Method for extracting high-purity fucoxanthin from seaweeds
A fucoxanthin, high-purity technology, applied in organic chemistry and other directions, can solve the problems of high purification cost and environmental pollution, and achieve the effect of good separation effect, high purity and less equipment and equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
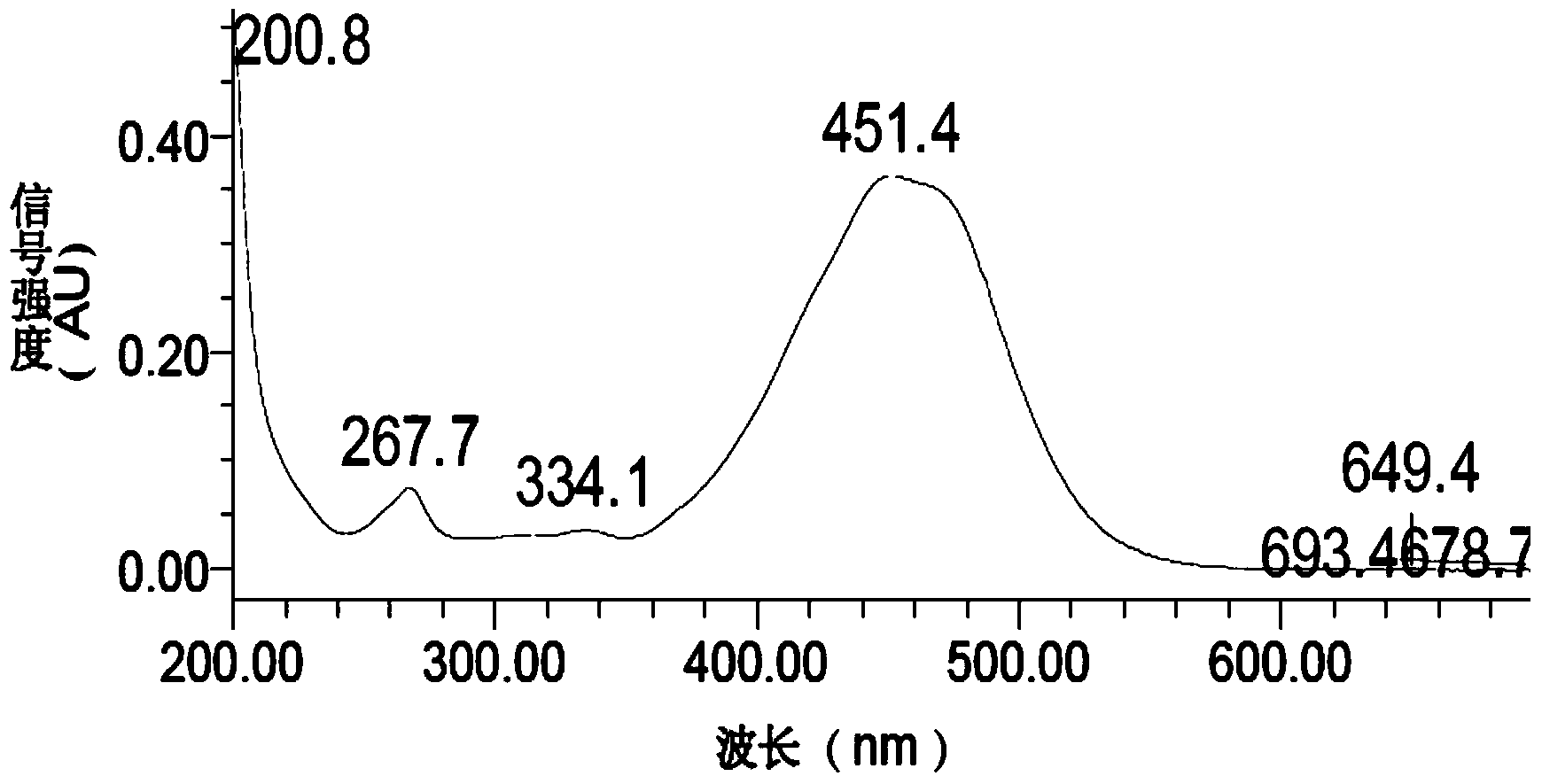
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
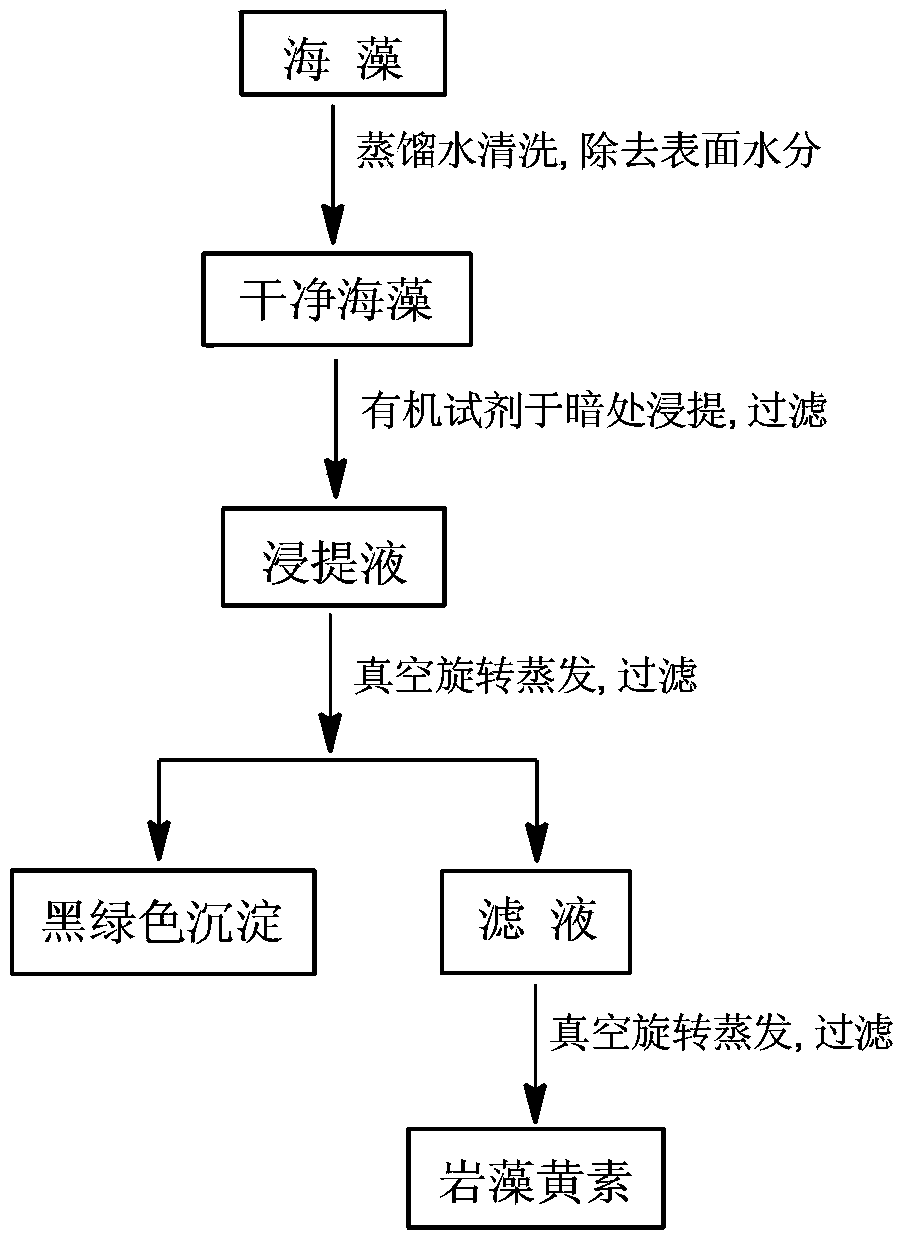
[0048] Wash fresh copper algae 3 times with seawater to remove surface impurities, then wash 2 times with distilled water to remove salt ions on the surface of the algae, and then use absorbent cotton to dry the surface water. Weigh 200g of copper algae into a 1000mL conical beaker, add 600mL of 80% (V / V) ethanol aqueous solution, seal the mouth of the conical beaker with two layers of safety film, extract in the dark for 12 hours, and filter. Continue to add 600mL of 80% (V / V) ethanol aqueous solution to the copper algae that has undergone the above extraction treatment, seal the mouth of the triangular beaker with two layers of safety film, extract in the dark for 12 hours, and filter. The copper algae was repeatedly extracted in the dark until the extract was colorless;
[0049] Combine the above extracts and pour them into a brown bottle, and evaporate in vacuum at 40°C. Pay attention to the changes of the solution when concentrating. When a large amount of black and green...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Thaw frozen sargassum at room temperature, wash 5 times with seawater to remove surface impurities, then wash 3 times with distilled water to remove salt ions on the surface of the algae, and then dry the surface with absorbent paper. Weigh 200g of Sargassum and put it into a 1000mL beaker, add 700mL of 75% (V / V) ethanol aqueous solution, seal the mouth of the beaker with two layers of safety film, extract in the dark for 8 hours, filter, and continue to add Sargassum Add 600mL of 80% (V / V) ethanol water solution again, seal the mouth of the triangular beaker with two layers of safety film, extract in the dark for 12 hours, and filter. The sargassum was repeatedly extracted in the dark until the extract was colorless;
[0054] Combine the above extracts and pour them into a brown bottle, and evaporate in vacuum at 38°C. Pay attention to the changes of the solution when concentrating. When a large amount of black and green precipitates gradually appear in the solution, f...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The same as the above-mentioned Example 1, the difference is that: copper algae dark leaching time is 24 hours; vacuum rotary evaporation temperature is 15 ° C; organic reagent is acetone; the ratio of copper algae to organic reagent is 200g:800ml.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com