A method for alkali-activated modified enzymatic lignin
A technology of enzymatic lignin and alkali activation, which is applied in the field of enzymatic lignin technology, can solve the problems of poor water solubility and low reactivity of enzymatic lignin, and achieve improved reactivity, convenient packaging and transportation, and easy commercialization Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
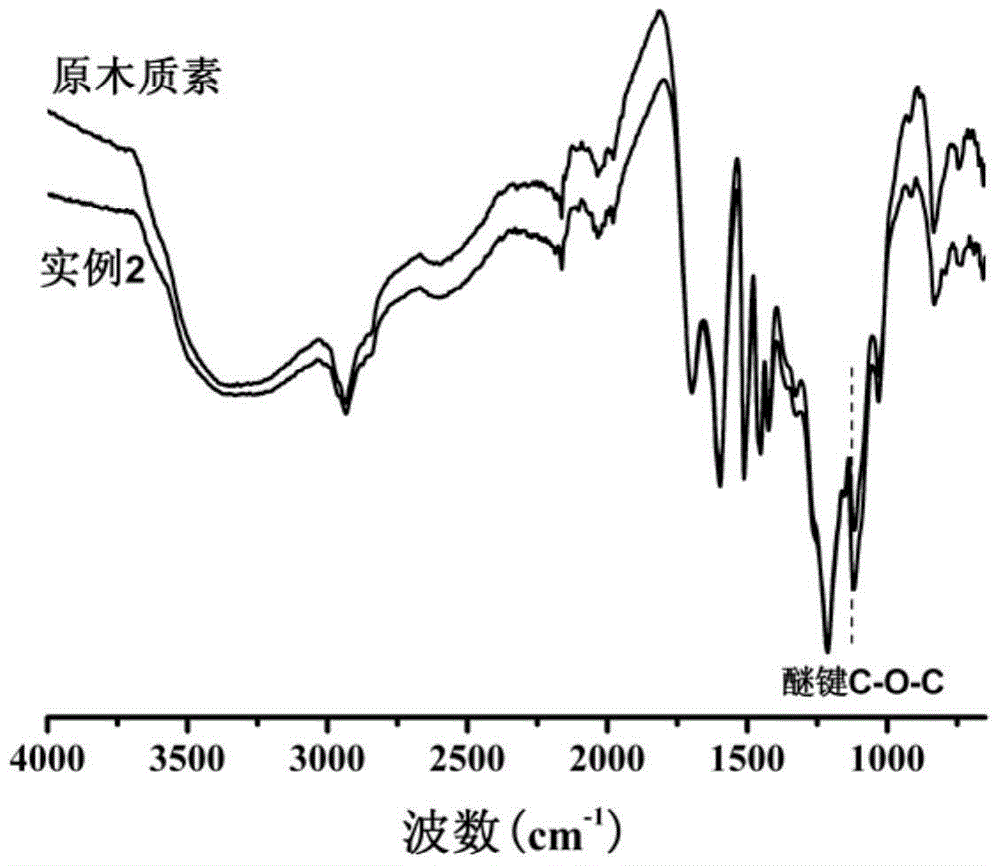
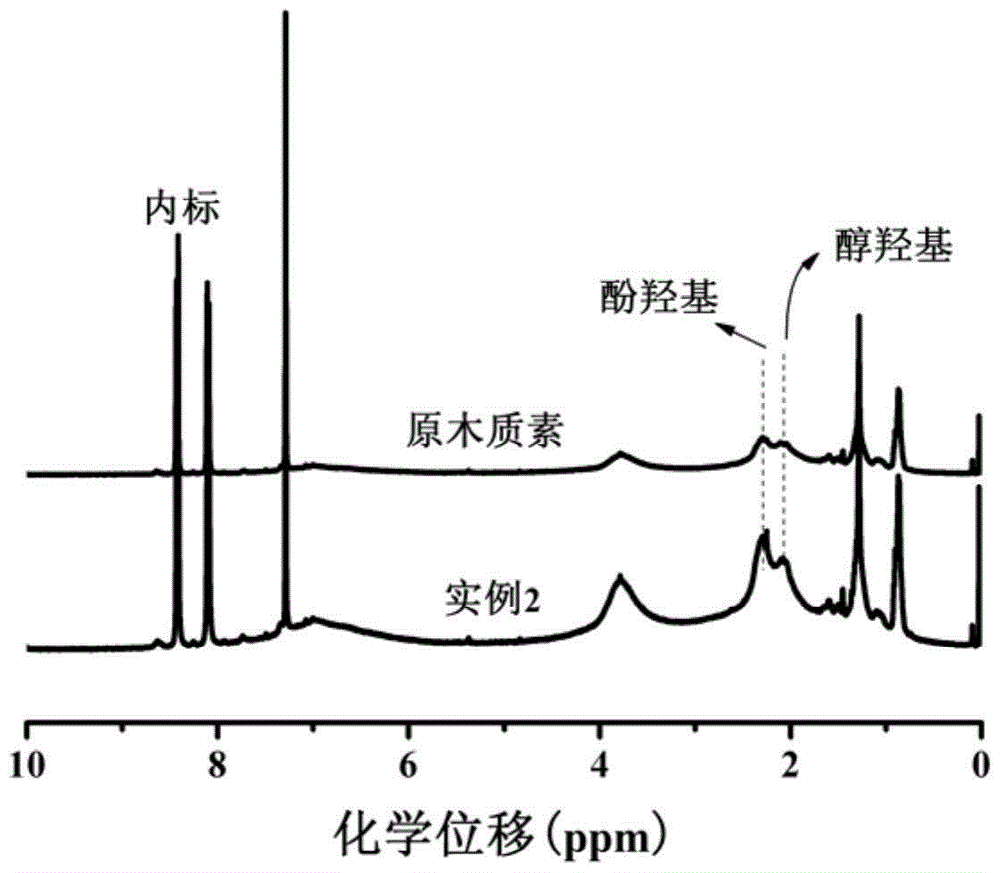
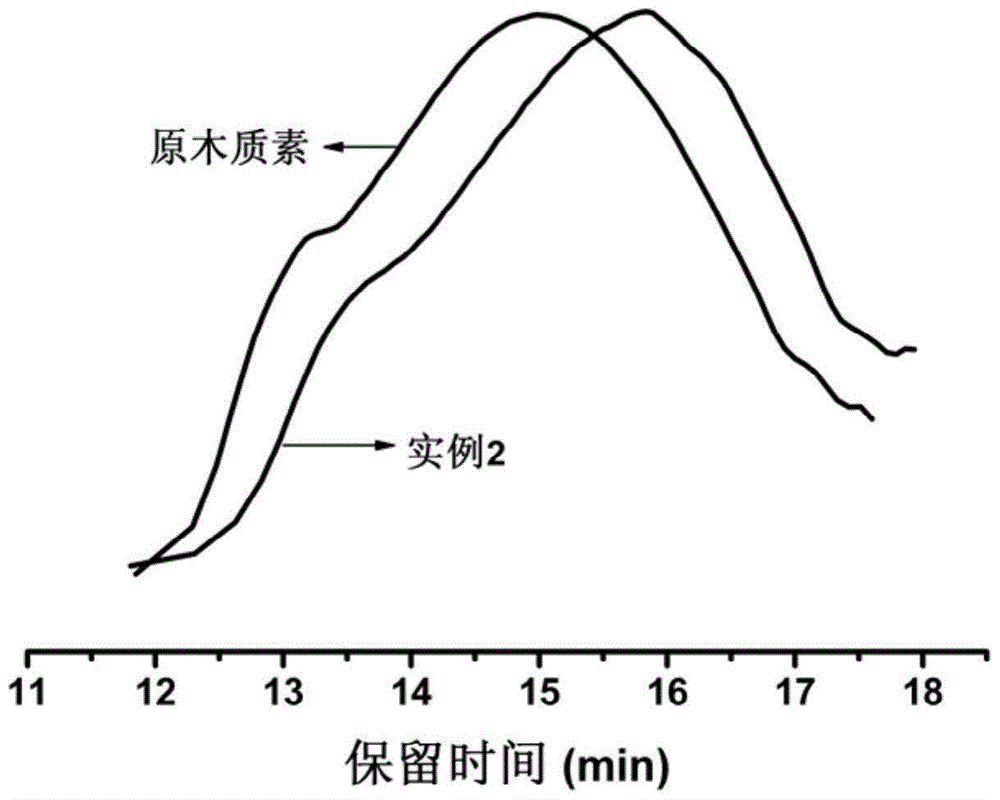
[0017] Biomass ethanol lignin:sodium hydroxide:water (mass ratio) is 1:0.4:5. Stir the sodium hydroxide and water at room temperature for 10 minutes until they are homogeneous, add the biomass ethanol lignin into the above alkaline solution, and fully stir for 30 minutes. Pour it into a hydrothermal reaction kettle with an oil bath at 160°C and react for 7 hours. After the reaction is completed, dilute with water and dilute with dilute hydrochloric acid (1.7molL -1 ) to adjust the pH to 1.0, filter, wash with water several times until neutral, and dry at 50°C to constant weight to obtain pure activated lignin. The phenolic hydroxyl content is 3.87%, the alcoholic hydroxyl content is 3.15%, and the active sites increase by 41%.
Embodiment 2
[0019] Roberts et al. (2011) proposed that the reaction mechanism of hydrothermal alkali-catalyzed degradation of lignin is as follows:
[0020]
[0021] Biomass ethanol lignin:sodium hydroxide:water (mass ratio) is 1:0.4:15. Stir the sodium hydroxide and water at room temperature for 10 minutes until they are homogeneous, add the biomass ethanol lignin into the above alkaline solution, and fully stir for 30 minutes. Pour it into a hydrothermal reaction kettle with an oil bath at 180°C and react for 3h. After the reaction is completed, dilute with water and dilute with dilute hydrochloric acid (1.7molL -1 ) to adjust the pH to 1.0, filter, wash with water several times until neutral, and dry at 50°C to constant weight to obtain pure activated lignin. The phenolic hydroxyl content is 4.17%, and the alcoholic hydroxyl content is 3.15%. Active sites increased by 45%.
[0022] The enzymolysis lignin used is any one of biomass butanol lignin, biomass ethanol lignin and bioma...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Biomass butanol lignin: potassium hydroxide: water (mass ratio) is 1:1.12:10. Potassium hydroxide and water were stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes until homogeneous, biomass butanol lignin was added to the above alkaline solution, and fully stirred for 30 minutes. Pour it into a hydrothermal reaction kettle with an oil bath at 180°C and react for 3 hours. After the reaction is completed, dilute with water and dilute with dilute hydrochloric acid (1.7molL -1 ) to adjust the pH to 1.0, filter, wash with water several times until neutral, and dry at 50°C to constant weight to obtain pure activated lignin. The phenolic hydroxyl content is 4.98%, and the alcoholic hydroxyl content is 3.25%. Active sites increased by 51%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com