Endosperm specific expression promoter
A molecular and sequence listing technology, applied in the field of endosperm-specific expression promoters, can solve the problems of increasing the metabolic burden of plants, being toxic, and detrimental to the normal growth of plants.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Embodiment 1, the cloning of promoter sequence
[0054] 1. Wheat Genomic DNA Extraction
[0055] Wheat varieties tested: Yunmai 33, Zhongguochun, Jimai 20 and Atlas66.
[0056] After the seeds of the four tested wheat varieties germinated for 7-10 days, fresh leaves were ground into powder in liquid nitrogen, and genomic DNA was extracted by CTAB method.
[0057] CTAB extraction buffer: 0.1M Tris-HCl (pH8.0), 20mM EDTA (pH8.0), 1.4M NaCl, 2% (w / v) CTAB, 2% (w / v) PVP40 and 3% (v / v) β-mercaptoethanol (add just before use).
[0058] Extraction steps:
[0059] 1. Take an appropriate amount of material (5g) and grind it fully in liquid nitrogen, transfer the ground powder into a pre-cooled 50ml centrifuge tube, add 20ml CTAB extraction buffer, vortex quickly, and lyse in a 65°C water bath for 45 minutes ;
[0060] 2. Add an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1, v / v), invert and mix thoroughly, centrifuge at 8000g at room temperature for 20 minutes, transfer...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Embodiment 2, transient expression experiment detects promoter activity
[0080] 1. Construction of transient expression vector
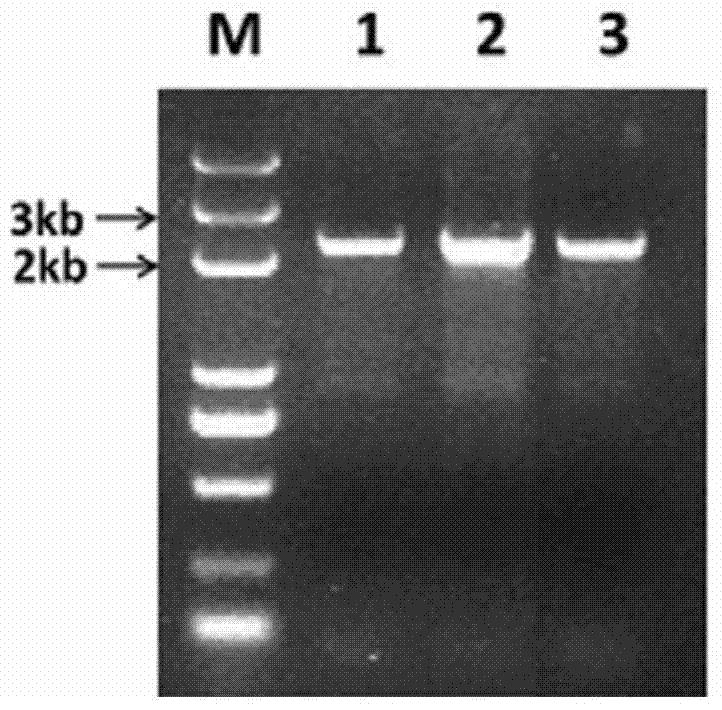
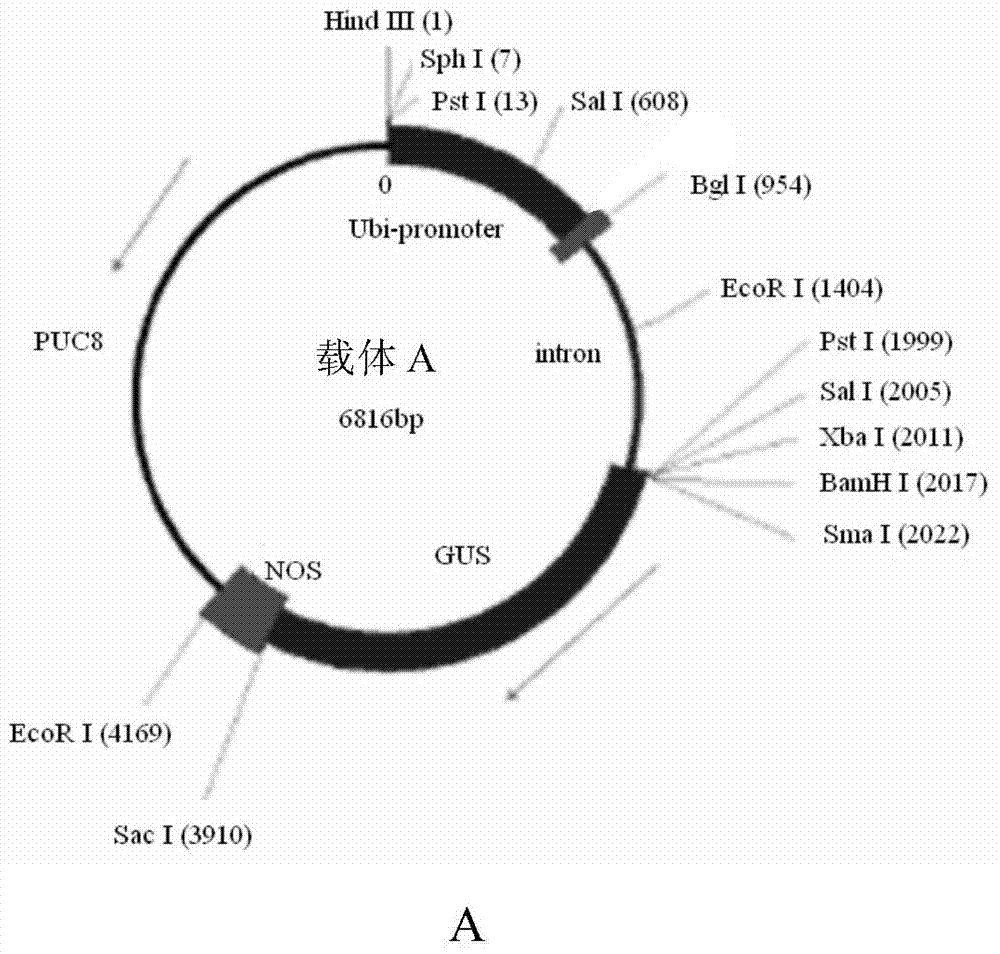
[0081] The pAHC25 vector was incompletely digested with EcoR I, and the 6800bp fragment was selected from the product to recover, and the recovered fragment was added to DNA ligase for self-ligation. The ligation system: T4 DNA ligase 1 μl; 2×T4 DNA ligase buffer 2.5 μl; recovered fragment (6800bp) 1.5 μl. Transformation after ligation is transformed into a usable vector, denoted as vector A, which carries the GUS gene, and its plasmid map is as follows: image 3 Shown in A.
[0082] The carrier A was completely digested with BamH I and Hind III. It can be clearly seen from the vector map that the fragment sizes after digestion should be 2000bp and 4800bp, and the results of restriction electrophoresis showed that the sizes of the two fragments were just in line with it ( image 3 Middle B), indicating that the vector A was constructed suc...
Embodiment 3
[0117] Embodiment 3, promoter activity analysis result in transgenic rice
[0118] 1. Construction of transgenic vector
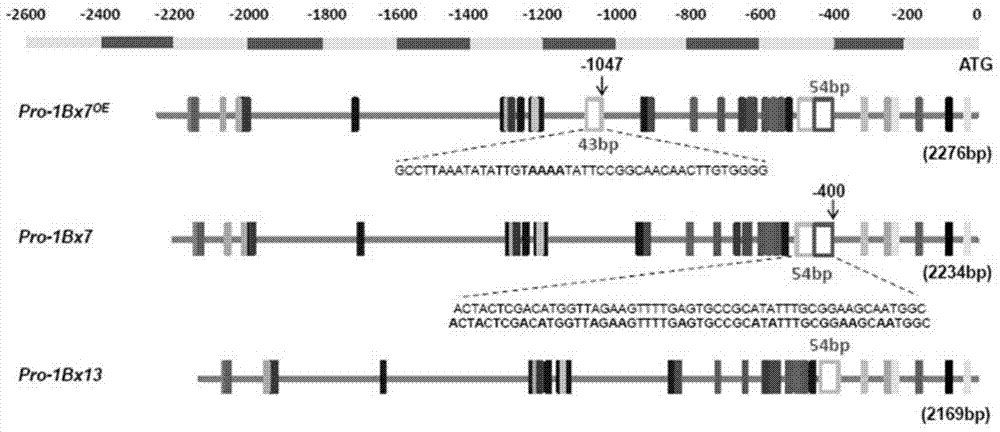
[0119] Obtain Pro-1Bx7 with embodiment 1 respectively OE Promoter sequence (sequence 1), Pro-1Bx7 promoter sequence (sequence 2) and Pro-1Bx13 promoter sequence (sequence 3) as templates, through primers 1Bx-PF2 and 1Bx-PR2 (see step 1 of Example 2 for the sequence) Perform PCR amplification.
[0120] The reaction system and reaction procedure are carried out with reference to Step 2 of Example 1.
[0121] After the reaction, each PCR product was double-digested with BamH I and Hind III, recovered from the gel, and connected to the large backbone fragment of the pCAMBIA1391Z vector (CAMBIA, Canberra, Australia) that had undergone the same double digestion to obtain a recombinant plasmid. Ligation system: T4 DNA ligase 1 μl; 2×T4 DNA ligase buffer 2.5 μl; pCAMBIA1391Z vector backbone fragment 1 μl; PCR product after digestion 0.5 μl.
[0122] The recombi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com