Cellulose and borneol compounded antibacterial material
An antibacterial material, cellulose technology, applied in the directions of fungicides, chemicals for biological control, biocides, etc., can solve the problems of no killing or inhibition of cellulose bacteria, bacterial contamination, etc., to achieve easy implementation, The effect of simple polymer structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
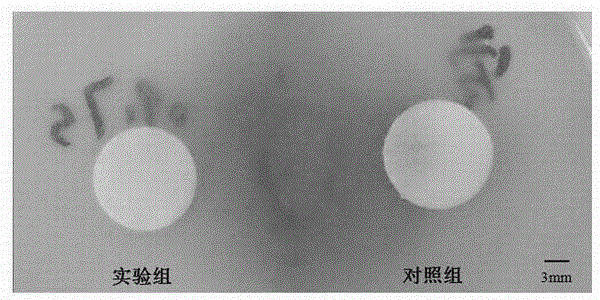
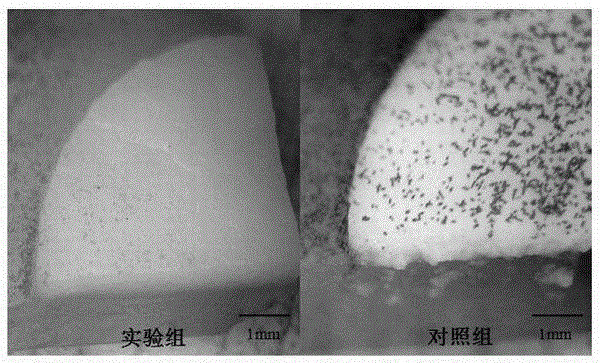
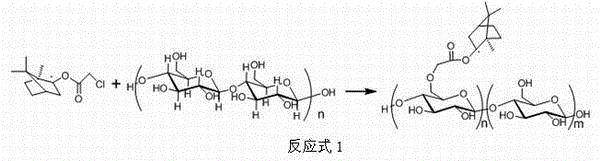
[0024] Weigh 1 g of L-borneol and dissolve it in tetrahydrofuran, add 1.5 eq of pyridine, and titrate the reaction with 1.5 eq of chloroacetyl chloride diluent. After the reaction, purify to obtain a colorless oily monomer. Stir the cellulose in 2M NaOH aqueous solution for 2h to carry out alkalization, dry the obtained alkaline cellulose, and dissolve the obtained chloroacetylated borneol derivatives and the ionic liquid-dissolved alkalized cellulose at a structural unit molar ratio of 2 : 1 ratio, stirred at 70°C for 48 hours, after the reaction was stopped, the reaction product was subjected to Soxhlet extraction with ethanol as a solvent, and the ionic liquid and chloroacetylated borneol derivatives were removed after reaction for 48 hours, and dried to obtain the product. The degree of modification is n>5%, and the antibacterial adhesion is greater than 5 days (using experimental strains: Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Mucor, Penicillium, etc.).
Embodiment 2
[0026] Weigh 1 g of D-borneol and dissolve it in tetrahydrofuran, add 1.5 eq of pyridine, and titrate the reaction with 1.5 eq of chloroacetyl chloride diluent. After the reaction, purify to obtain a colorless oily monomer. Stir the cellulose in 2M NaOH aqueous solution for 2h to carry out alkalization, dry the obtained alkaline cellulose, and dissolve the obtained chloroacetylated borneol derivatives and the ionic liquid-dissolved alkalized cellulose at a structural unit molar ratio of 2 : 1 ratio, stirred at 70°C for 48 hours, after the reaction was stopped, the reaction product was subjected to Soxhlet extraction with ethanol as a solvent, and the ionic liquid and chloroacetylated borneol derivatives were removed after reaction for 48 hours, and dried to obtain the product. The degree of modification is n>5%, and the antibacterial adhesion is greater than 5 days (using experimental strains: Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Mucor, Penicillium, etc.).
Embodiment 3
[0028] Weigh 1 g of Iso-borneol and dissolve it in tetrahydrofuran, add 1.5 eq of pyridine, and titrate the reaction with 1.5 eq of chloroacetyl chloride diluent. After the reaction, purify to obtain a colorless oily monomer. Stir the cellulose in 2M NaOH aqueous solution for 2h to carry out alkalization, dry the obtained alkaline cellulose, and dissolve the obtained chloroacetylated borneol derivatives and the ionic liquid-dissolved alkalized cellulose at a structural unit molar ratio of 2 : 1 ratio, stirred at 70°C for 48 hours, after the reaction was stopped, the reaction product was subjected to Soxhlet extraction with ethanol as a solvent, and the ionic liquid and chloroacetylated borneol derivatives were removed after reaction for 48 hours, and dried to obtain the product. The degree of modification is n>5%, and the antibacterial adhesion is greater than 5 days (using experimental strains: Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Mucor, Penicillium, etc.).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com