Method for removing metal ions in water by utilizing magnetically-separated steel slag tailings
A technology of metal ions and heavy metal ions, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high treatment cost and limitations, and achieve good sedimentation performance, easy to master, and treatment effect. stable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
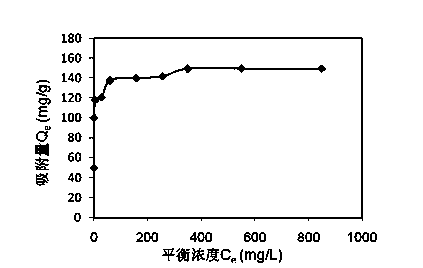
[0024] Example 1: Weigh 0.2g of steel slag tailings powder with a particle size of 90-150 mesh, add 200ml of pH neutral cadmium-containing solutions of different concentrations, put it in a constant temperature shaker, and keep it at a temperature of 25°C and a speed of 150r / min. Samples were taken after 24 h of reaction. After the water sample was precipitated for 30 minutes, it was filtered to measure the concentration of cadmium in the water. The concentration of cadmium was measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometer, and the treatment effect is shown in the attached figure 1 , where the adsorption capacity of tailings for cadmium ions in water increases with the increase of the initial concentration, and the maximum adsorption capacity is about 150mg / g.
Embodiment 2
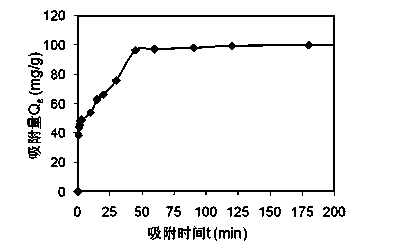
[0025] Example 2: Weigh 1 g of steel slag tailings powder with a particle size of 90-150 mesh, add 1000 ml of pH neutral cadmium-containing solution with a concentration of 100 mg / L, mix under the condition of a constant temperature magnetic stirrer, and take samples at different times. The water sample was centrifuged at 4000r / min for 10 minutes, and then filtered to measure the concentration of cadmium in the water. The concentration of cadmium was measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometer, and the treatment effect is shown in the attached figure 2 , it can be seen from the figure that when the reaction time is longer than 1h, the removal effect is better and remains stable.
Embodiment 3
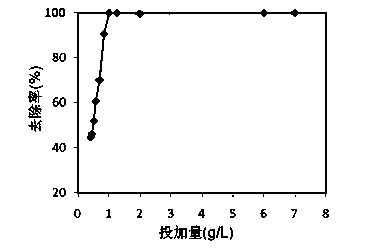
[0026] Example 3 : Weigh the steel slag tailings powder with different weight and particle size of 90~150 mesh, that is, add 100ml concentration of 100mg / L pH neutral cadmium-containing solution with different dosing ratios, put it in a constant temperature shaker, Samples were taken after reacting for 24 hours at 25°C with a rotational speed of 150r / min. After the water sample was precipitated for 60 minutes, it was filtered to measure the concentration of cadmium in the water. The concentration of cadmium is measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometer, and the treatment effect is shown in the attached image 3 , it can be seen from the figure that at a certain concentration, there is an optimal dosage ratio.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com