Method for recovering lead-containing raw material by using wet process
A raw material, wet process technology, applied in the field of waste lead-acid battery recycling and regeneration, can solve the problems of large consumption of desulfurizer, generation of alkali mist, inclusion of impurities, etc., to achieve high-efficiency recovery methods and eliminate environmental pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
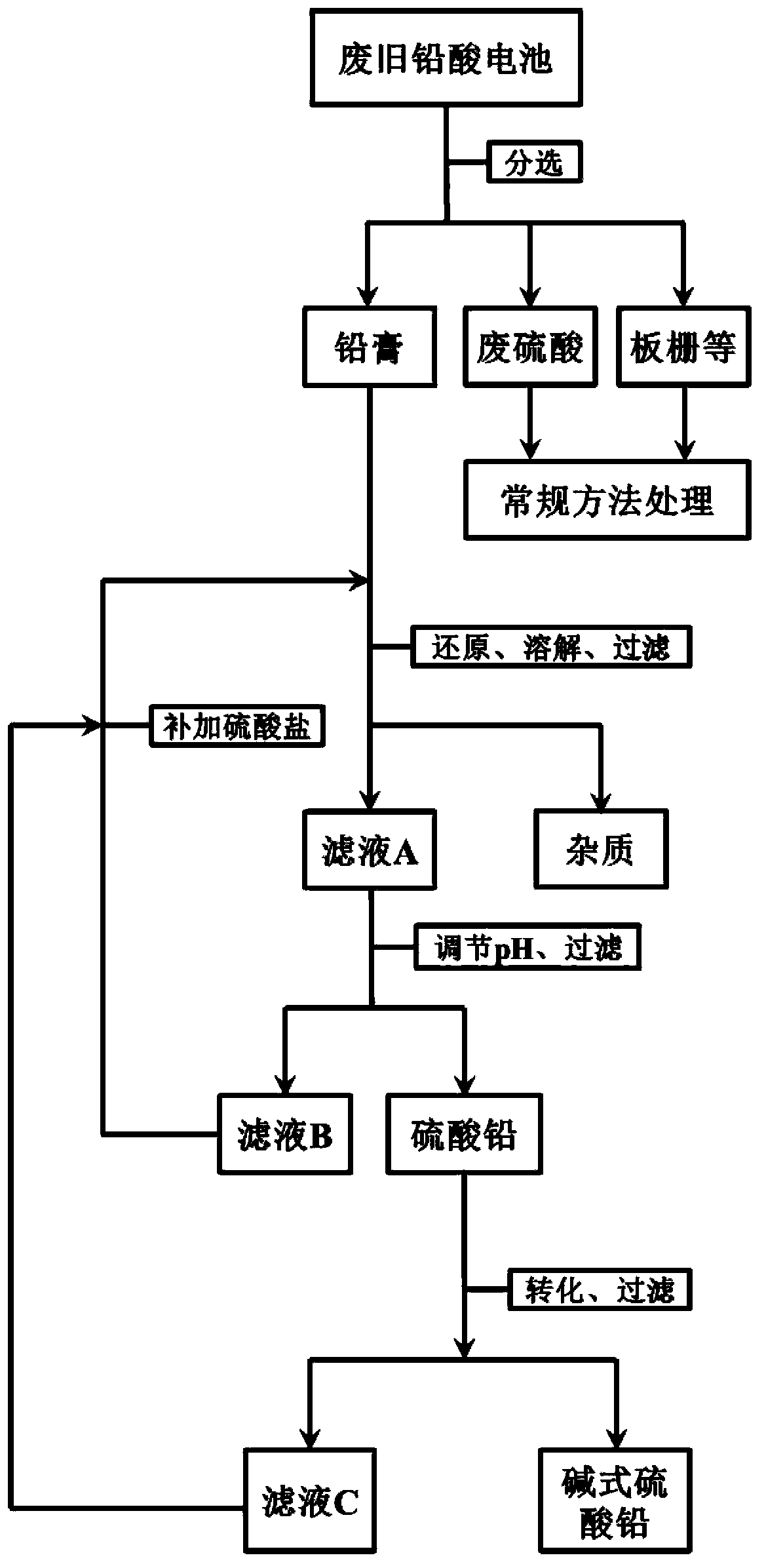
[0069] Take a commercially available waste valve-regulated sealed lead-acid battery with a specification of 12V, 7Ah and a weight of 2 kg. The treatment process is as follows:
[0070] 1) Break it up and separate the lead plaster, grid, waste sulfuric acid and waste plastic.
[0071]2) Put 1 kg of lead paste into 10L reactor 1, which contains excess iron powder, 0.01mol / L iron sulfate, 1mol / L sodium sulfate, 0.9mol / L diethylenetriamine , adding sodium carbonate-sodium bicarbonate buffer solution to maintain the pH value of the solution between 10.0±0.2 during the reaction. Stir at a constant temperature of 50°C for 1 hour until the reddish-brown lead dioxide reacts completely.
[0072] 3) Filter and separate the solution in the process of 2) to obtain filtrate A and filter residue.
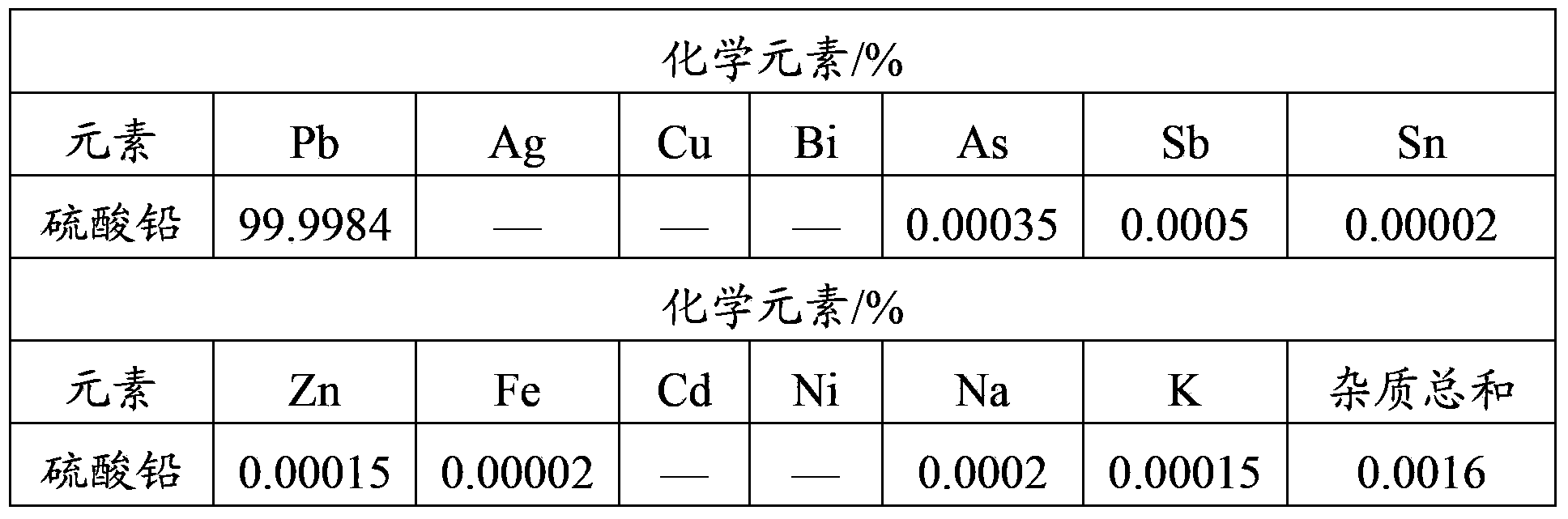
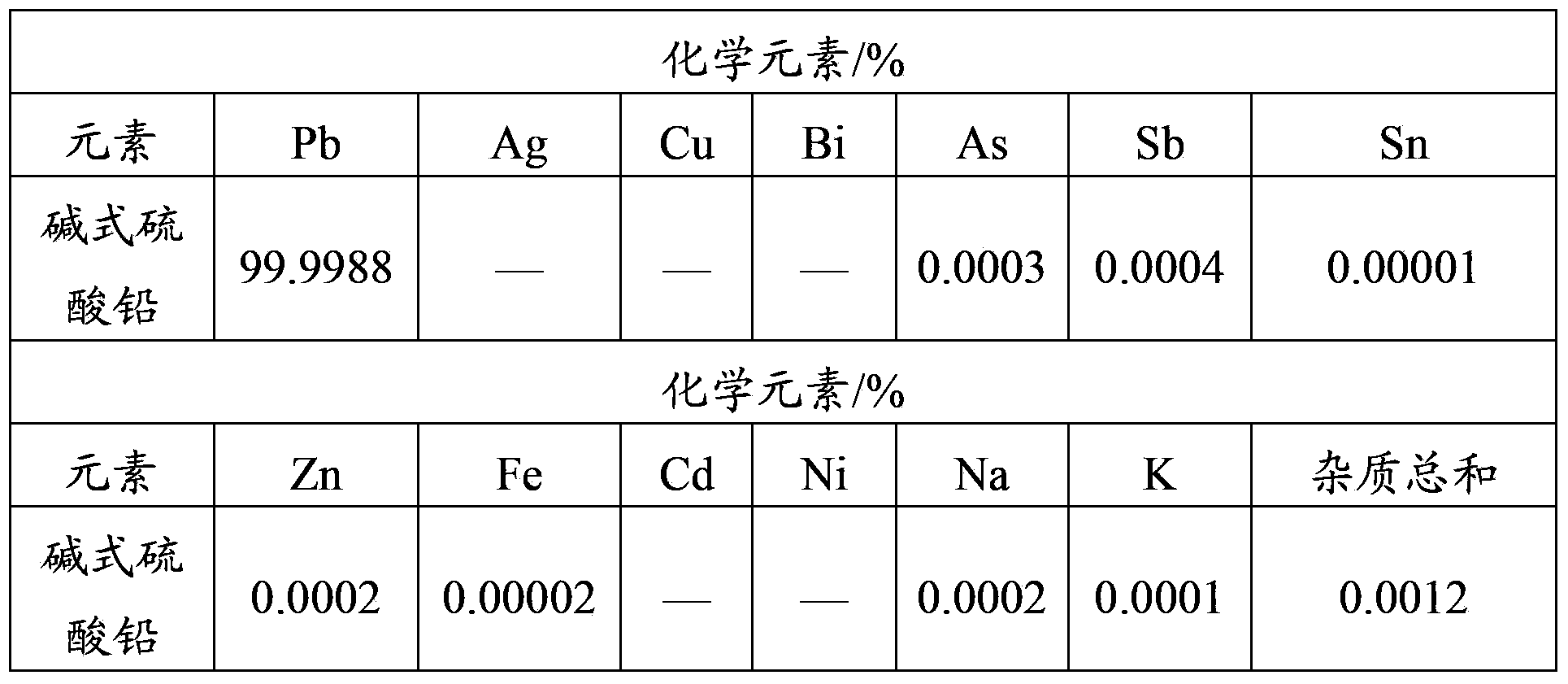
[0073] 4) Transfer the filtrate A into the 10L reactor 2, stir at a constant temperature of 75°C, add sulfuric acid to adjust the pH of the solution to 5.0, and precipitate the lead salt in the ...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Take a 12V, 100Ah waste lead-acid battery for backup power supply, weighing 30 kg, and the specific treatment process is as follows:
[0086] 1) Crush it and sort out the lead paste for later use.
[0087] 2) Configure 50L solution, which contains 0.5mol / L sodium sulfate, 0.001mol / L cobalt chloride, 1.5mol / L phenylalanine, and use sodium hydroxide solution to maintain the pH value of the solution during the reaction process between 7.0±0.2 , and then add 10 kg of lead paste obtained in the process of 1) and excess lead powder to the solution, and stir for 1.5 hours at a constant temperature of 65°C until the reddish-brown lead dioxide reacts completely.
[0088] 3) Filter the solution obtained in 2) and separate 50L of filtrate A and filter residue.
[0089] 4) Put 50L of filtrate A at a constant temperature of 80°C, add perchloric acid to adjust the pH value to below 4.5, so that all lead salts are precipitated in the form of lead sulfate.
[0090] 5) Filter the reac...
Embodiment 3
[0099] 1) Break a 60kg, 12V, 200Ah lead-acid battery and separate the lead paste.
[0100] 2) Add 40L of a solution containing 0.7mol / L ammonium sulfate, 0.05mol / L manganese nitrate, and 0.8mol / L histidine to reactor 1, and use 10% potassium hydroxide solution to maintain the pH of the solution during the reaction process. Between 8.5-9.5, add 2 kg of lead paste obtained in process 1). Stir for 0.75 hours under the condition of a constant temperature of 70°C, and feed in an appropriate amount of sulfur dioxide gas, so that the lead dioxide is completely reduced and dissolved by the lead powder and sulfur dioxide in the lead paste.
[0101] 3) Filter the solution after the reaction in process 2) to obtain filtrate A and filter residue.
[0102] 4) Filtrate A is kept at a constant temperature of 60°C, and hydrogen chloride gas is passed through to adjust the pH value of filtrate A to gradually decrease to completely precipitate lead sulfate.
[0103] 5) Filter the solution aft...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com