Coxsackie A16 type virus mutant strain capable of effectively infecting mice
A technology of A16 and mutant strains, applied in the field of virology, can solve the problem of little research on CA16 mouse infection models
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] Example 1, mouse-adapted strain G08-MAV has higher toxicity to mouse cells
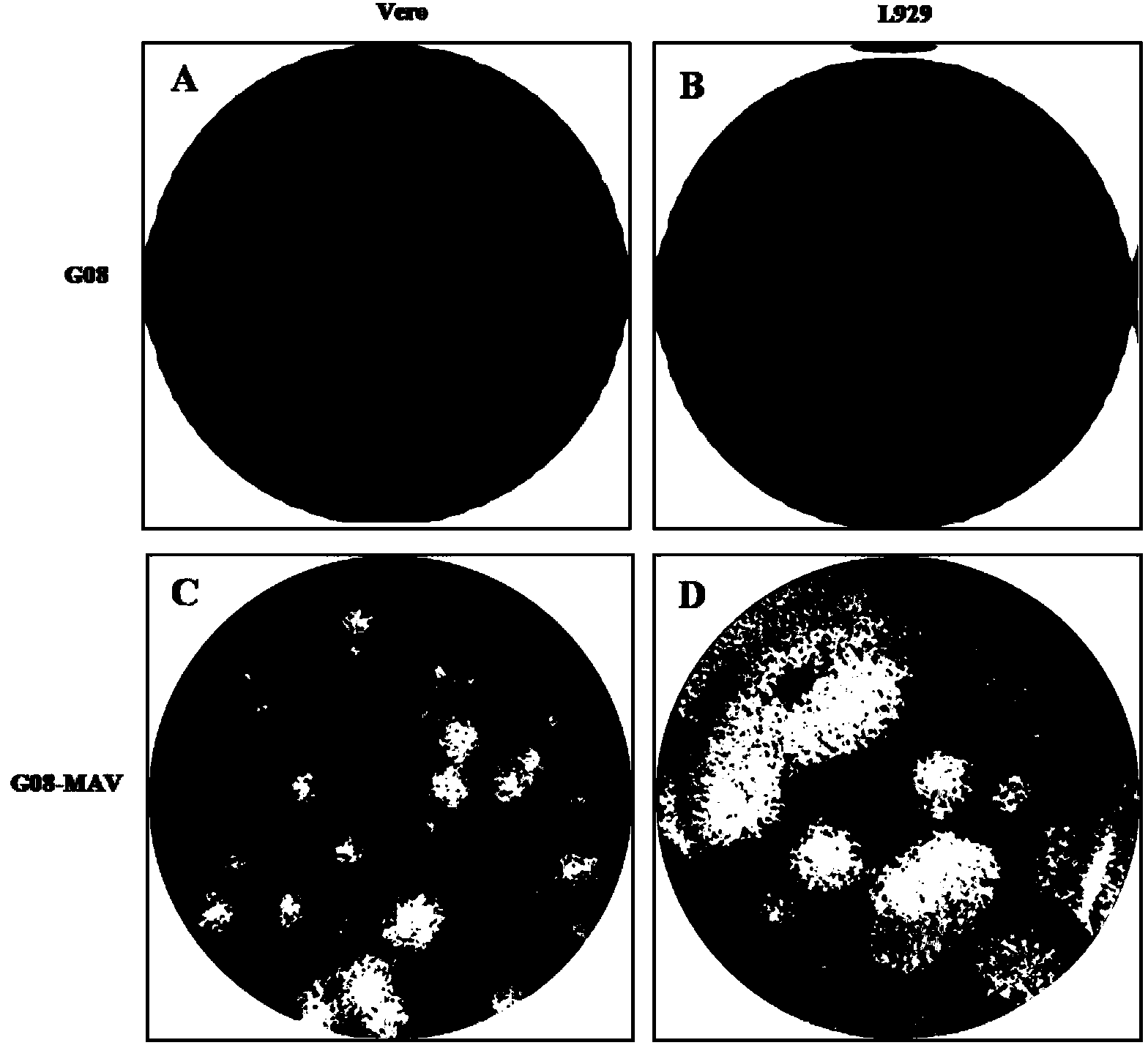
[0083] Vero cells were infected with CA16 (MOI=0.01) wild strain G08 or mouse-adapted strain G08-MAV, and both G08 and G08-MAV caused severe lesions in Vero cells after 24 hours ( figure 1 A, 1D); CA16 (MOI=0.01) G08 or mouse-adapted strain G08-MAV infected mouse cells L929, and G08-MAV infected L929 cells for 24 hours, and severe lesions occurred ( figure 1 E), all lesions after 48h ( figure 1 F), while G08 infected L929 cells 24h and 48h without lesion ( figure 1 B, 1C). In order to further compare the toxicity of G08 and G08-MAV on cells, plaque experiments were performed on Vero and L929 cells.
[0084] The results showed that the plaque size of G08 and G08-MAV in Vero was not much different ( figure 2 A, 2C), the plaques of G08-MAV on L929 were significantly larger than those of G08 ( figure 2 D, 2B), indicating that the mouse-adapted G08-MAV has significantly enhanced toxicity on m...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Example 2. The pathogenicity of G08-MAV in mice is significantly enhanced
[0086] Use 1.35×10 6 G08 of TCID50 and 1.35×10 4 The TCID50 mouse-adapted strain G08-MAV was injected intraperitoneally into 7-day-old ICR mice, and the mortality rates of the mice were 26.7% and 71% ( image 3 B), 7-day-old mice died 6 days after infection with G08-MAV, and 7-day-old mice infected with G08 died after 9 days. After infection, the mice showed clinical symptoms of slow response, ataxia, leg weakness followed by paralysis and even death ( image 3 A, 3C), some mice died without paralysis after infection, and the mice either continued to lose weight two to three days before death, or gradually lost weight accompanied by paralysis of at least two legs. The clinical symptoms of G08-MAV-infected mice were significantly more severe than those of G08-infected mice ( image 3 C).
[0087] Animal infection experiments showed that mouse-adapted virus G08-MAV could cause more serious le...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Example 3, intraperitoneal injection of G08-MAV can effectively infect 2-week-old ICR mice
[0089] 1.35×10 4 TCID50 mouse-adapted strain G08-MAV intraperitoneally infected 2-day-old, 5-day-old, 10-day-old, 14-day-old and 21-day-old ICR mice. and 10-day-old mice observed for 14 days after infection showed approximately the same mortality rates of 79% and 80%, respectively, 14-day-old mice had a 50% mortality rate, and 21-day-old mice did not die after infection ( Figure 4 A), as the age increases, the lethality of mouse-adapted virus to mice shows a downward trend. The younger the infected mice are, the earlier they die, and the 2-day-old mice appear 4 days after infection. die( Figure 4 A). Mice aged two weeks and below showed clinical symptoms of slow response, ataxia, leg weakness and then gradual emaciation, paralysis and even death after infection ( Figure 4 B).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com