Distillation method and detection method of organic components in flue gas desulfurization solution
A technology for desulfurization solution and flue gas, which is applied in the field of detection of organic components in flue gas desulfurization solution and distillation of organic components in flue gas desulfurization solution, which can solve interference, shorten service life of expensive components such as chromatographic columns, and difficulty in maintaining equipment Problems such as rising operating costs and other issues, to ensure authenticity and reliability, and to avoid oxidation damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
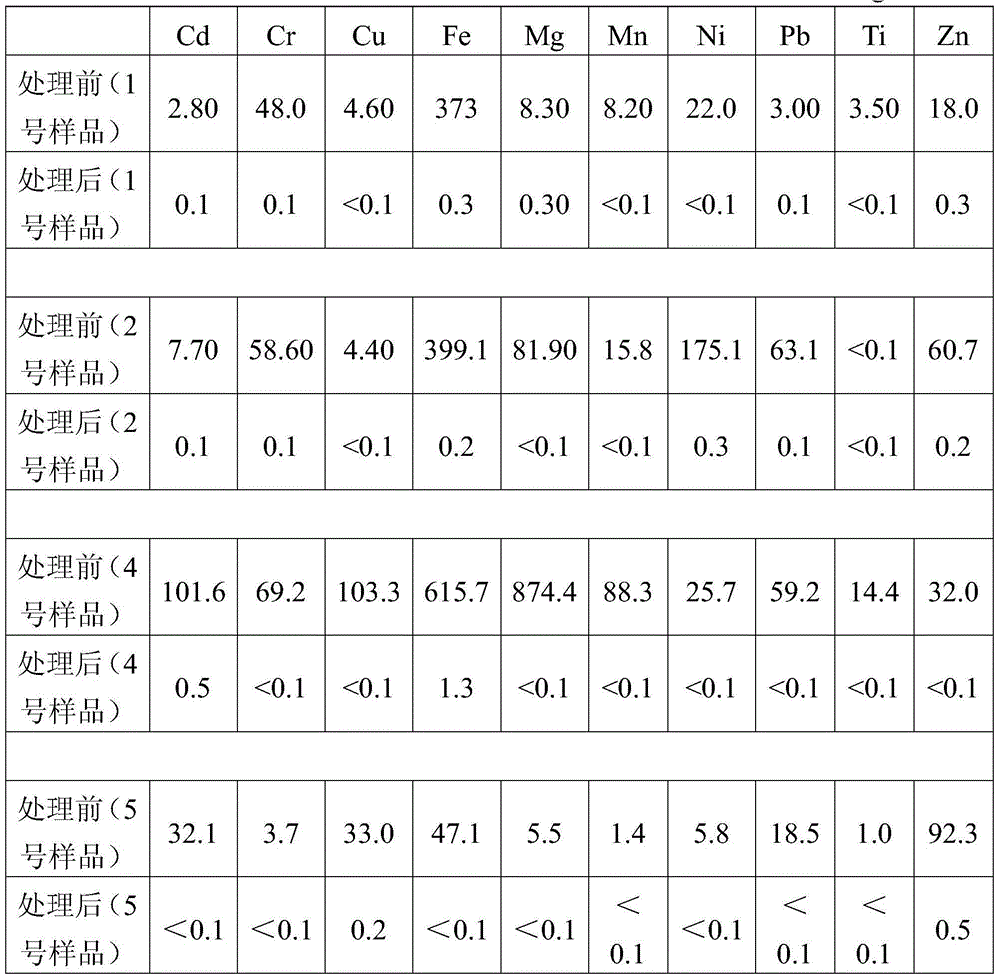
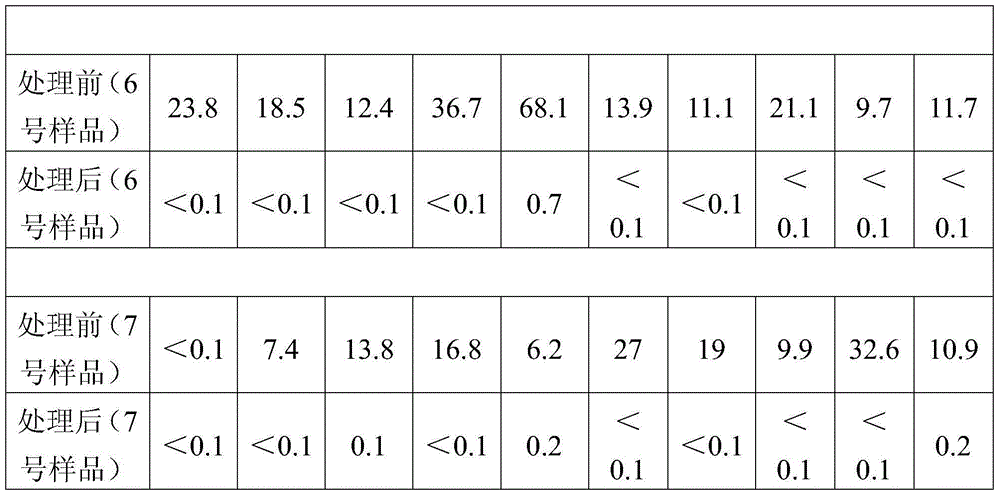
[0034] Detection and analysis of "desulfurization rich liquid".
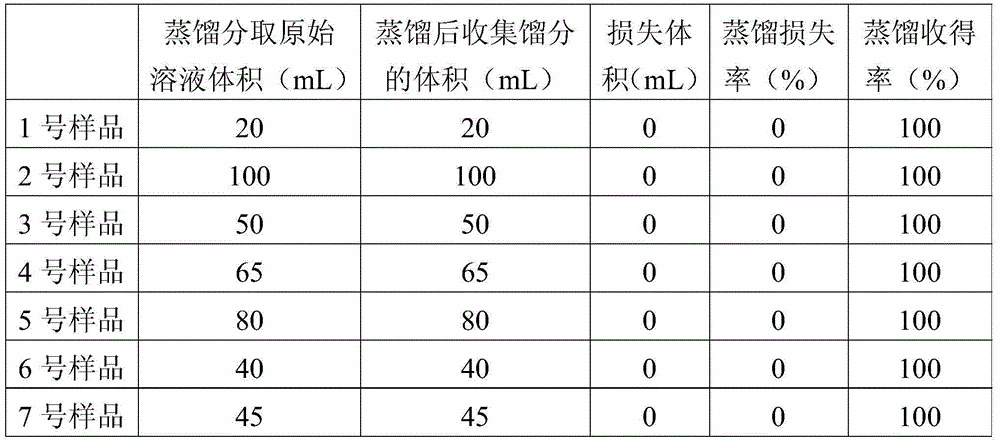
[0035] Measure 20mL of "desulfurization rich solution" (i.e. sample No. 1) in a distillation flask, distill at 300°C and collect fractions; when the remaining desulfurization solution in the evaporation container is half of the original volume (i.e. Collect the fractions and transfer them to other containers for storage; add sodium hydroxide to the remaining desulfurization solution in the evaporation vessel and dissolve completely, adjust the pH of the solution to 12 and then distill and collect the fractions at 300°C; until the solution is completely evaporated to dryness and no longer produces thick white smoke , use the previously transferred fraction to rinse back into the evaporation container along the wall, shake vigorously to rinse, soak, wash, and dissolve the evaporated solid residue in the evaporation container, distill and combine the collected fractions at 300 ° C; until Only dry inorganic solid ma...
example 2
[0038] Detection and analysis of "desulfurization poor solution".
[0039] Measure 100mL of "desulfurization poor solution" (i.e. sample No. 2) and distill at 350°C; transfer the collected fraction when the remaining desulfurization solution in the container is one-third of the original volume (i.e. about 30mL); add potassium hydroxide to adjust The pH of the remaining solution is 14 and it is distilled completely at 350°C. First use half of the transferred fraction (ie about 30mL) to wash the residue, then distill and combine the collected fractions at 350°C until the solution is completely evaporated to dryness, and then use the transferred fraction again. The last remaining half (ie about 30 mL) of the fractions was washed with solid residues and distilled at 350°C and combined to collect fractions until the solution was completely evaporated to dryness. In addition, the chromatographic parameters were set: the injection volume was 2 microliters, and the split ratio was 1:4...
example 3
[0041] Detection and analysis of "desulfurization poor solution".
[0042] Measure 50mL of "desulfurization poor solution" (that is, sample No. 3), set the distillation temperature at 320°C, transfer the distillate when the remaining solution is about 20mL, and add sodium hydroxide to control the pH of the solution to 13. In addition, the chromatographic parameter settings: the injection volume is 2.5 microliters, the split ratio is 1:30; in addition, the desulfurization solution is distilled and separated according to the same method as in Example 1 and the fractions are detected by GC-MS.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com