Method, primer, probe and kit for screening and identifying BCR-ABL unusual fusion types
A very common and integrated technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of monitoring, cost increase, low sensitivity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0120] Extraction of blood RNA: add 1ml of 1× red blood cell lysate to a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, take 0.5ml of the blood sample to be tested, and mix by inversion. Centrifuge at 4000rpm for 3min, aspirate and discard the supernatant, add red blood cell lysate and wash once to obtain the desired cells; add 1 ml TotalRNA Isolation Reagent (Shanghai Pufei Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), blow and suck repeatedly until there is no obvious cell clump, add chloroform 200 μl, vortex for 30 s, and let stand on ice for 10 min. Next, centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C. Transfer 450 μl of the supernatant to another centrifuge tube with a pipette, add an equal volume of pre-cooled isopropanol, invert and mix, and then let stand on ice for 10 min. Centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C. Then wash and centrifuge once with 75% ethanol and absolute ethanol, respectively. Dry at room temperature for 5 min, add 50 μl DEPC-H2O to dissolve, and obtain RNA extract.
[0121] The formula for...
Embodiment 2
[0123] Reverse transcription: Take 4 μl of the RNA extract in Example 1 (concentration about 200 ng / μl), add 1 μl Primer mix (ReverTra AceqPCR RT Kit, purchased from Toyobo (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) and 3 μl DEPC-H2O, and mix well. Pre-denaturation at 70°C for 5 min; after quenching on ice for 1 min, add 4 μl 5* RT buffer (ReverTra Ace qPCR RT Kit), 1 μl Enzyme Mix (ReverTra Ace qPCR RT Kit), and add 7 μl DEPC-H 2 0 to a total volume of 20 μl. The reaction was performed at 37°C for 60 minutes and then inactivated at 98°C for 5 minutes to obtain the cDNA of the blood sample to be tested.
Embodiment 3
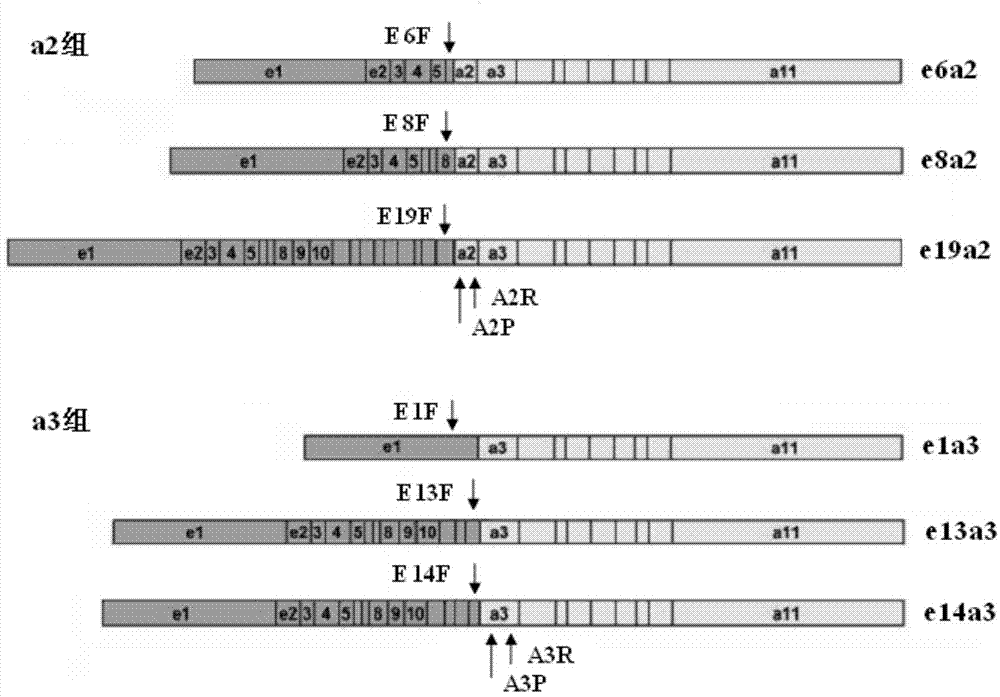
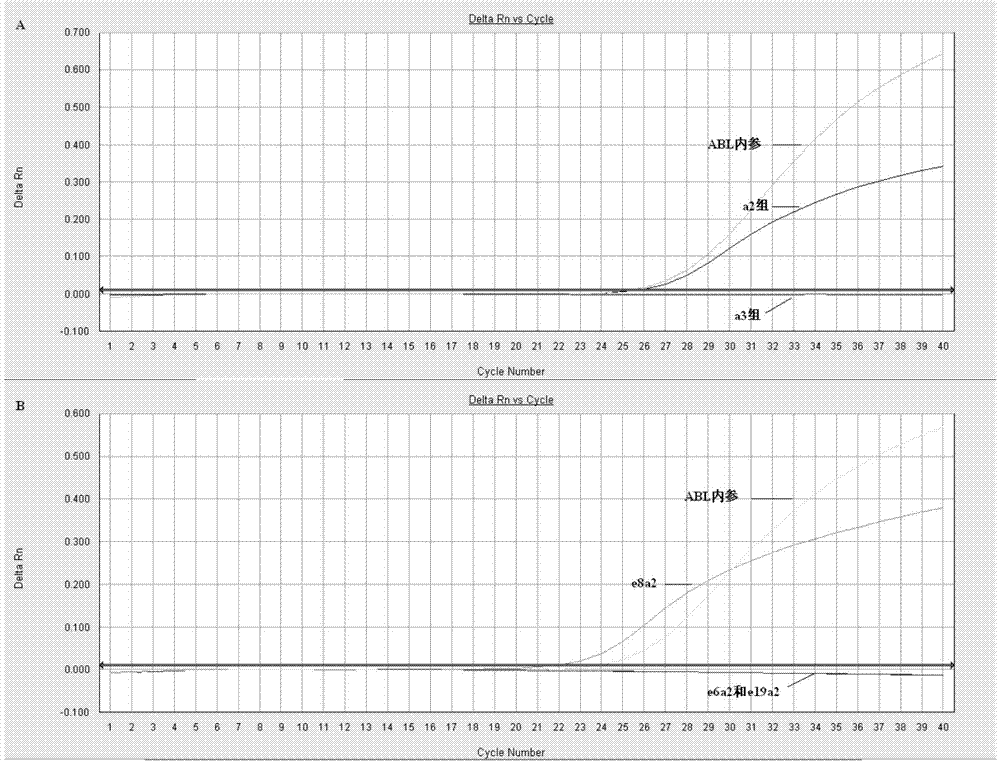
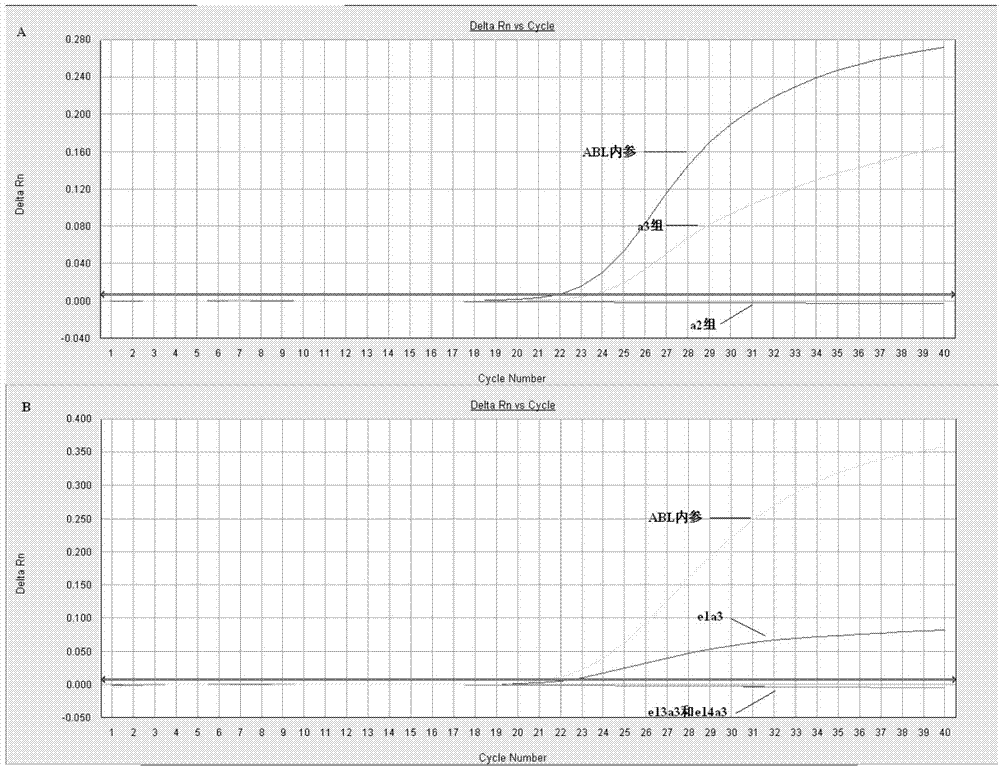
[0125] Fluorescent PCR primary screening: Prepare primary screening reagents according to the materials and dosages shown in Table 1. The primary screening reagent contains three reaction tubes: one tube each for group a2, group a3 and ABL; ABL is the internal reference detection tube, which is used to judge whether the RNA extraction quality meets the requirements. 2 μl each of the cDNA obtained in Example 2 was added. The detection was performed according to the following procedure: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 30s; 95°C for 10s, 58°C for 35s, a total of 40 cycles; fluorescence was collected at 58°C. HUNDERBIRD Probe qPCR Mix was purchased from Toyobo (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0126] Table 1
[0127]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com