Production method of sea-buckthorn transparency liquid facial soap
A technology of transparent liquid and production method, which is applied in the field of daily chemicals to achieve the effect of low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
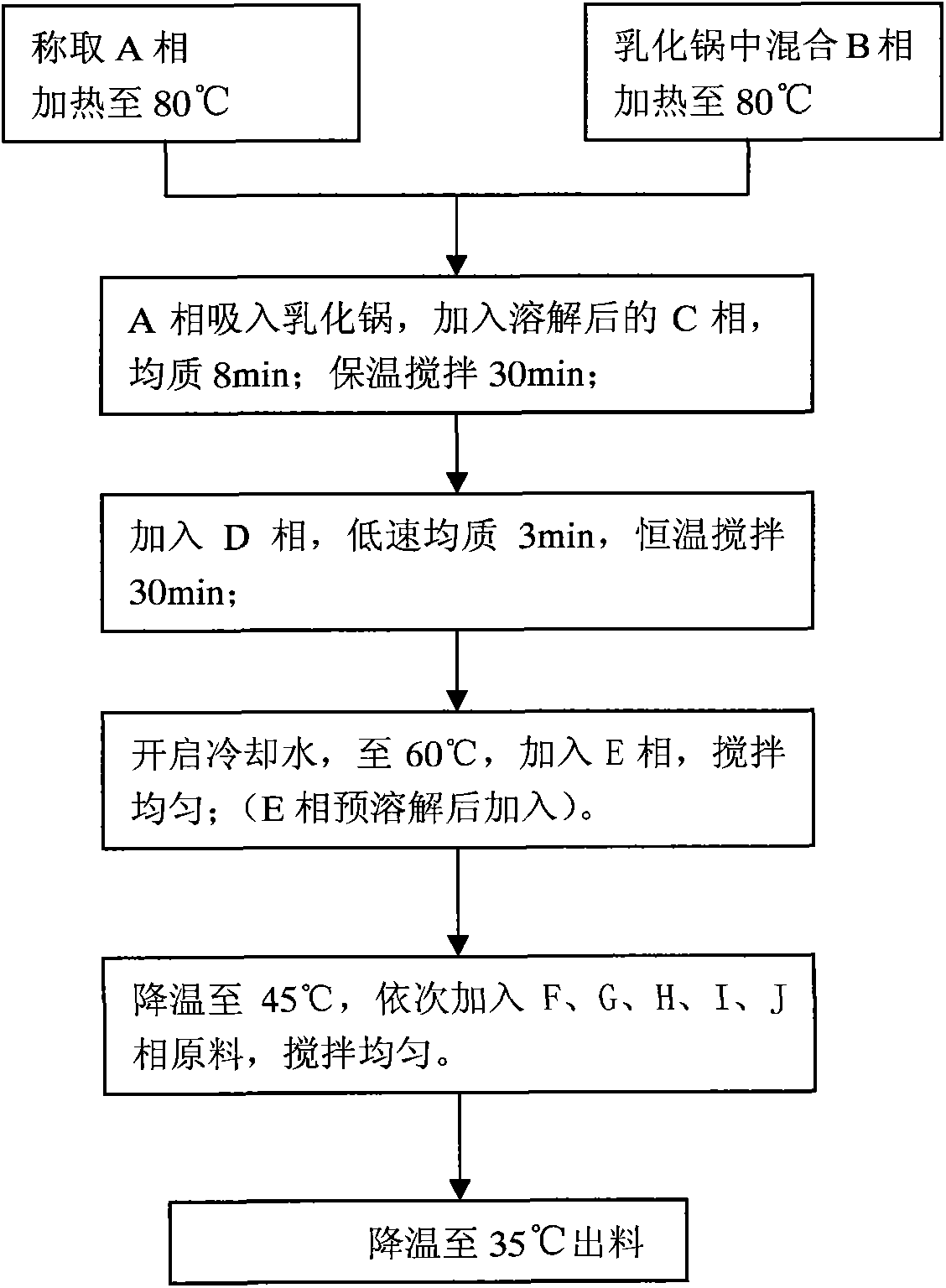
[0028] (1) Mix phase A: weigh 6 parts by weight of lauric acid and 1.5 parts by weight of myristic acid, mix them in a water pot until uniform, and heat to 80°C;
[0029] (2) Mix phase B: add 10 parts by weight of glycerin to a vacuum emulsification stirring pot and then copolymerize with 5 parts by weight of acrylic esters, or 5 parts by weight of stearyl ether-20 methacrylate Mix the material, add water and heat to 80°C, stir until the material is evenly dispersed;
[0030] (3) Mixing Phase A, Phase B and Phase C: Inhale the final mixture obtained in step (1) into a vacuum emulsification stirring pot and mix it with the mixture obtained in step (2), then add 2.86 parts by weight and the purity is 91.5 % potassium hydroxide, 10 parts by weight of water, homogenized for 8 minutes, and incubated for 30 minutes;
[0031] (4) Mix phase A, phase B, phase C, and phase D: add 0.2 parts by weight of cocamide MEA and sodium laureth sulfate of 4 parts by weight to the mixture finally ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] (1) Mix phase A: weigh 6 parts by weight of lauric acid and 1.5 parts by weight of myristic acid, mix them in a water pot until uniform, and heat to 80°C;
[0042] (2) Mix phase B: add 15 parts by weight of glycerin to a vacuum emulsification stirring pot and then copolymerize with 5 parts by weight of acrylic acid esters, or 5 parts by weight of steareth-20 methacrylate Mix the material, add water and heat to 80°C, stir until the material is evenly dispersed;
[0043] (3) Mix phase A, phase B and phase c: suck the mixture finally obtained in step (1) into a vacuum emulsification stirring pot and mix it with the mixture finally obtained in step (2), then add 2.86 parts by weight and the purity is 91.5 % potassium hydroxide, 10 parts by weight of water, homogenized for 8 minutes, and incubated for 30 minutes;
[0044] (4) Mix phases A, B, C and D: add 0.2 parts by weight of cocamide MEA and 6 parts by weight of sodium laureth sulfate to the final mixture obtained in ste...
Embodiment 3
[0054] (1) Mix phase A: weigh 8 parts by weight of lauric acid and 2 parts by weight of myristic acid, mix them in a water pot until uniform, and heat to 80°C;
[0055] (2) Mix phase B: add 10 parts by weight of glycerin to a vacuum emulsification stirring pot and then copolymerize with 5 parts by weight of acrylic esters, or 5 parts by weight of stearyl ether-20 methacrylate Mix the material, add water and heat to 80°C, stir until the material is evenly dispersed;
[0056] (3) Mix phase A, phase B and phase C: suck the mixture finally obtained in step (1) into a vacuum emulsification stirring pot and mix it with the mixture finally obtained in step (2), then add 3.81 parts by weight and the purity is 91.5 % potassium hydroxide, 10 parts by weight of water, homogenized for 8 minutes, and incubated for 30 minutes;
[0057] (4) Mix phase A, phase B, phase C, and phase D: add 0.2 parts by weight of cocamide MEA and sodium laureth sulfate of 4 parts by weight to the mixture final...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com