Low-power-supply-voltage programmable gain amplifier
A low power supply voltage, programming gain technology, applied in differential amplifiers, DC-coupled DC amplifiers, gain control, etc., can solve the problem of poor linearity and signal-to-noise ratio of analog circuits, can not make up for circuit defects, limit circuit design applications, etc. problems, achieve the effect of reducing power consumption, enriching the circuit structure, and maintaining various performances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
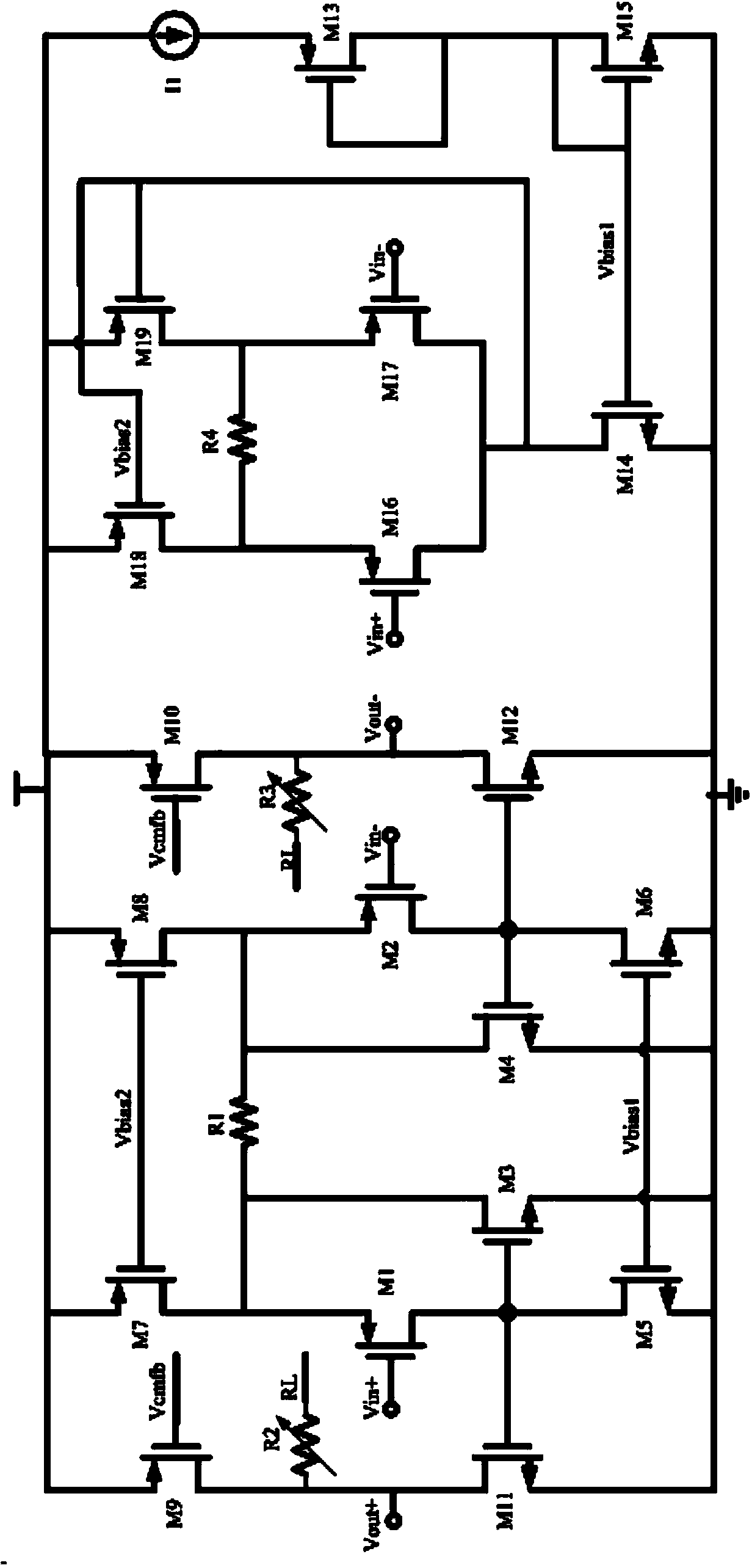
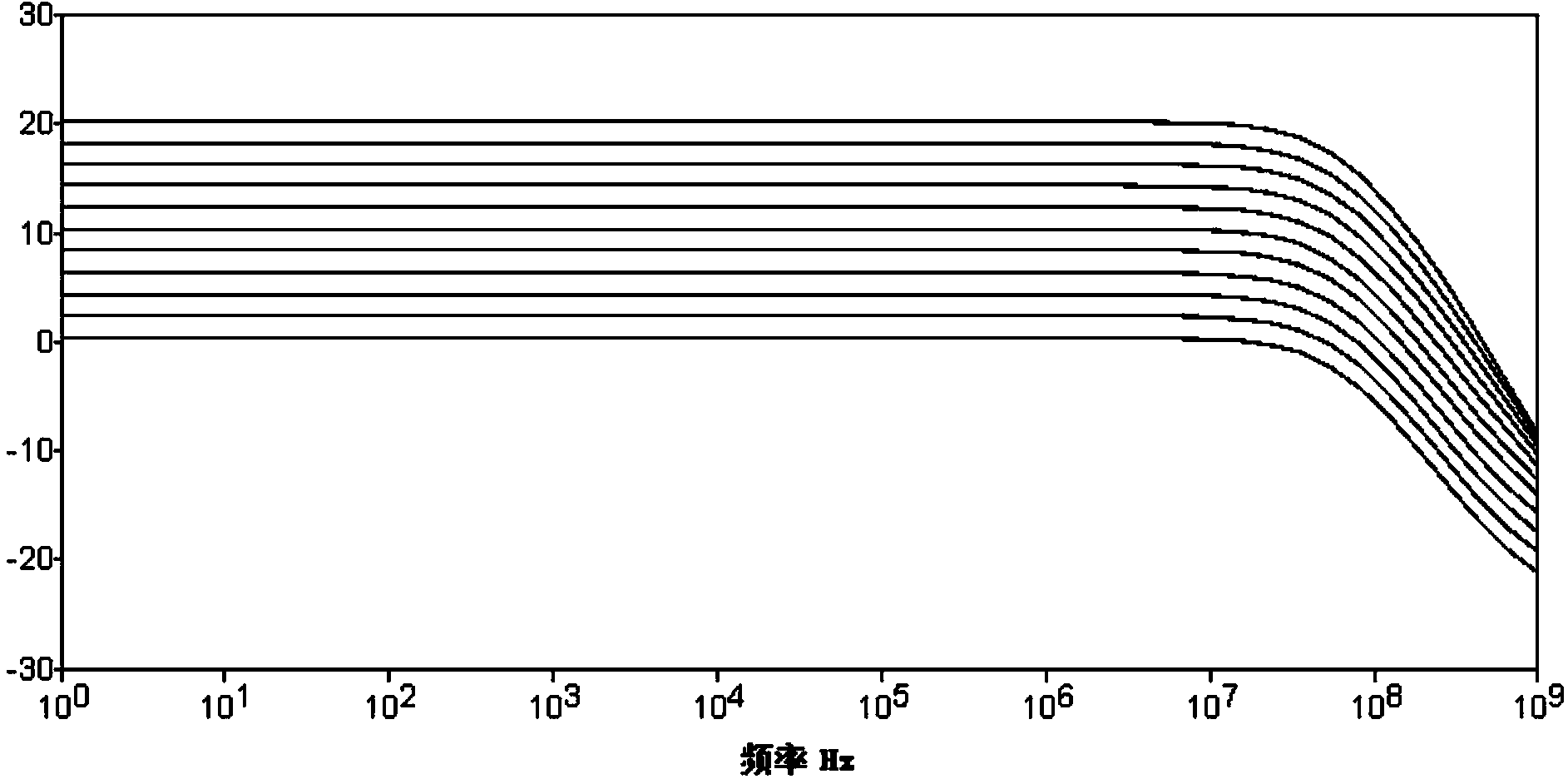
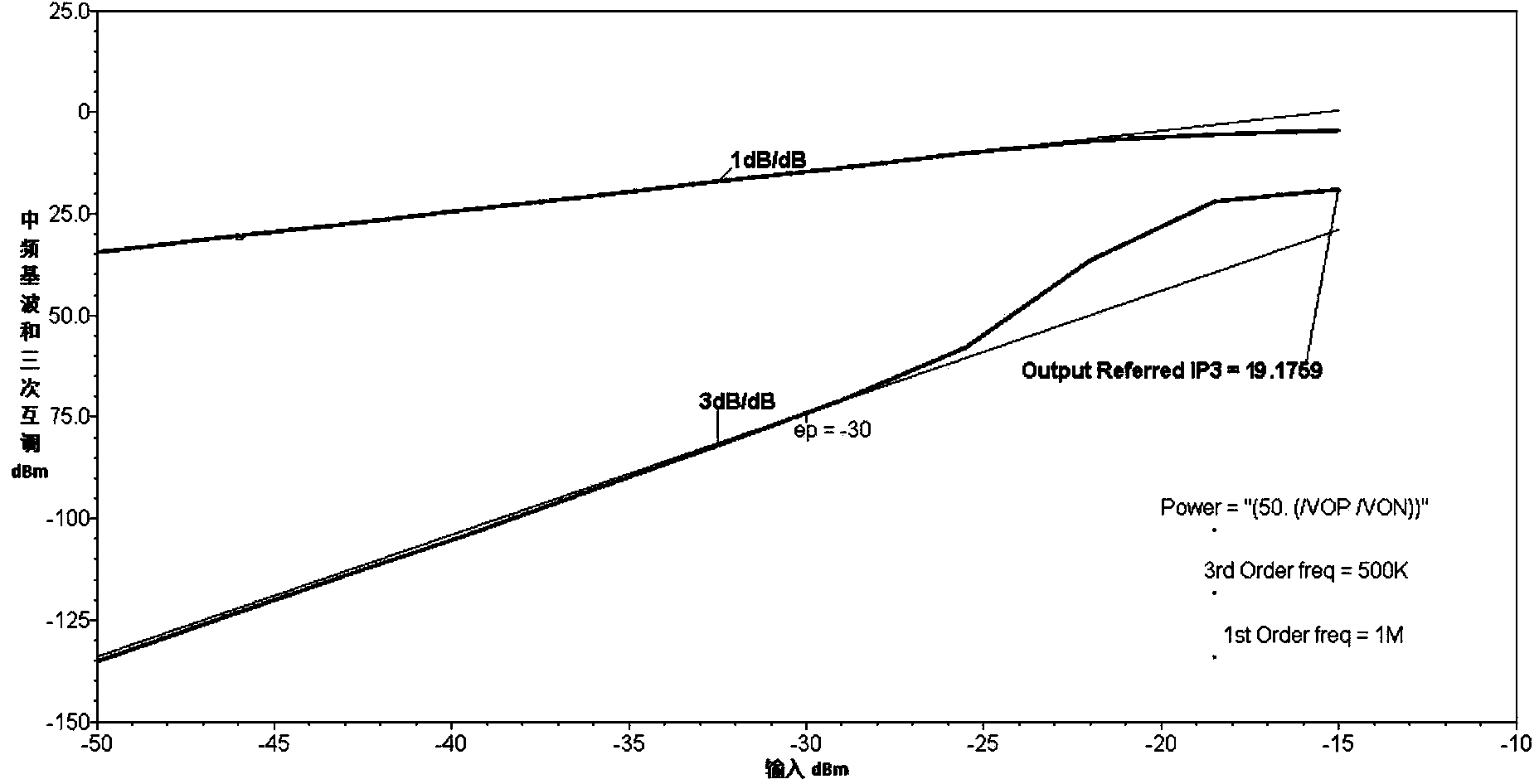
[0020] Such as figure 1 Shown is a programmable gain amplifier with low power supply voltage, which has the characteristics of low power supply voltage for normal operation, which can effectively reduce the power consumption of the circuit. The tail current source of the programmable gain amplifier is biased in the linear region, and a transconductance stage proportional to the differential input transconductance stage is used to form a master-slave structure with the differential input transconductance stage. The tail current source of the master transconductance stage The gate and the gate of the differential input transistor are respectively connected to corresponding ports of the slave transconductance stage in the operational amplifier. Neglecting the channel modulation effect of the transconductance, under the fluctuation of the input voltage or supply voltage, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com