Ni-ti porous material miniature parts and its sintering method
A technology of porous materials and micro parts, which is applied in the field of rapid sintering to prepare porous material parts, can solve the problems of low product qualification rate, low product purity and high molding temperature, and achieve the effect of simplifying the process flow, uniform pores and excellent performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
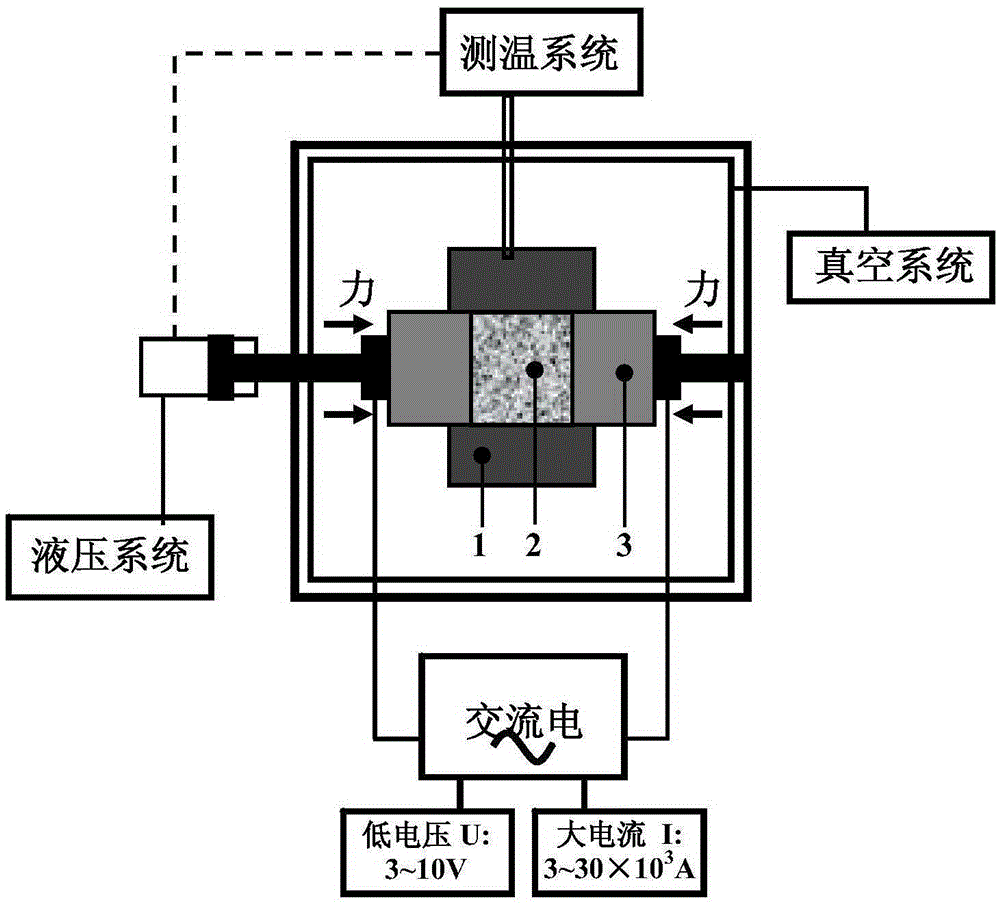
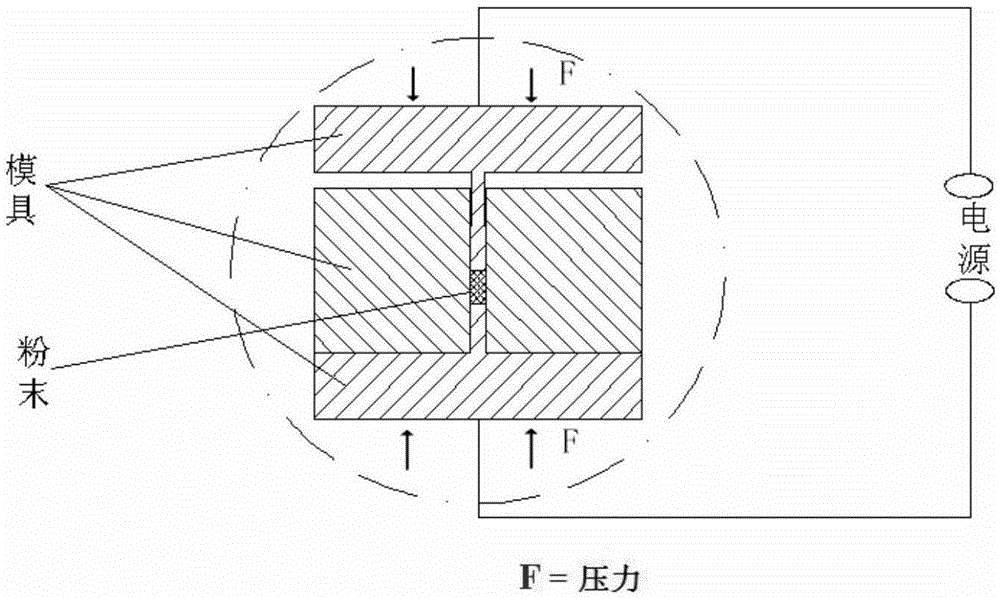
[0038] Weigh the Ni and Ti powders shown in the above table according to the prefabrication process parameters, put them into the mold and fix them with chucks. Under the condition of vacuum ≤ 0.01Pa and a pressure of 50MPa on both ends at the same time, at a speed of 10℃ / s Raise the temperature to 200°C, keep it warm for 30s, then raise the temperature to 800°C at a rate of 50°C / s, and sinter 3 times in the range of 800°C-400°C; the powder is formed in the mold and sintered, and finally the power is turned off and air-cooled to take out the parts That's it.
Embodiment 2
[0040] Weigh the Ni and Ti powders shown in the above table according to the prefabrication process parameters, put them into the mold and fix them with chucks. Under the condition of vacuum ≤ 0.01Pa and a pressure of 150MPa on both ends at the same time, at a speed of 20℃ / s Raise the temperature to 300°C, hold it for 120s, then raise the temperature to 1200°C at a speed of 100°C / s, and sinter 15 times in the range of 1200°C-800°C; the powder is formed in the mold and sintered, and finally the power is turned off and air-cooled to take out the part That's it.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Weigh the Ni and Ti powders shown in the above table according to the prefabrication process parameters, put them into the mold and fix them with chucks. Under the condition of vacuum ≤ 0.01Pa and a pressure of 150MPa on both ends at the same time, at a speed of 20℃ / s Raise the temperature to 200°C, keep it warm for 60s, then raise the temperature to 1000°C at a rate of 50°C / s, and sinter 5 times in the range of 1000°C-600°C; the powder is formed in the mold and sintered, and finally the power is turned off and air-cooled to take out the parts That's it.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com