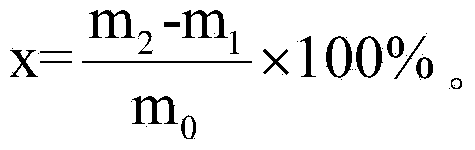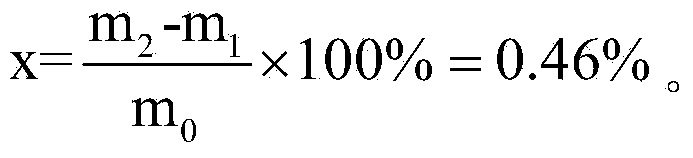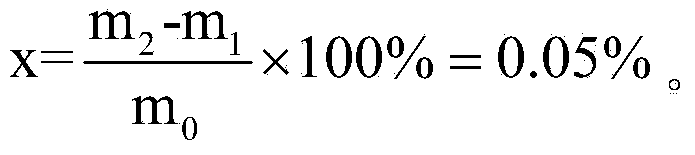Method for measuring content of free carbon in molybdenum carbide
A detection method and technology for free carbon, applied in the field of chemical analysis, can solve the problems of inability to evaluate the total free carbon content of molybdenum carbide catalysts, difficulty in detecting free carbon in molybdenum carbide, and difficulty in free carbon content, etc., and achieve low cost and small pore size. , The effect of easy filtration and separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The detection method of free carbon content in the present embodiment molybdenum carbide comprises the following steps:
[0023] Step 1. Add molybdenum carbide powder into nitrohydrochloric acid and stir, so that molybdenum carbide is dissolved in nitrohydrochloric acid, and free carbon is dispersed in nitrohydrochloric acid as an insoluble substance; the volume V of said nitrohydrochloric acid satisfies: V≥20m 0 , where m 0 is the mass of molybdenum carbide powder, m 0 The unit of V is g, and the unit of V is mL; the quality m of molybdenum carbide powder described in the present embodiment 0 is 1.0012g, and the volume V of nitrohydrochloric acid is 20mL;
[0024] Step 2. Put the filter paper in a drying box, and heat it at 150°C for 30 minutes to carry out the first drying treatment. After the first drying treatment, the mass of the filter paper is m 1 It is 0.0922g; The filter paper is a binder-free glass fiber filter paper with a filter aperture of 1.2 μm;
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The detection method of free carbon content in the present embodiment molybdenum carbide comprises the following steps:
[0029] Step 1. Add molybdenum carbide powder into nitrohydrochloric acid and stir, so that molybdenum carbide is dissolved in nitrohydrochloric acid, and free carbon is dispersed in nitrohydrochloric acid as an insoluble substance; the volume V of said nitrohydrochloric acid satisfies: V≥20m 0 , where m 0 is the mass of molybdenum carbide powder, m 0 The unit of V is g, and the unit of V is mL; the quality m of molybdenum carbide powder described in the present embodiment 0 is 10.0008g, and the volume V of nitrohydrochloric acid is 200mL;
[0030] Step 2. Put the filter paper in a drying box, and heat it at 180°C for 20 minutes to carry out the first drying treatment. After the first drying treatment, the mass of the filter paper is m 1 It is 0.2422g; The filter paper is a binder-free glass fiber filter paper with a filter aperture of 0.7 μm;
[...
Embodiment 3
[0034] The detection method of free carbon content in the present embodiment molybdenum carbide comprises the following steps:
[0035] Step 1. Add molybdenum carbide powder into nitrohydrochloric acid and stir, so that molybdenum carbide is dissolved in nitrohydrochloric acid, and free carbon is dispersed in nitrohydrochloric acid as an insoluble substance; the volume V of said nitrohydrochloric acid satisfies: V≥20m 0 , where m 0 is the mass of molybdenum carbide powder, m 0 The unit of V is g, and the unit of V is mL; the quality m of molybdenum carbide powder described in the present embodiment 0 is 0.5003g, and the volume V of nitrohydrochloric acid is 15mL;
[0036] Step 2. Place the filter paper in a drying oven, and heat it at 120°C for 60 minutes to carry out the first drying treatment. The mass of the filter paper after the first drying treatment is m 1 It is 0.0923g; The filter paper is a binder-free glass fiber filter paper with a filter aperture of 3.0 μm;
[...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com