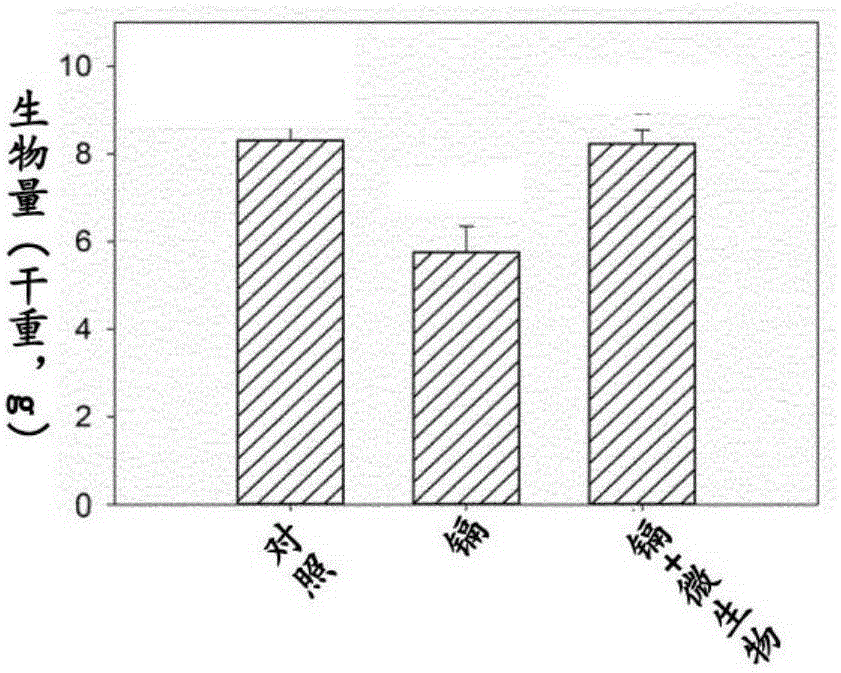
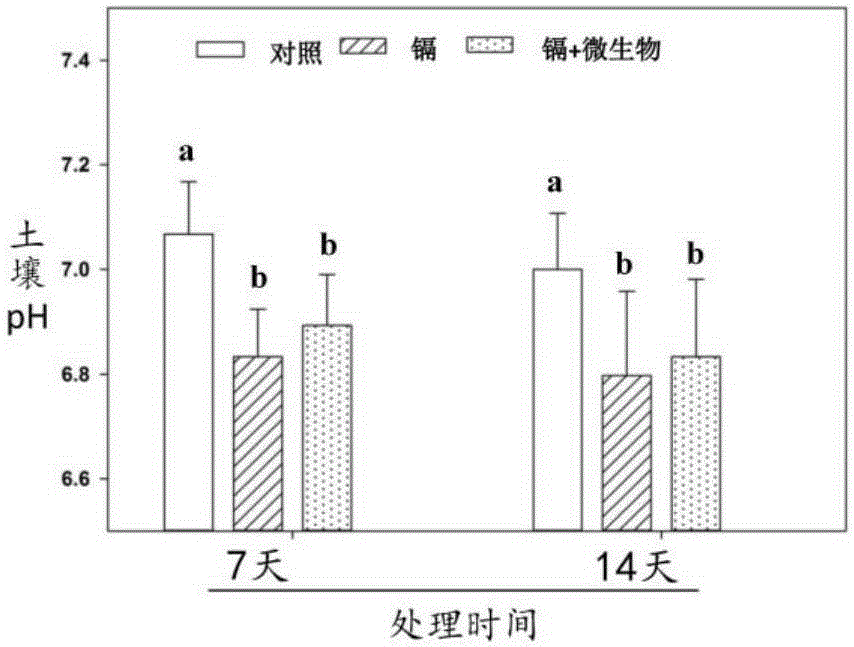
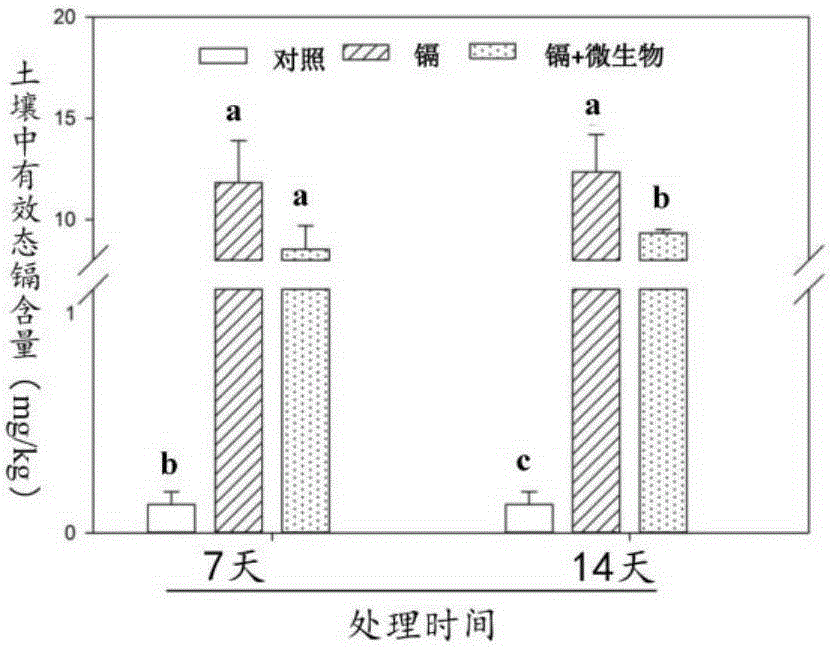
Method for reducing cadmium content of rice grains in cadmium-polluted rice field by using cadmium-resisting microorganisms
A technology for rice grains and microbes, applied in the field of bioremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil, to achieve good ecological and social benefits, easy operation, and wide application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0079] ③ Preparation of cadmium-resistant microbial culture substrate
[0080] A. Determination of optimum temperature and pH of Aspergillus aculeatus and Bacillus cereus:
[0081] Inoculate 1mL of the bacterial suspension of the two strains into 200mL of newly prepared and sterilized liquid medium, and adjust according to different temperature (10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40°C) and pH value (4, 5°C). , 6, 7, 8, 9) under the conditions of shaking culture for 36 hours, by measuring the absorbance value, determine the growth temperature of the strain;
[0082] Bacillus cereus ( Bacillus cereus ) grows well at 15-40°C, can grow at pH 4-9, and the optimum pH is 6-7; Aspergillus aculeatus fungus ( Aspergillus aculeatus ) grows well at 10-35°C, can grow at pH 4-7, and the optimum pH is 6;
[0083] B. Preparation of bacterial suspension:
[0084] Take the cadmium-resistant fungi and bacteria obtained from the above screening, and insert them into the corresponding sterile liquid cul...
Embodiment 1
[0103] 1. Embodiment one: adaptability test
[0104] The culture medium was sawdust and sand (v / v=3:1, pH=6.5); the culture medium was divided into two parts, and one part was inoculated with the suspension of the two strains screened above at 5% inoculum (1:1 Proportional mixing), the other was not inoculated. The rice seedlings that had been raised were planted in the two substrates respectively, and the other substrate inoculated with cadmium-tolerant microorganisms was left idle; fertilized with the nutrient solution formula of the International Rice Research Institute, and treated at 7 days, 21 days, 40 days and 60 days respectively The rice rhizosphere soil and idle soil were taken to screen for microorganisms while observing the growth of rice.
[0105] Analysis of the test results: The test results showed that during the whole treatment period, the growth of rice in the matrix of the inoculated strain and the non-inoculated strain were consistent, and the growth cycle...
Embodiment 2
[0106] 2, embodiment two: pot test
[0107] The indica rice '9311' was selected as the material, moved to non-polluted paddy soil for 30 days after germination, and fertilized with the nutrient solution formula of the International Rice Research Institute; v / v=3:1, pH=6.5), mix well and put it in a sterilizing pot (127°C) for high temperature sterilization for 1h, with 1.5mMCdSO 4The solution was poured until the soil cadmium concentration reached 20mg / kg, and after a week of balance, the Aspergillus aculeatus fungus and Bacillus cereus (1:1) were inoculated, treated with cadmium alone, cadmium plus Aspergillus aculeatus fungus, and cadmium plus Bacillus cereus The treatment was the control; the prepared matrix was divided into plastic buckets (40cm in height, 25cm in diameter), the rice seedlings raised were rinsed with tap water, rinsed with sterilized ultrapure water three times, and then planted in the above plastic buckets. Three plants per barrel; 5 groups of treatments...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com