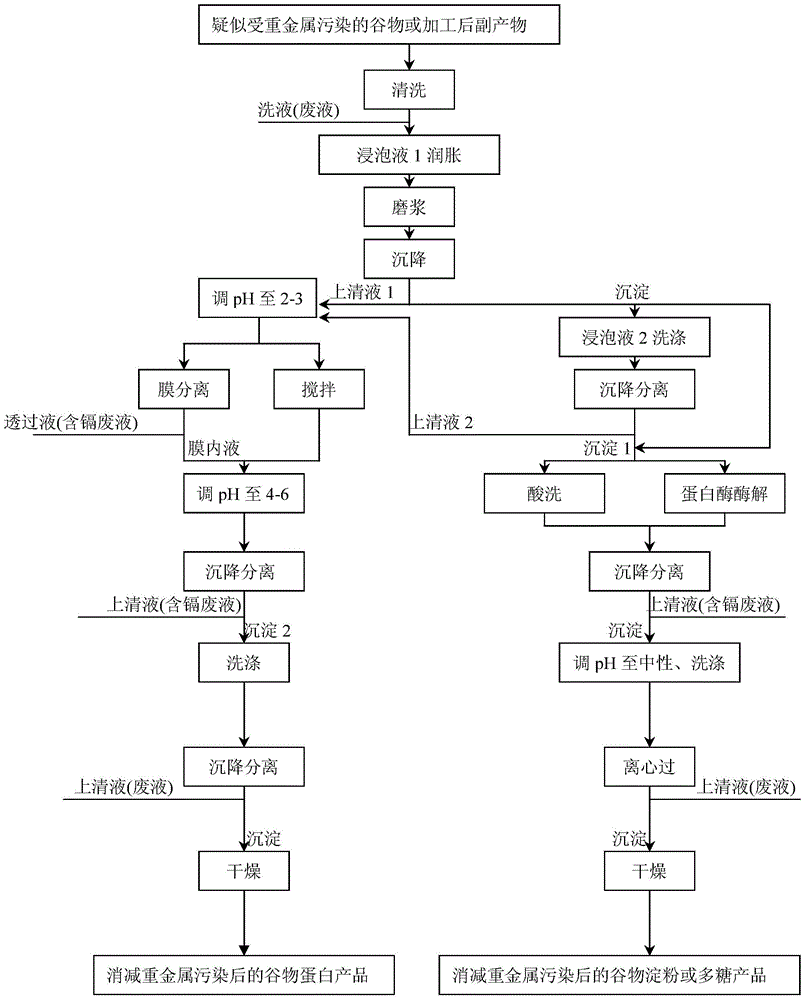
Method of reducing heavy metals of cereals
A heavy metal and grain technology, applied in the field of grain and grain processing by-products, can solve the problem of high cost, achieve low cost, good effect, and reliable technical process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Example of removing heavy metals from rice
[0043] The initial test value of the raw rice sample used in the test: starch content 78.52%, moisture content 12.23%, crude protein content 7.21%, cadmium content 0.382mg / kg, lead content 0.165mg / kg, arsenic content 0.085mg / kg, mercury content 0.013 mg / kg, nickel content 0.71mg / kg, copper content 3.592mg / kg.
[0044] Step 1: Take 1000g of the above-mentioned raw rice, wash it with 1500g of tap water, and wash it twice;
[0045] Step 2: Add 4000 g of soaking solution 1 (0.4% NaOH solution) to the washed rice, stir and soak for 3 hours at room temperature to fully swell the rice, and grind the swollen rice with a colloid mill for 100 Mesh sieve;
[0046] Step 3: Sedimentation and separation of the slurry to obtain precipitate 1, adjust the pH of the supernatant to 2.0 with 0.1N hydrochloric acid, and dialyze in a hydrochloric acid solution of pH 2.0 with a molecular weight cut-off of 1000D for 24 hours to allow hea...
Embodiment 2
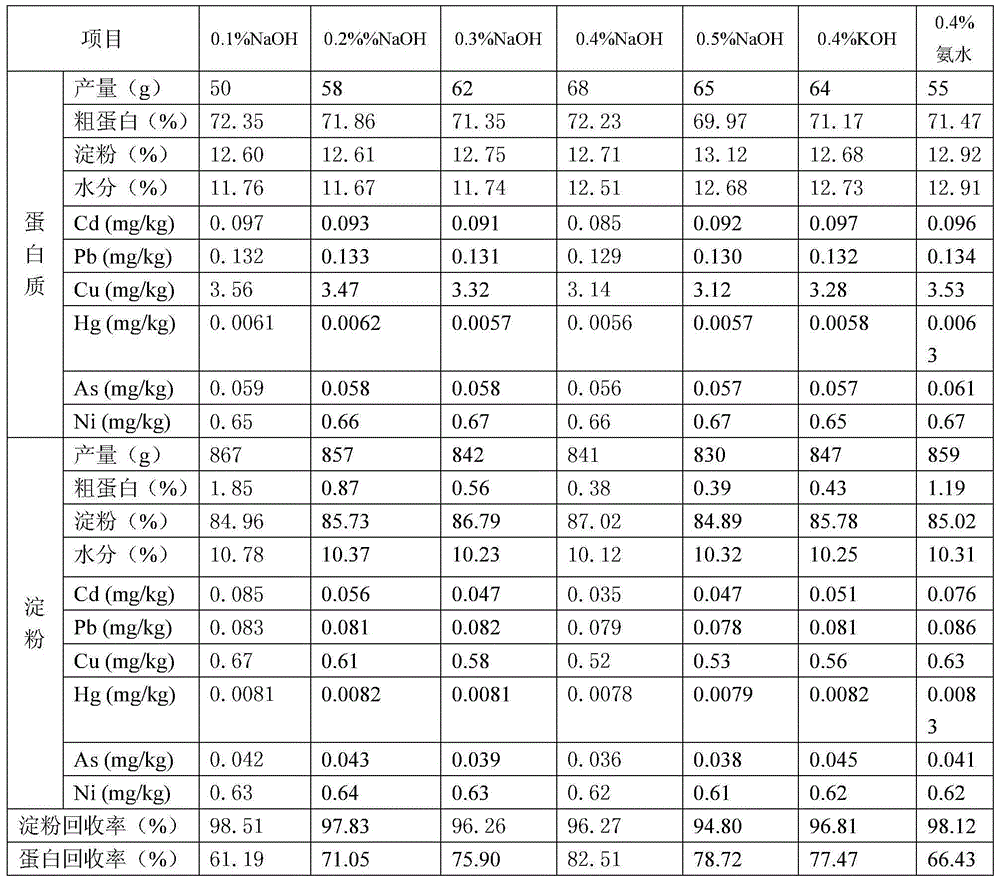
[0051] Example 2 Comparison of the removal of heavy metals from rice by different soaking solutions 1
[0052] The method in Example 1 was adopted to remove heavy metals in rice, and the raw rice used in the test was the same sample as in Example 1. Just change the soaking solution 1 in Step 2 of Example 1, and the effects of different soaking solutions 1 on removing heavy metals from rice are shown in Table 1.
[0053] Table 1 Treatment effect of different soaking solution 1
[0054]
[0055] Table 1 shows that, using the selected soaking solution 1 to carry out the corresponding heavy metal removal treatment, the heavy metal content in the obtained product all meets the national standard (see the national standard of the People's Republic of China, standard number GB 2762-2012), wherein, 0.4% NaOH The effect of removing heavy metals from solution is relatively good, and the protein recovery rate is also the highest.
Embodiment 3
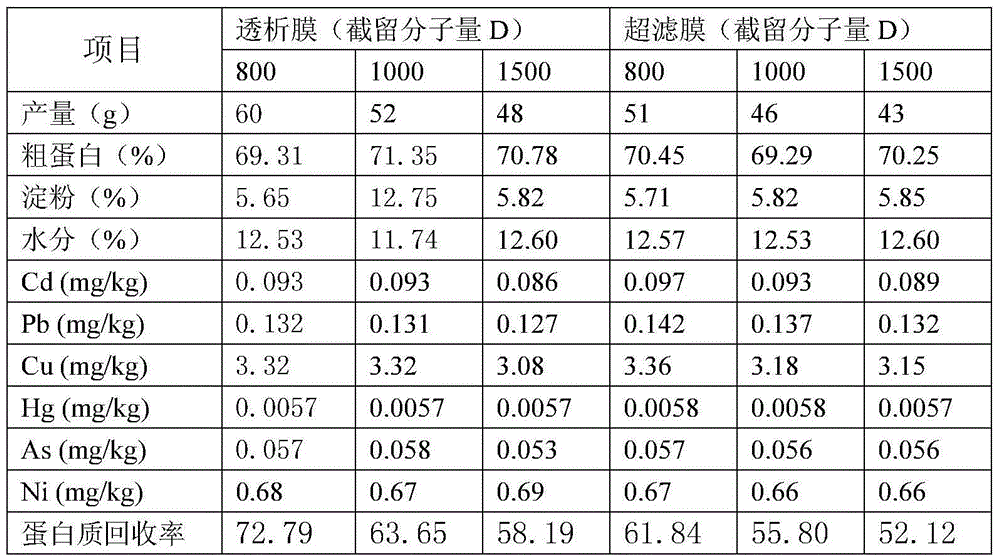
[0056] Example 3 Comparison of removing heavy metals from rice protein under different membrane separation conditions
[0057] The method in Example 1 was adopted to remove heavy metals in rice, and the raw rice used in the test was the same sample as in Example 1. Just change the conditions of the supernatant membrane separation and removal of heavy metals in Step 3 of Example 1, wherein the volume of the supernatant is concentrated to about 35% by ultrafiltration, and the removal effect of heavy metals is shown in Table 2.
[0058] Table 2 Effects of different membrane separations on heavy metal removal
[0059]
[0060] Table 2 shows that in the selected dialysis bag and ultrafiltration membrane, the product recovery rate decreases with the increase of the molecular weight cut-off, and the effect of removing heavy metals is not much different, and the cadmium and lead heavy metal contents of the obtained rice protein all meet the national standards (See National Standar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com