Elemental analysis determination method and device
A technology of elemental analysis and determination method, applied in the field of instrumental analysis, to achieve the effect of sharp peak shape, accurate determination results, and improved sample heating and pyrolysis rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
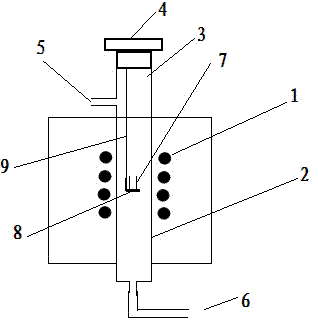
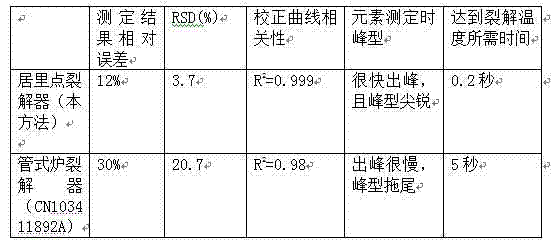
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] A determination method for elemental analysis, which is characterized in that an inorganic compound that can release hydrogen during cracking is added to the sample to be tested to make it evenly mixed with the sample, and then the mixture is cracked at a temperature of 800 ° C, so that the elements form volatile Atomic spectrometer measurement; the inorganic compound that releases hydrogen by cracking refers to: sodium hydrosulfide or hydrogen iodide; wherein the weight of the added inorganic compound is 15 times of the sample weight. The measured elements refer to: arsenic, mercury, antimony, bismuth, selenium, germanium, tin, lead and tellurium.
[0061]
Embodiment 2
[0063] A determination method for elemental analysis, adding an inorganic compound that can release hydrogen during cracking to the sample to be tested to make it evenly mixed with the sample, and then cracking the mixture at a temperature of 600 ° C to make the elements form volatiles and be measured by atomic spectrometer ; The inorganic compound that releases hydrogen by cracking refers to: sodium hydrosulfide; wherein the weight of the added inorganic compound is 35 times the weight of the sample. The measured elements refer to: arsenic, mercury, antimony, bismuth, selenium, germanium, tin, lead and tellurium.
Embodiment 3
[0065] A determination method for elemental analysis, adding an inorganic compound that can release hydrogen during cracking to the sample to be tested to make it evenly mixed with the sample, and then cracking the mixture at a certain temperature, so that the elements form volatiles and are measured by an atomic spectrometer; The inorganic compound that decomposes and releases hydrogen refers to: potassium hydrogen sulfide or hydrogen sulfide; wherein the weight of the added inorganic compound is 50 times the weight of the sample. The measured elements refer to: arsenic, mercury, antimony, bismuth, selenium, germanium, tin, lead and tellurium. The crucible or foil filled with the sample during lysis can hold a sample weight of 20 mg.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Curie point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Curie point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com