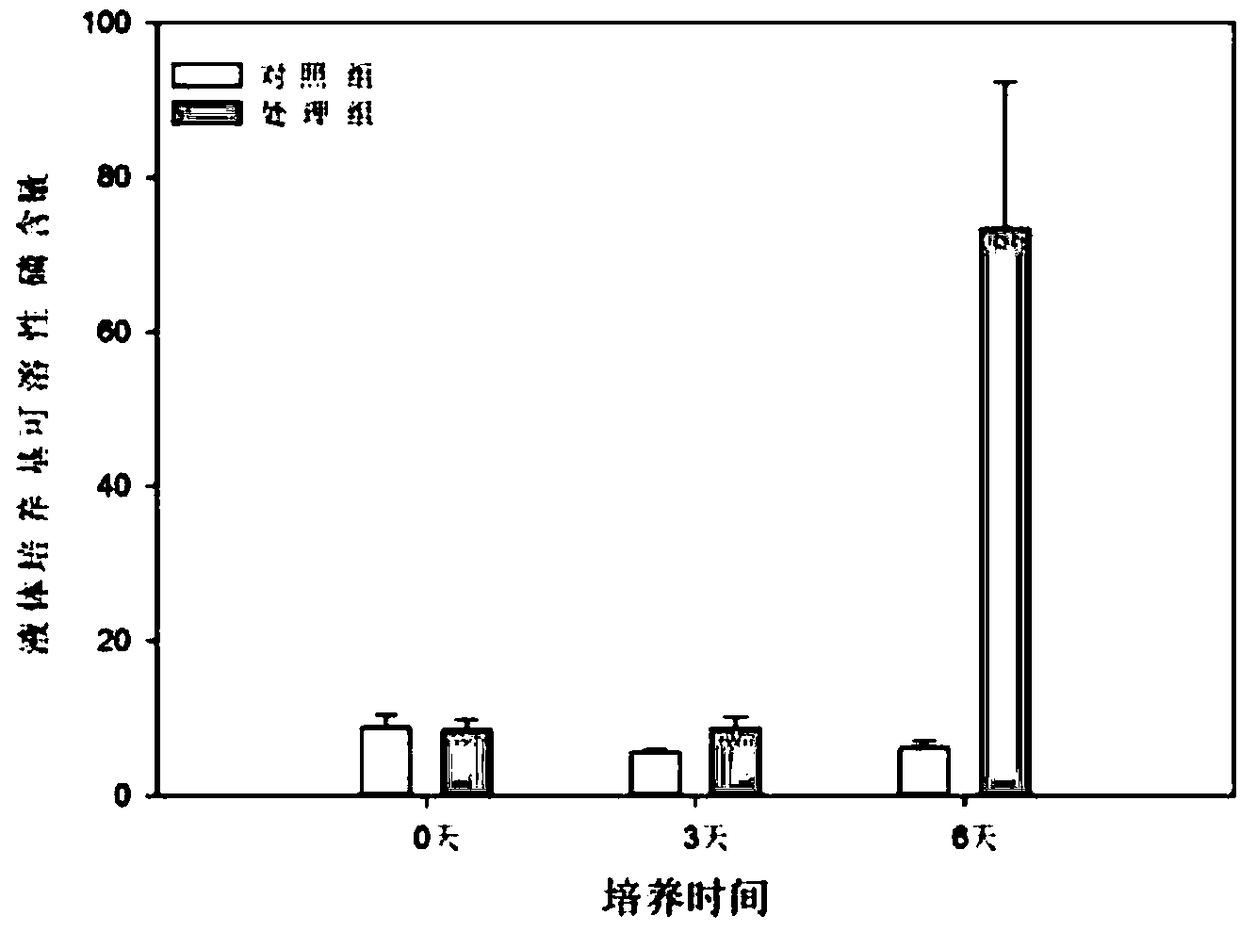
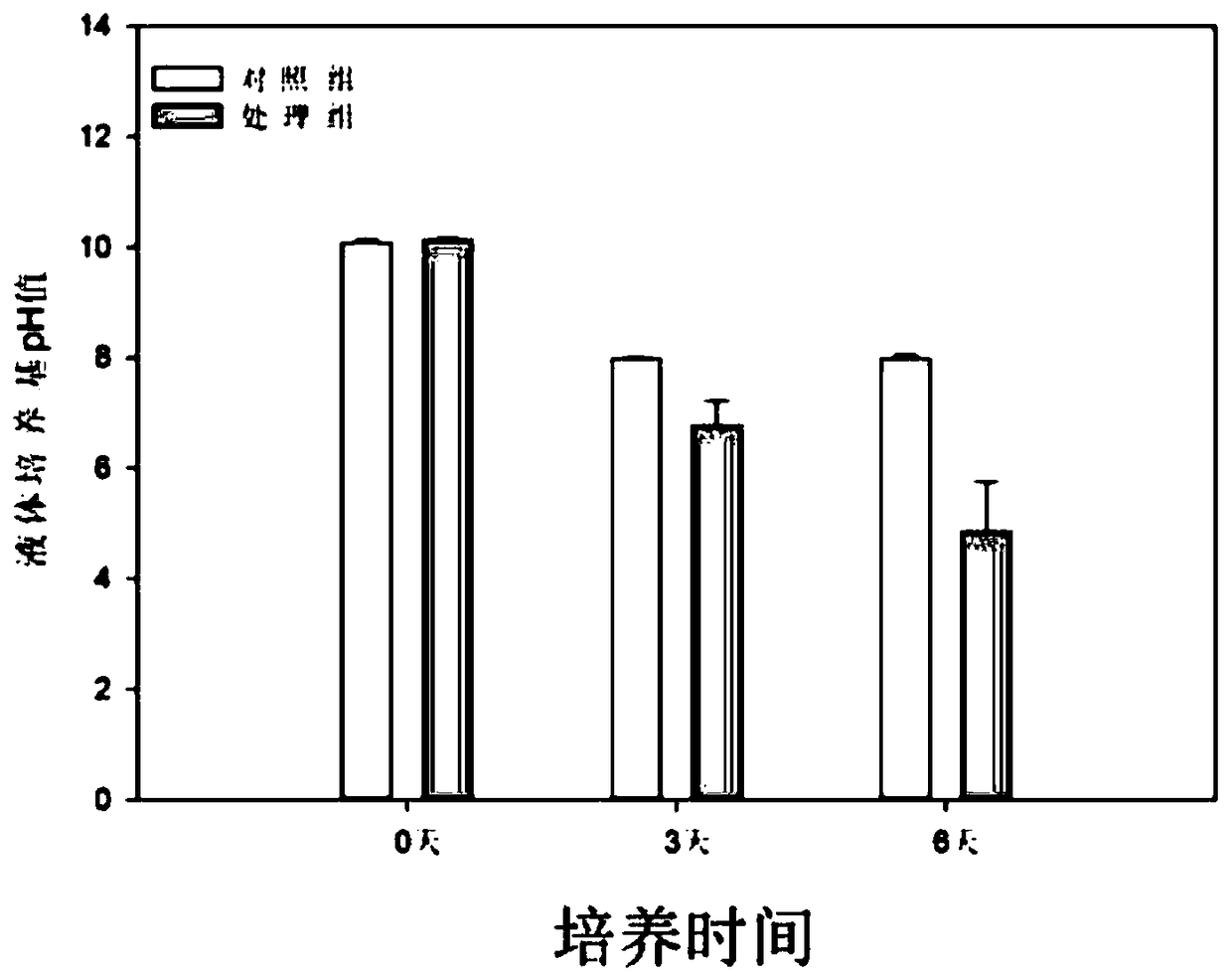
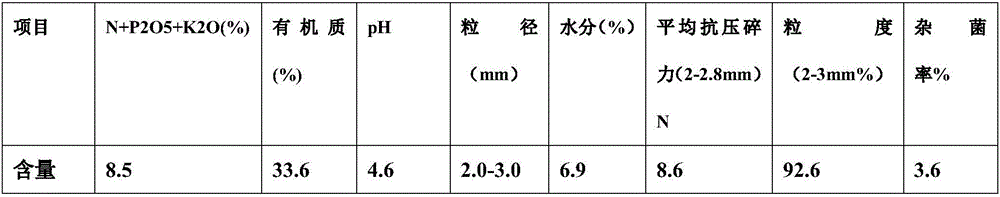
Aspergillus aculeatus P93, biofertilizer preparation prepared from same and application thereof
ActiveCN107779407AEffective dissolutionRich varietyCalcareous fertilisersFungiEcological environmentTri calcium phosphate
The invention discloses aspergillus aculeatus P93, a biofertilizer preparation prepared from same and application thereof. The aspergillus aculeatus P93 has the preservation number of CGMCC NO.14150.Microbial inoculum prepared from the aspergillus aculeatus P93 has obvious effects of promotion of crop growth, yield increasing and activation of soil phosphorus. and the microbial inoculum P93 can dissolve multiple insoluble phosphorus, ground phosphate rock, iron phosphate, zinc phosphate and tricalcium phosphate are efficiently dissolved in a liquid culture medium, and dissolution rate reaches12.1-94.2%; under soil conditions, five insoluble phosphorus sources are used, then the microbial inoculum P93 is inoculated, and soil available phosphorus is improved by 257.8-1004.6%; the microbialinoculum P93 is inoculated for promoting phosphorus absorption of corns, and total phosphorus of a corn plant is increased by 3.4-136.4%; and phosphorus dissolving capability is higher than that of phosphorus dissolving penicillium bilaiae (ATCC 20851) which is reported at present and internationally recognized. The microbial inoculum disclosed by the invention has significance on conservation ofphosphorus resources in agricultural production in China, the sustainable yield increase of cereals and protection of farmland ecological environment.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Preparation method of phosphate-solubilizing microbial agent and application thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of a phosphate-solubilizing microbial agent and application thereof and belongs to the field of microbial technology. The preparation method of the phosphate-solubilizing microbial agent comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of a liquid state phosphate-solubilizing microbial solution; and (2) preparation of a solid state phosphate-solubilizingmicrobial agent. The application of the solid state phosphate-solubilizing microbial agent comprises the following steps: (1) during building and planting, the solid state phosphate-solubilizing microbial agent is applied by a broadcasting mode, and the application amount is 10-20 kg / Mu; and (2) during sowing, the solid state phosphate-solubilizing microbial agent and seeds undergo seed dressing (1 kg of ryegrass seeds are stirred into 5-8 kg of the solid state phosphate-solubilizing microbial agent), and sowing is conducted. The phosphate-solubilizing microorganism, namely Aspergillus aculeatus has endophilicity with ryegrass, has capabilities of secreting IAA, siderophore, ACC deaminase and organic acid, can effectively promote plant growth while solubilizing phosphate, can improve soilfertility, and can greatly increase content of rapidly available phosphorus in soil. The preparation is convenient, application method is simple, and a broadcasting or seed dressing method, etc. can be adopted for inoculation; and cost is low, and operation is simple.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Sustained-release fertilizer for preventing soil salinization and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN106431626AProlong survival timeFree from influenceSuperphosphatesCalcareous fertilisersBacillus megateriumInorganic compound
The invention relates to a sustained-release fertilizer for preventing soil salinization. The sustained-release fertilizer is characterized by being prepared from 25wt% to 35wt% of vegetable garden soil, 5wt% to 10wt% of active functional bacteria, 5wt% to 15wt% of mineral powder material, 25wt% to 30wt% of organic fertilizer, 15wt% to 20wt% of inorganic compounded fertilizer and water, wherein the sum of weight percent of all the ingredients is 100%, the active functional bacteria comprise lactic acid bacteria, bacillus subtilis, bacillus megaterium, trichoderma, aspergillus niger, monascus, trichoderma harzianum, aspergillus aculeatus and yeasts, the mineral powder material is one or a mixture of more of peat, zeolite, vermiculite, montmorillonite, calcium carbonate and expanded perlite, the fineness of the mineral powder material is smaller than or equal to 200 meshes, the organic fertilizer contains decomposed manure, a rapeseed cake fertilizer and straws, and the weight ratio of the manure to the rapeseed cake fertilizer to the straws is (5.5 to 7.5): (2.5 to 3.5): (0.5 to 1.5).
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
Soy processing method, processed soy power and processed soy liquid
InactiveCN1927033AAvoid damageImprove qualityGlycosylasesFood preparationPentagalacturonic acidSoybean preparation
The present invention refers to a method of processing soy by using specific enzyme, in other words, by using a pectinase produced by microorganisms from Aspergillus genera (such as pectinmethylesterase enzyme, produced by the microorganism Aspergillus oryzae; or the enzymes pectintranseliminase, polygalacturonase and pectinesterase, produced by the microorganism Aspergillus niger; or betagluconase(endo-1,3(4)-), produced by the microorganism Aspergillus aculeatus), which is capable of efficiently producing a processed soy powder and liquid with substantially no unpleasant odor, characteristic of products derived from soy, and an ameliorated digestion-absorption coefficient for human body, using soy in its integral form, in other words, utilizing all nutrients present in soy.
Owner:BRASFANTA INDA E COMERCIO
Method for bioconversion of chlorogenic acids in plants by adopting aspergillus aculeatus
ActiveCN103421853AShort conversion timeEfficient conversionMicroorganism based processesFermentationDicaffeoylquinic acidCaffeic acid
The invention relates to a method for directionally converting and purifying chlorogenic acids by using aspergillus aculeatus CCTCC No.M2011264 and an enzyme liquid of the aspergillus aculeatus. The method comprises the following steps: the aspergillus aculeatus is inoculated to a liquid or solid enzyme generation culture medium, the fungus or enzyme obtained from fermentation is used for converting plant extracting solution or powder containing the chlorogenic acids. According to the invention, 1, 5-dicaffeoylquinic acid in the system of the method is reserved in the solution rather than being converted, and the solution can be purified as partial compositions are consumed during the conversion process (for example, 99% above of 4, 5-dicaffeoylquinic acid with property extremely similar to the that of the 1, 5-dicaffeoylquinic acid is consumed), so that the follow-up separation and purification steps are eliminated, and the method can be taken as a novel method for purifying the 1, 5-dicaffeoylquinic acid; besides, through controlling the conversion condition, the limitation that only caffeic acid, ferulic acid and quinic acid can be obtained by adopting the conventional conversion method is overcome.
Owner:巴州正达绿源生物科技有限公司
Bagasse saccharifying method
InactiveCN108713629AGood saccharification effectIncrease saccharification rateFood processingAnimal feeding stuffTrichoderma reeseiGenus Kluyveromyces
The invention discloses a bagasse saccharifying method which comprises the following steps: (1) pretreatment of bagasse: sterilizing bagasse with infrared ray, and regulating the moisture content of bagasse to 15%-20% through microwave drying or addition of water; (2) saccharification: adding zymophyte in bagasse, then fermenting at the temperature of 25-30 DEG C, stopping fermentation when ethylalcohol is generated, sterilizing bagasse with infrared ray, then adding citric acid, dimethyl sulfoxide tetrabutylammonium chloride and dimethyl sulfoxide imidazolium salt in the sterilized bagasse,and degrading for 2-6 hours at the room temperature, wherein the zymophyte comprises trichoderma reesei, aspergillus niger, aspergillus aculeatus and kluyveromyce; and (3) enzyme deactivation: puttingthe saccharified bagasse at a high temperature of above 100 DEG C for sterilization for 10-30 min. The bagasse saccharifying method has the advantages that the saccharifying rate is high, and the fermentation end-point is easy to control.
Owner:GUANGXI XIUMEI ZHUANGXIANG ENERGY ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION CO LTD
Benzoquinone derivative from aspergillus aculeatus and application of benzoquinone derivative
InactiveCN103058846AGood antitumor activityOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsBenzoquinone CompoundPerylene derivatives
The invention relates to a benzoquinone derivative from aspergillus aculeatus and application of the benzoquinone derivative. The structural formula of the compound is shown in the specification. Experiments prove that the benzoquinone compound has good antitumor activity. The benzoquinone derivative can be used for preparing cell proliferation inhibition drugs or antitumor drugs for antitumor study.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Application of plant essential oil in inhibiting mycete in air
ActiveCN109792990AHigh antibacterial activityBroad antibacterial spectrumBiocideFungicidesPenicillium herqueiCinnamyl acetate
The invention provides application of plant essential oil in inhibiting mycete in the air. The plant essential oil is characterized in that cinnamon essential oil is mainly prepared from cinnamyl aldehyde, cinnamyl acetate, coumarin and benzaldehyde; oregano essential oil is mainly prepared from carvacrol, 5-methyl-2,4-diisopropyl phenol, thymol and 3-methyl-4-isopropyl phenol; clove essential oilis mainly prepared from eugenol, caryophyllene, humulene and caryophyllenol. In order to fully investigate the effect of the plant essential oil on the inhibition of the mycete in the air in a museum, the three kinds of plant essential oil are used for performing inhibition tests on penicillium oxalicum, penicillium herquei and aspergillus aculeatus respectively, and the three kinds of plant essential oil are compounded to perform synergistic effect inhibition tests on the penicillium oxalicum, penicillium herquei and aspergillus aculeatus respectively. Tests show that the three kinds of plant essential oil have obvious antibacterial effects on the three kinds of mycete either alone or in combination and have good application potential as an antifungal agent in the air.
Owner:广西民族博物馆
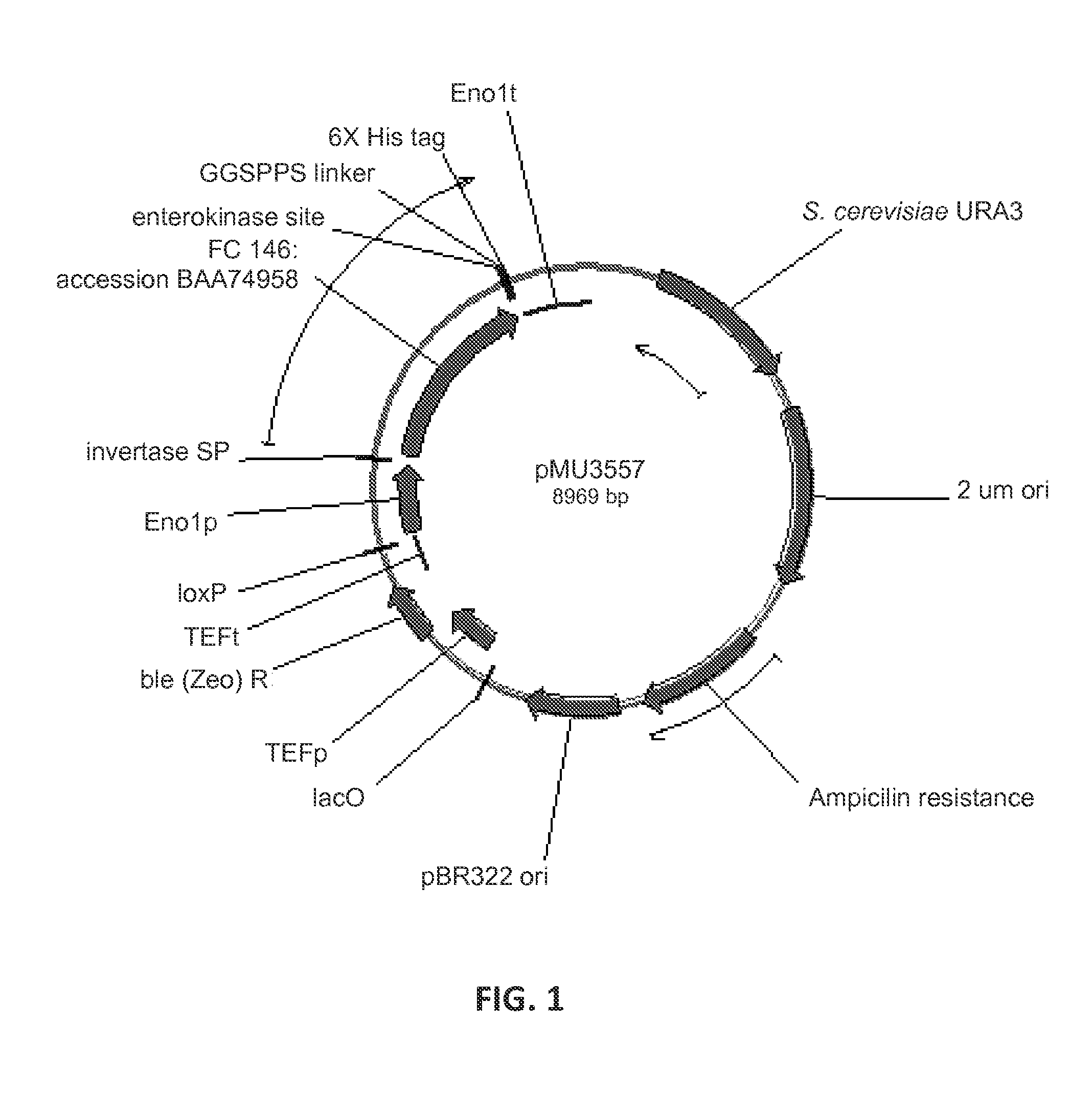
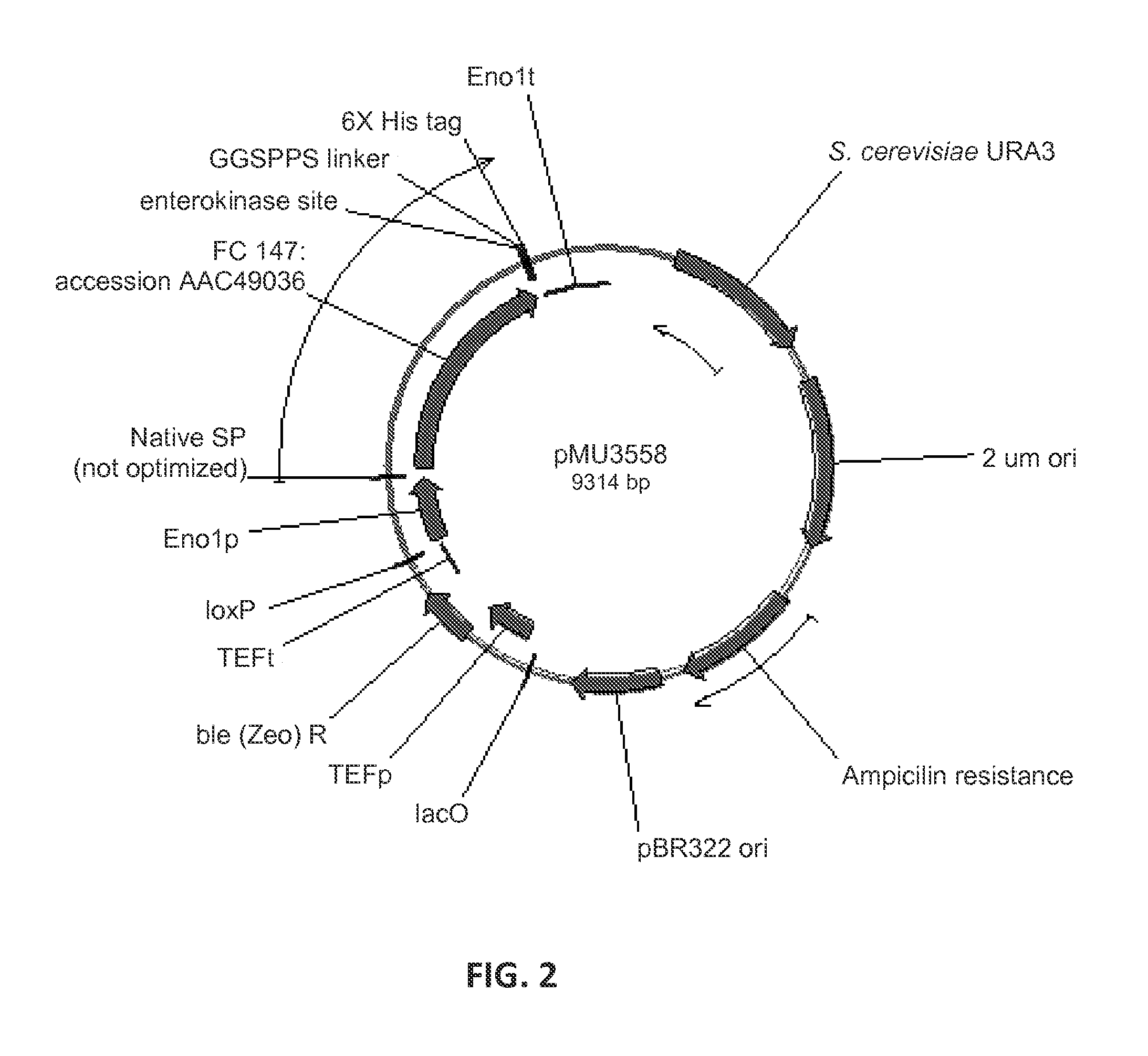
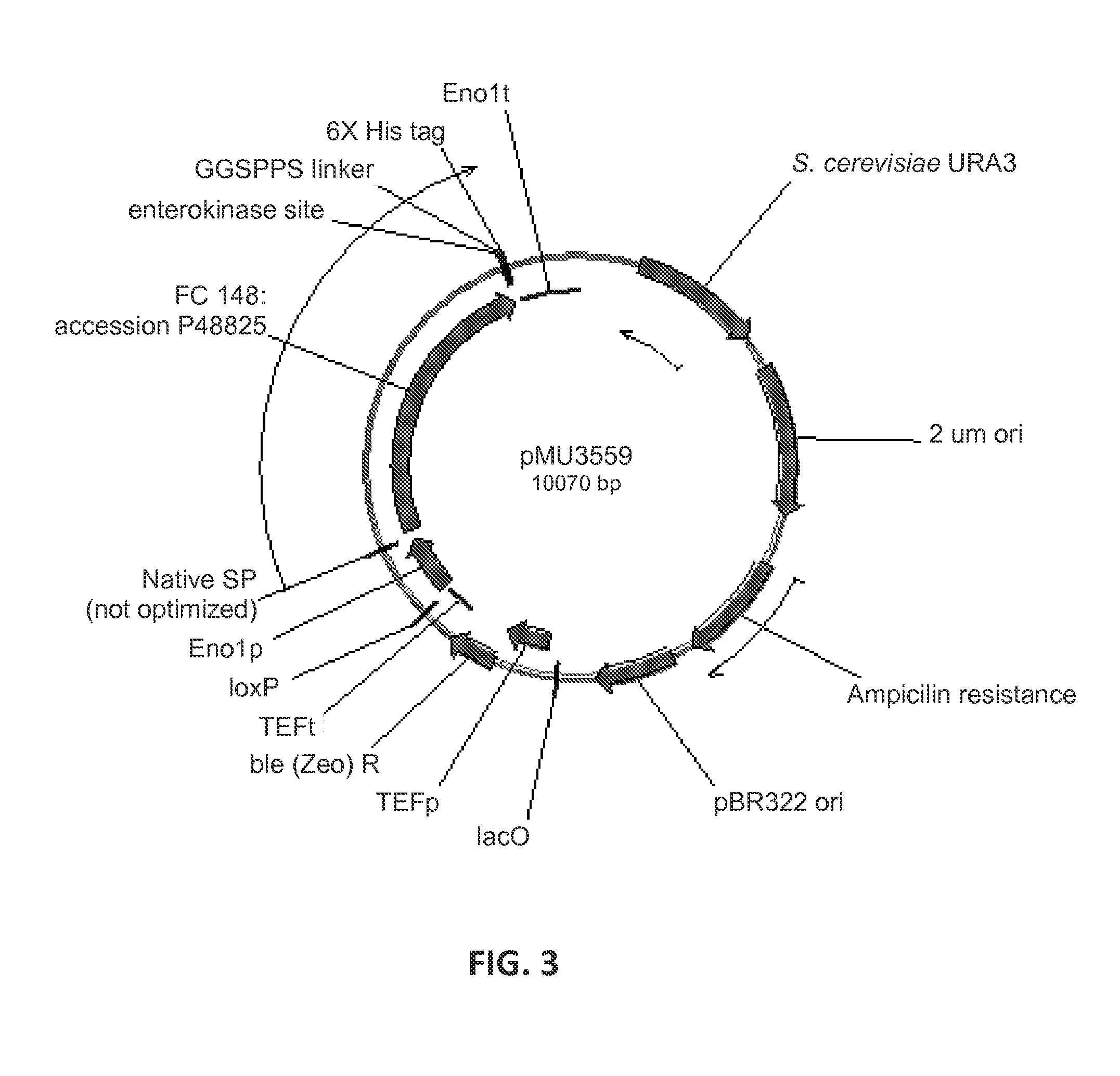
Expression of beta-glucosidases for hydrolysis of lignocellulose and associated oligomers
The present invention provides for heterologous expression of beta-glucosidase (BGL) polypeptides encoded by Humicola grisea, Candida wickerhamii, Aspergillus aculeatus, Aspergillus oryzae, Penicillium decumbens, Chaetomium globosum, Neocallimastix frontalis, Debaryomyces hansenii, Kluyveromyces marxianus, or Phytophthora infestans in host cells, such as the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The expression in such host cells of the corresponding genes, and variants and combinations thereof, result in improved specific activity of the expressed BGL. Thus, such genes and expression systems are useful for efficient and cost-effective consolidated bioprocessing systems.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
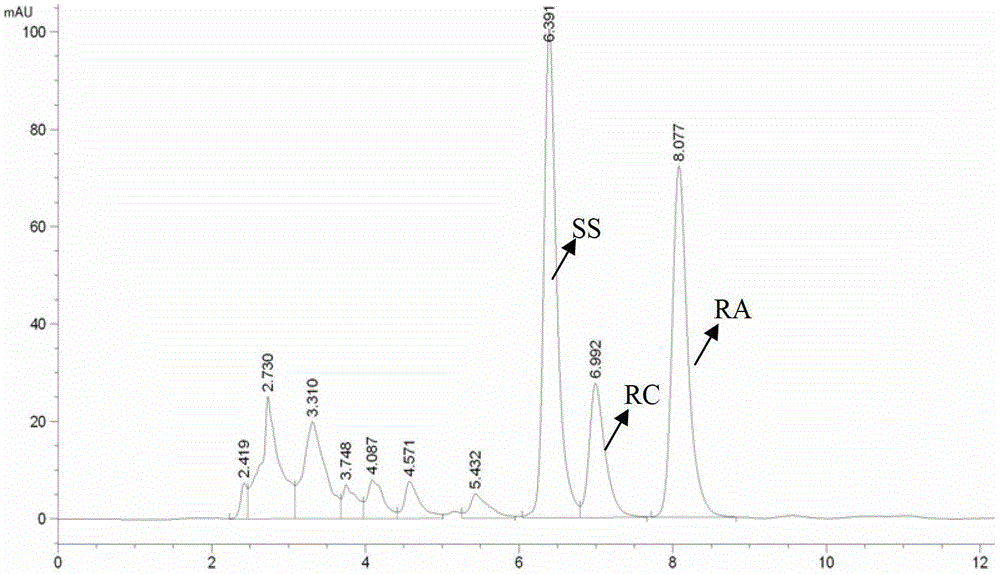
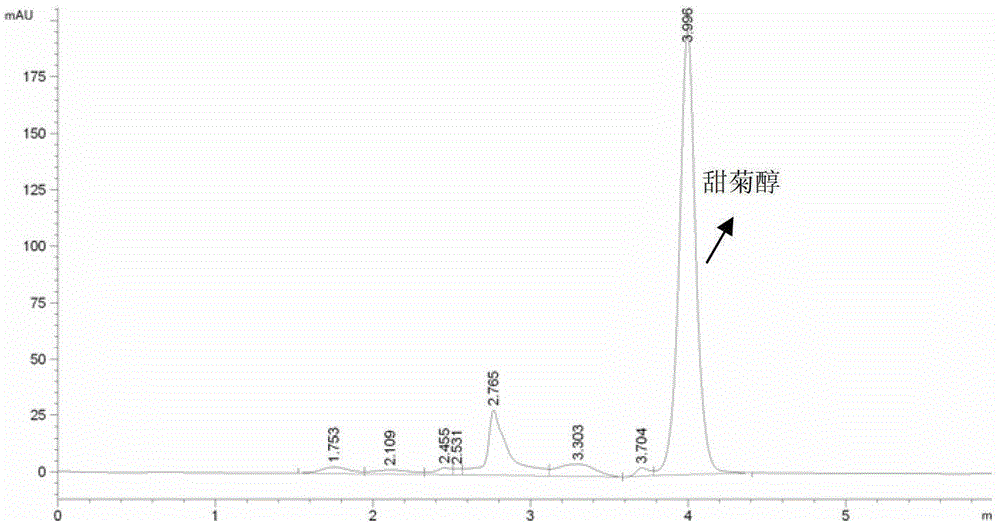
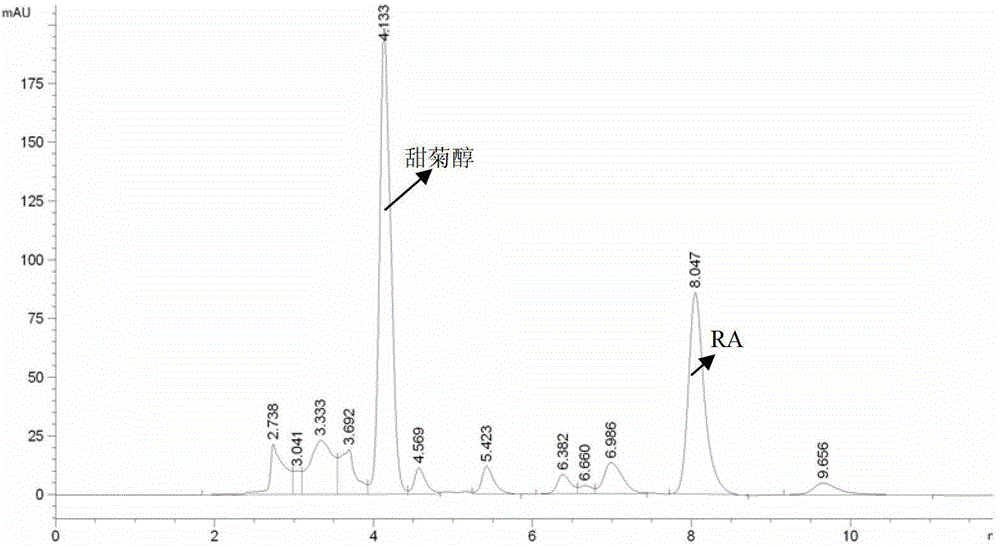
A kind of method utilizing Aspergillus aculeatus to prepare steviol and purify rebaudioside A
ActiveCN103014076BImprove qualitySimple processMicroorganism based processesFermentationPurification methodsAlcohol
The invention relates to a method for converting stevioside or rubusoside raw materials into steviol by utilizing Aspergillusaculeatus ZJ (the preservation number of which is CCTCC No:M2011264) bacterium and enzymes thereof, and purifying rebaudioside A (RA). The method specially comprises the steps of: acting Aspergillusaculeatus or fermentation liquor thereof or extracted enzyme liquor on the stevioside or stevia rabaudiana extract liquid, and converting ingredients, except RA, of the stevioside to product steviol; settling and separating the steviol from the solution; purifying and separating by adopting a conventional crystallization and other purification methods, wherein the RA in the system is not converted and left in the solution; and purifying the RA by adopting the following convention extracting, separating and purifying method. The invention provides a method for converting stevioside into steviol by utilizing Aspergillusaculeatus bacterium and enzyme liquor thereof, and purifying rebaudioside A. According to the method, the conditions are mild, the environment compatibility is good, and the process equipment is simple, thus application values are high.
Owner:巴州正达绿源生物科技有限公司
Coding gene of alpha-L-rhamnosidase mutant and expression vector of coding gene
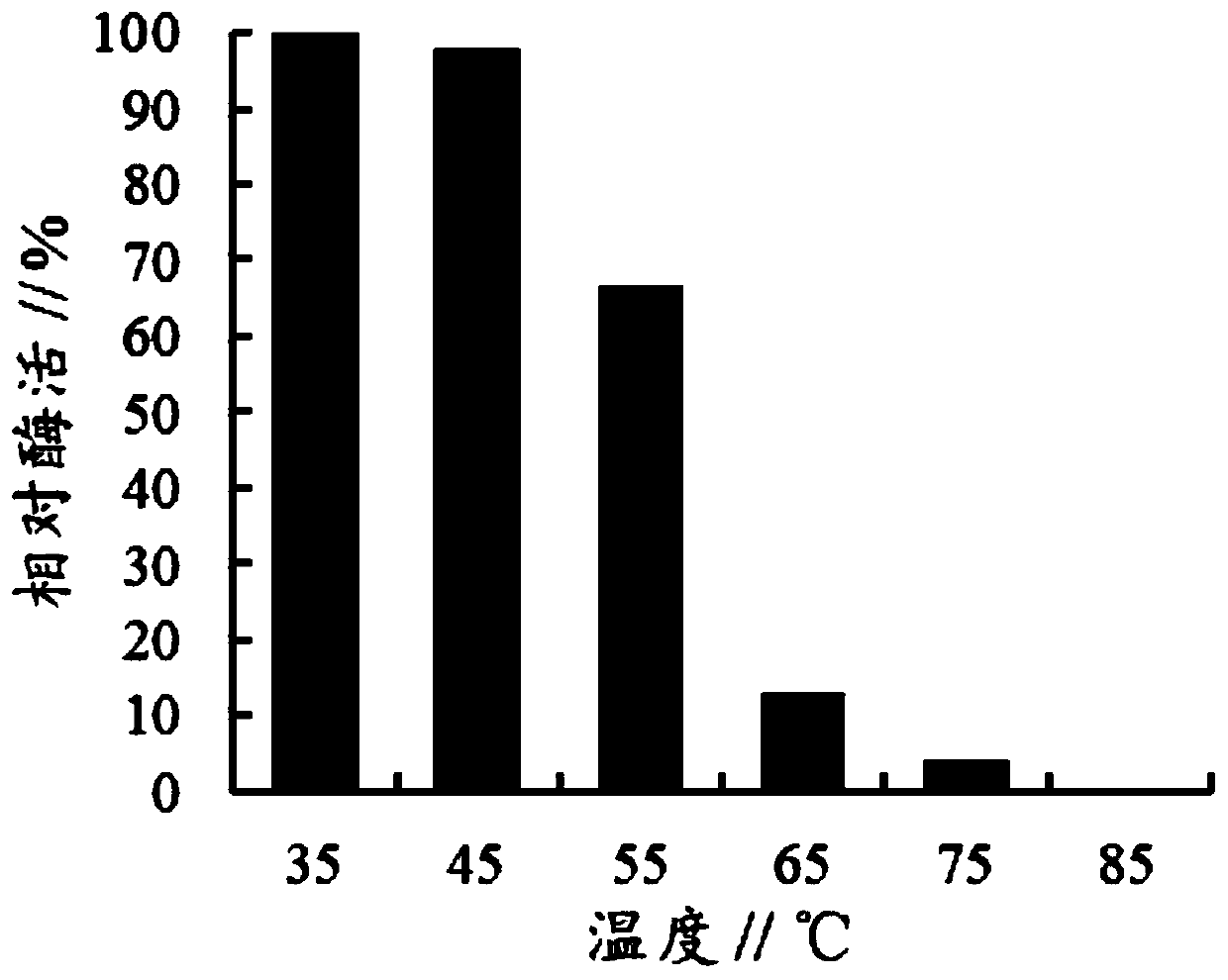
ActiveCN111575304AHigh activityImprove heat stabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The invention discloses a coding gene of an alpha-L-rhamnosidase mutant. The nucleotide sequence of the alpha-L-rhamnosidase mutant is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. According to the invention, site mutation is carried out on the basis of an aspergillus aculeatus wild type alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene; the similarity between the mutated alpha-L-rhamnosidase mutant gene and the wild type alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene is 99.89%; and compared with the wild type alpha-L-rhamnosidase mutant gene, after being expressed in pichia pastoris, the mutated alpha-L-rhamnosidase mutant gene has the advantages that enzyme activity and heat resistance of alpha-L-rhamnosidase are obviously improved. According to the method, catalytic performance and stability of the alpha-L-rhamnosidase under a high-temperature conditioncan be improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
Benzoquinone spiro compound derived from aspergillus aculeatus and application of benzoquinone spiro compound
InactiveCN103058971AGood antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryStructural formulaAntitumor activity
The invention relates to a benzoquinone spiro compound derived from aspergillus aculeatus and application of the benzoquinone spiro compound. The structural formula of the compound is shown in the specification. Experiments prove that the benzoquinone spiro compound has good antitumor activity. The benzoquinone spiro compound can be used for preparing cell proliferation inhibition drugs or antitumor drugs for antitumor study.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Strain for producing ratgalacturonorhamnan hydrolase at high yield
ActiveCN107988086AReduce manufacturing costFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial transformation and particularly relates to an Aspergiulls aculeatus mutant strain for producing ratgalacturonorhamnan hydrolase at high yield.According to the Aspergills aculeatus mutant strain disclosed by the invention, Aspergiulls aculeatus DSM2344 is used as an original strain and an ultraviolet mutagenesis method is adopted to selectfor obtaining a mutant strain Aspergiullus aculeatus T13 with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2017784. After a mutant strain solid is subjected to solid shake flask fermentation for 3.5 days, theenzyme activity of the ratgalacturonorhamnan hydrolase reaches 63.7u / g, which is increased by 41.6 percent compared with that of an original strain; unexpected technical effects are achieved. The Aspergiulls aculeatus mutant strain provided by the invention can be widely applied to fermentation production of the ratgalacturonorhamnan hydrolase; the production cost of the enzyme is favorably reduced and promotion and application of the ratgalacturonorhamnan hydrolase in the food industry are promoted.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP +1
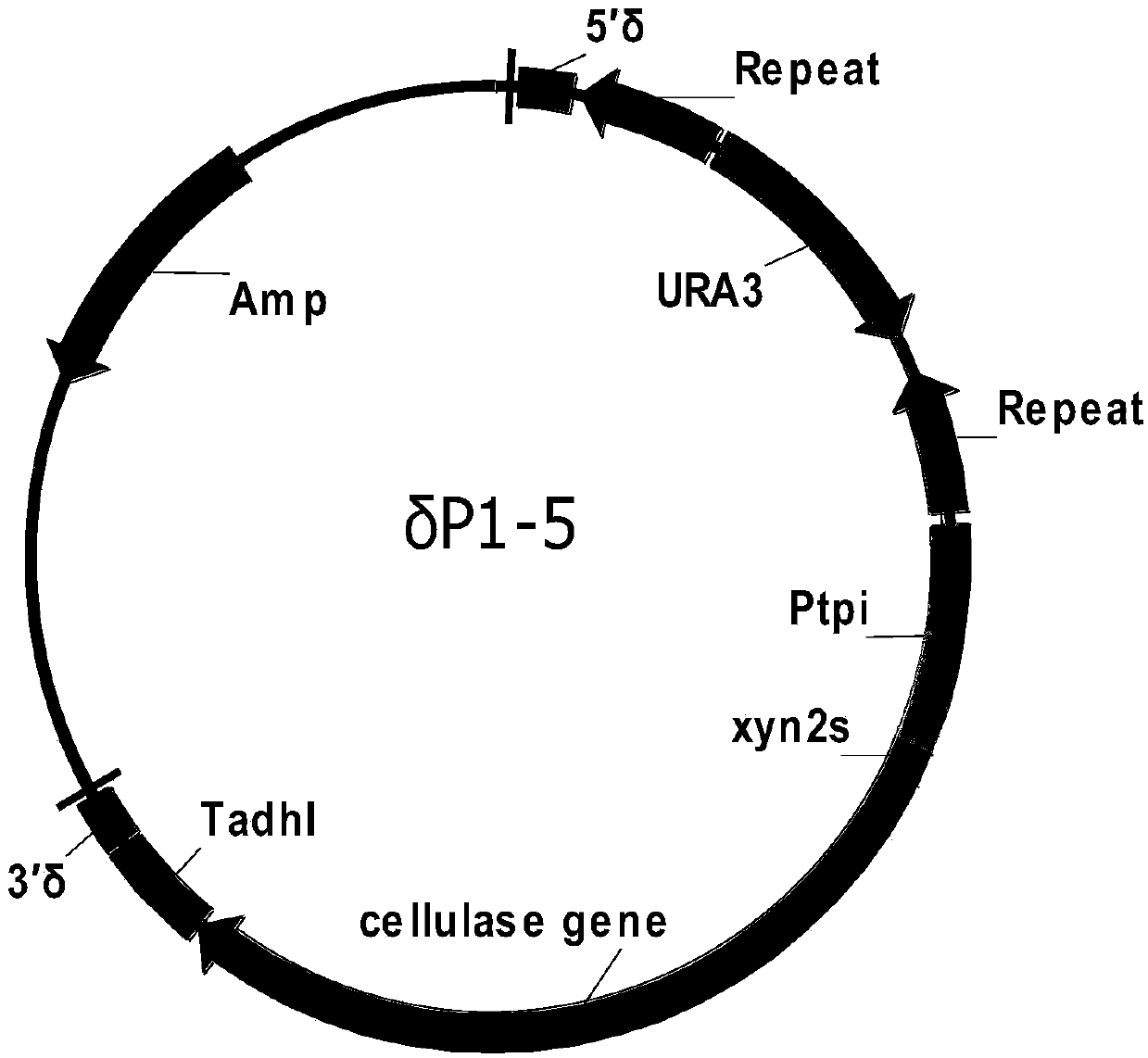
Saccharomyces cerevisiae industrial strain capable of delta integration and secretion and expression of cellulase and application thereof
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae industrial strain capable of delta integration and secretion and expression of cellulase and an application thereof. The saccharomyces cerevisiae industrial strain has a preservation number of CGMCC NO. 16825. The industrial strain R delat BEC, with the preservation number of CGMCC NO. 16825 is applied to ethanol production. The strain R delta BEC, with the preservation number CGMCC NO. 16825, secretes and expresses five kinds of cellulase: trichoderma reesei CBH1, CBH2 and EG2; aspergillus aculeatus BGL1 and CBH1. The bacteria can cooperate with prior commercial cellulase to efficiently degrade cellulose and improve the yield of ethanol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Honey pomelo sac stomach nourishing and fermenting beverage
InactiveCN106107383AIncrease added valueAvoid wastingFood ingredient as taste affecting agentFood ingredient as mouthfeel improving agentAdditive ingredientNitrogen source
The invention discloses a honey pomelo sac stomach nourishing and fermenting beverage and relates to the technical field of preparation of honey pomelo beverages. A preparation method comprises the following steps of debittering pomelo sac powder: by using aspergillus aculeatus, aspergillus niger, aspergillus terreus and the like as strains and using corn steep liquor as a nitrogen source, adding water, and then fermenting the pomelo sac powder to produce naringinase, wherein the ratio of mass fraction of the honey pomelo sac powder to the corn steep liquor to the water is 100:(10 to 30):(150 to 400); mixing the debittered pomelo sac powder with rhizoma dioscoreae powder and fructus amomi powder according to the ratio of mass fraction being (80 to 100):(40 to 60):(30 to 50), and preparing a mixture into a crude product by techniques such as fermenting; after fermenting, blending the crude product with honey according to the mass ratio being (80 to 100):(2.5 to 10), bottling a mixture, and sterilizing the mixture to obtain a finished product. The honey pomelo sac is used as a raw material, so that the waste of honey pomelo surface skin with abundant essential oil components is avoided, and an added value of the honey pomelo sac is improved. The prepared honey pomelo sac stomach nourishing and fermenting beverage has no other additives, has certain stomach nourishing efficacy, and is a health-care beverage with higher health-care value.
Owner:广东衎衎实业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com