Catalyst for selectively reducing saturated aldehyde, and production method thereof
A catalyst and selective technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, etc., can solve the problem of low conversion rate of saturated aldehydes to unsaturated aldehydes, catalysts Deterioration and other problems, to achieve the effect of simplifying the purification stage and important industrial value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
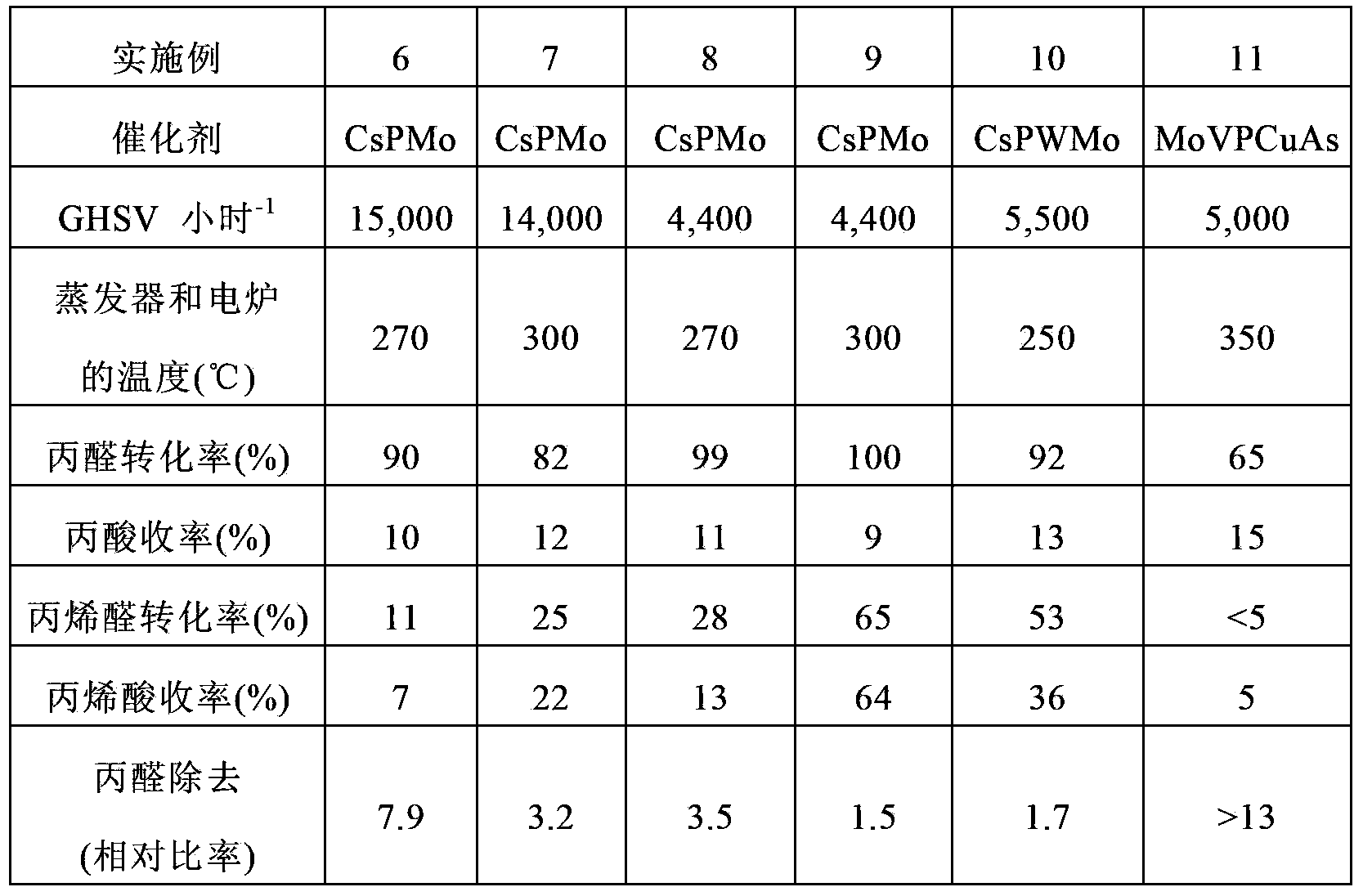
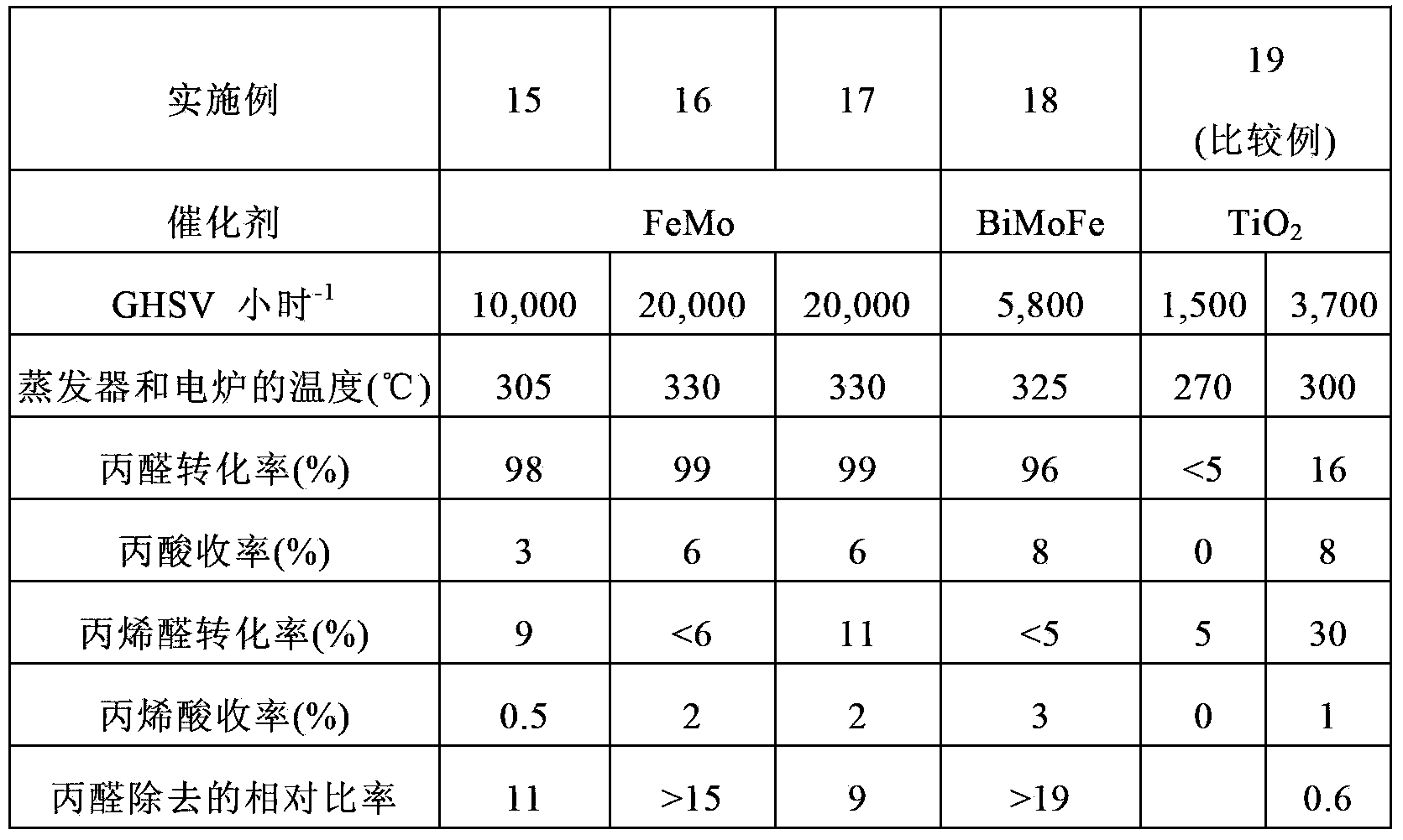
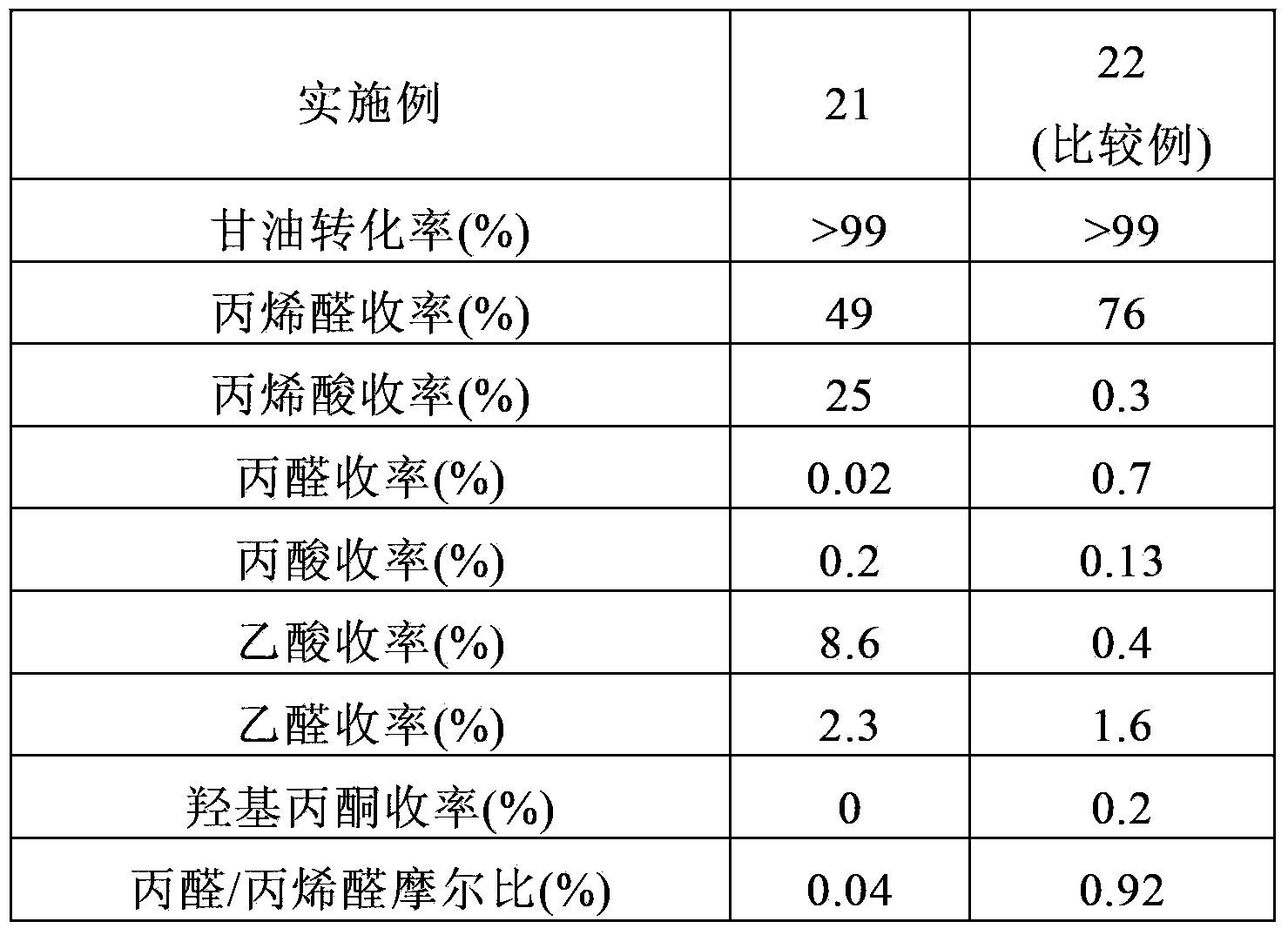
Embodiment 1
[0162] CsPM
[0163]100 g of phosphomolybdic acid were dissolved in 200 ml of pure water and stirred at ambient temperature for 2 hours while diluting 32.7 g of a 48.5% by weight aqueous CsOH solution in 20 ml of pure water. The resulting aqueous CsOH solution was added dropwise to the aqueous phosphomolybdic acid solution at ambient temperature with stirring over 2 hours. The resulting yellow slurry was dried with a rotary evaporator at 60°C under reduced pressure to obtain a powder, which was then further dried with a drier at 120°C for 10 hours at ambient pressure. The resulting dry powder had the following composition:
[0164] Cs 2.5 P 1.0 Mo 12 .
[0165] The powder was further calcined in air at 250° C. for 3 hours in a muffle furnace.
Embodiment 2
[0167] CsPWMo
[0168] 50 g of phosphotungstomolybdic acid were dissolved in 20 ml of pure water and stirred at ambient temperature for 2 hours while diluting 13.4 g of a 48.5% by weight aqueous CsOH solution in 50 ml of pure water. The resulting aqueous CsOH solution was added dropwise to the aqueous phosphotungstomolybdic acid solution at ambient temperature with stirring over 2 hours. The resulting yellow slurry was dried with a rotary evaporator at 60°C under reduced pressure to obtain a powder, which was then further dried with a drier at 120°C for 10 hours at ambient pressure. The resulting dry powder had the following composition:
[0169] Cs 2.5 P 1.0 W 6 Mo 6 .
[0170] The powder was further calcined in air at 250° C. for 3 hours in a muffle furnace.
Embodiment 3
[0172] MoVPCuAs
[0173] 100 g of molybdenum trioxide, 6.3 g of vanadium pentoxide, 1.1 g of copper oxide, 8.0 g of 85% by weight orthophosphoric acid, and 1.8 g of 60% by weight arsenic acid were mixed in 1000 ml of pure water. Hydrogen peroxide was added to the resulting mixture and refluxed for 6 hours until a clear reddish-brown solution was obtained. A small amount of insoluble matter was removed from the resulting solution, and the solution was evaporated to dryness by using a water bath. The resulting dry powder had the following composition:
[0174] Mo 10 V 1.0 P 1.0 Cu 0.2 As 0.2 .
[0175] The powder was further calcined in air at 310° C. for 5 hours in a muffle furnace.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com