Preparation method of phosphate-solubilizing microbial agent and application thereof
A technology of microbial inoculum and phosphorus-dissolving bacteria, which is applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of insufficient soil organic matter, reduce insoluble phosphorus content, secondary environmental damage, etc., and achieve the effects of simple application method, improvement of fertility status, and promotion of growth.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] 1. Example 1: Phosphorus-dissolving ability of phosphorus-dissolving microbial bacterial agent
[0032] The phosphate-soluble microorganism Aspergillus aculeatus was inoculated into a solid medium containing 0.5% insoluble inorganic phosphorus by the spot method, and cultured upside down at 30°C for 7 days to observe the change of colonies in the medium. The result is as figure 1 As shown, a white lysis zone appeared around the colony, indicating that the phosphorus-soluble microorganism Aspergillus aculeatus fungus can dissolve insoluble phosphorus.
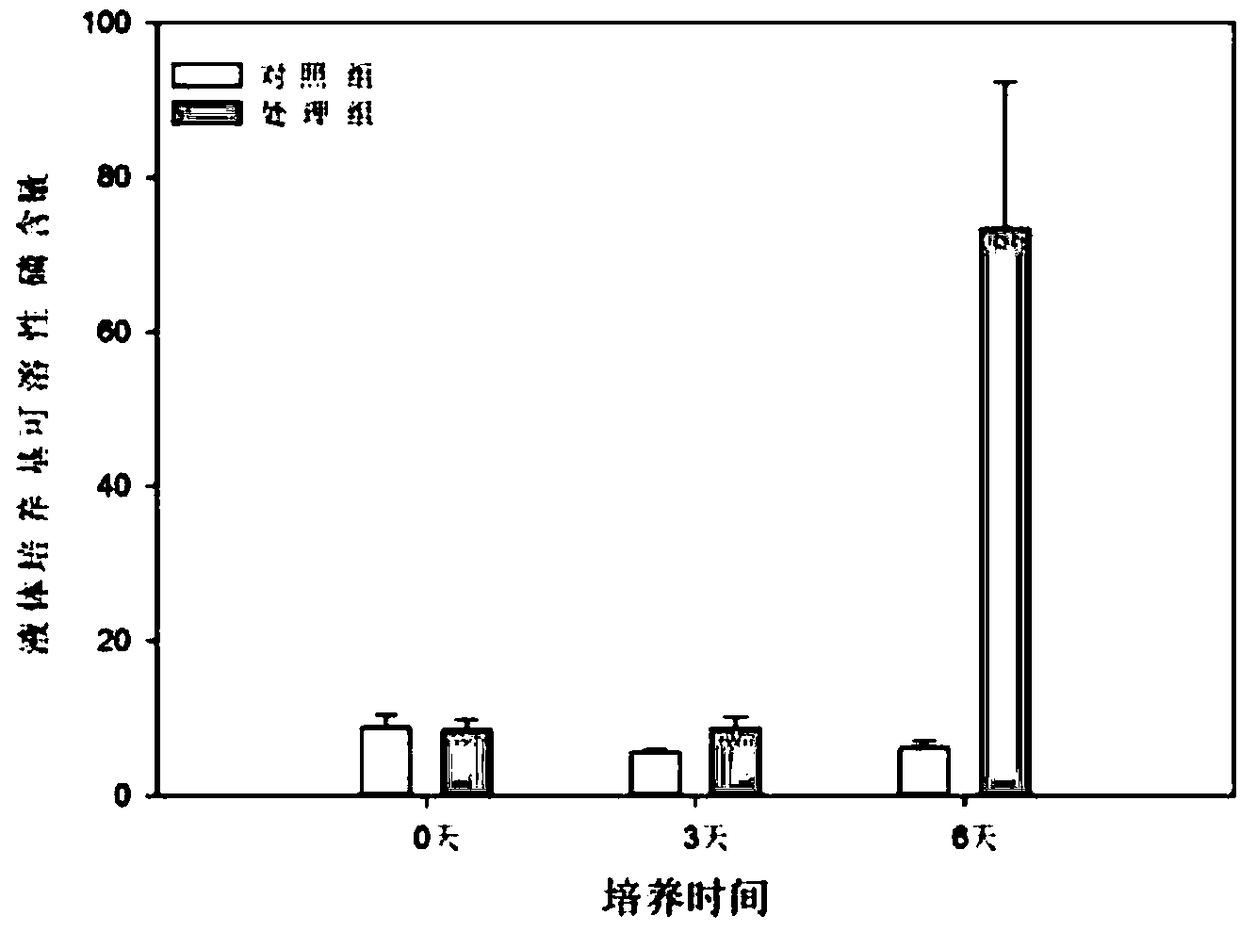
[0033] The bacterium solution of the phosphorus-dissolving microorganism Aspergillus aculeatus fungus (the number of bacteria in the bacterium solution is 1×10 9 ~9×10 9 CFU / mL range), with 3% inoculum amount into tricalcium phosphate liquid medium, cultivated in Erlenmeyer flask, using molybdenum antimony anti-colorimetric method to measure the concentration of soluble phosphorus in the fermentation broth, the results...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: the ability of phosphate-dissolving microbial bacterial agent to secrete organic acid
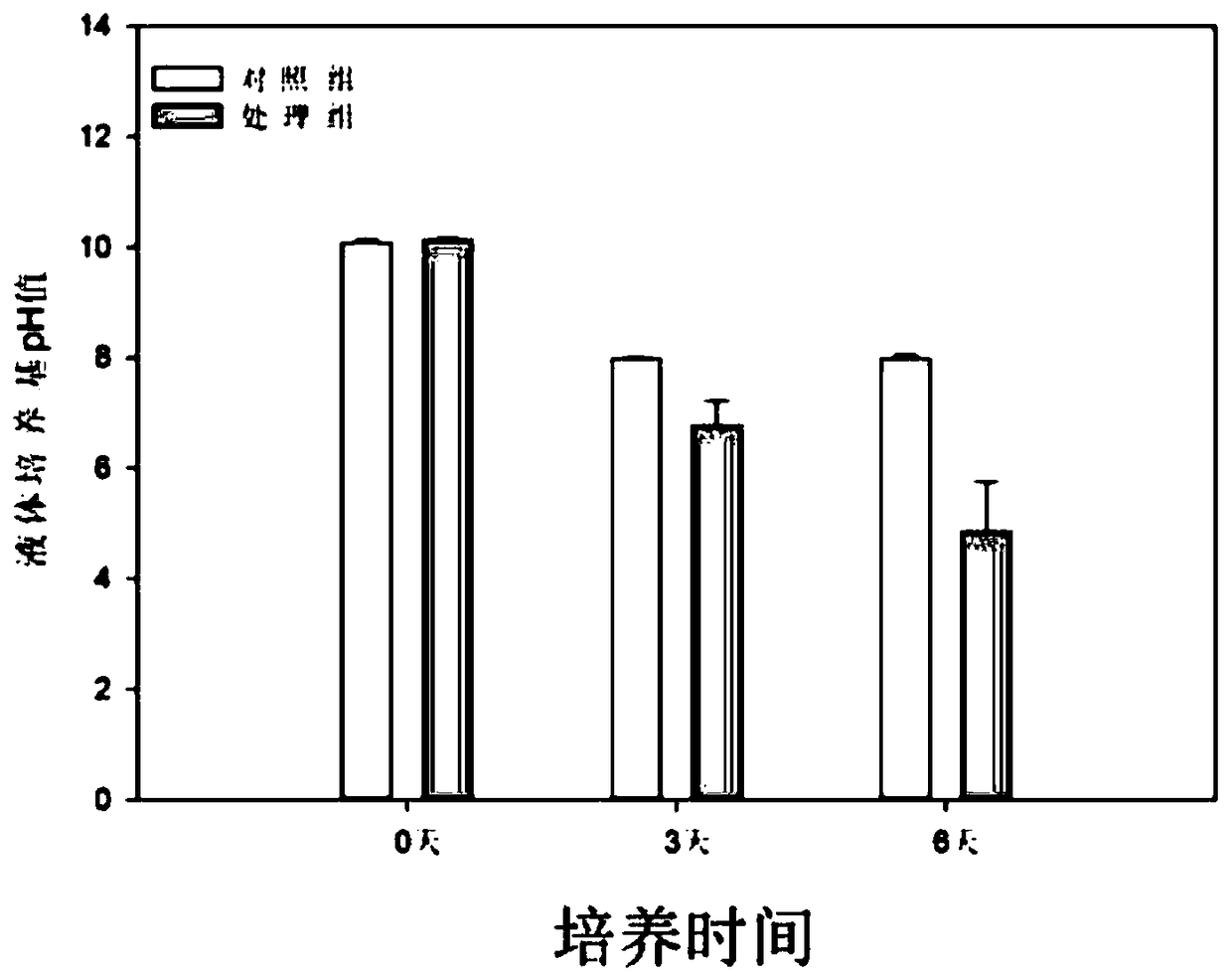
[0035] The principle of the phosphorus-soluble microorganism Aspergillus aculeatus fungus to dissolve inorganic phosphorus is to secrete organic acids, so as to dissolve the insoluble inorganic phosphorus in the soil into soluble available phosphorus for plant absorption and utilization; using tricalcium phosphate liquid medium, through high-efficiency liquid phase Chromatography was used to determine the type and concentration of organic acids in the fermentation broth. The results are shown in Table 1. In the tricalcium phosphate liquid medium added to fungi, the content of organic acids increased with the prolongation of the culture time. The main organic acids Acid species include: tartaric acid, citric acid, and glycine, thus demonstrating that the mechanism by which fungi dissolve tricalcium phosphate is through the secretion of organic acids.
[0036] Table 1 The...
example 3
[0038] Example 3: Preparation of Phosphorus-Solubilizing Microbial Inoculum and Its Use in Pot Experiment of Ryegrass
[0039] The bacterial liquid of Aspergillus aculeatus fungus (the number of bacteria in the bacterial liquid is 1×10 9 ~9×10 9 within the range of CFU / mL), with 3% inoculum amount into 100mL Martin’s (Martin) liquid medium, 30°C, 170r / min shaking culture for 48h, the liquid phosphate-dissolving bacteria solution was obtained; 20mL of the above-mentioned liquid phosphorus-dissolving bacteria Add 100g of sand and peat to the solid medium (v / v=2:1), adjust the pH to 6, and incubate at 30°C for 3 days to make a solid phosphorus-dissolving microbial bacterial agent.
[0040] The ryegrass pot experiment set up a treatment group and a control group. The treatment group was treated with 5g / pot of the above-mentioned solid microbial agent (500g of phosphorus-deficient and insoluble phosphorus soil in each pot), and the control group was treated with inactivation at 12...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com