A treatment method for high-concentration heavy metal polluted construction waste
A construction waste and treatment method technology, applied in construction waste recycling, solid waste removal, recycling technology, etc., can solve the problems of secondary pollution, large damage, high cost, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Elution and purification treatment of polluted construction waste in electroplating plants
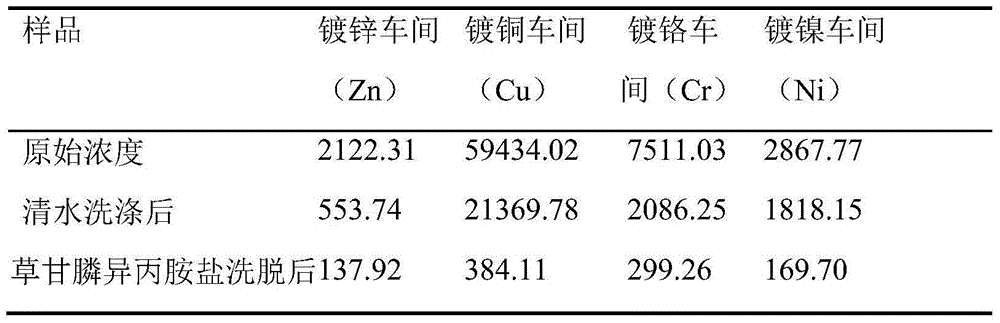
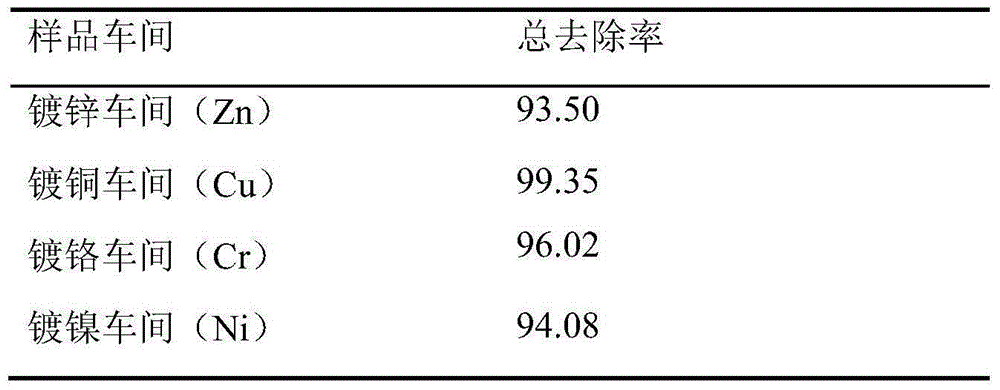
[0029] Take the treatment of construction waste in different workshops of an electroplating factory in Guangdong as an example. The electroplating factory has been in operation for 13 years. At present, the walls and bricks of several conventional workshops are seriously polluted. The construction waste used in this embodiment is the wall concrete blocks and bricks of four different workshops of galvanizing, copper plating, chrome plating and nickel plating. The specific heavy metal concentration of the construction waste after the surface layer is stripped is: galvanizing workshop (Zn) 2122.31mg / kg, copper plating workshop (Cu) 59434.02mg / kg, chrome plating car
[0030] Cr (Cr) 7511.03mg / kg, nickel plating workshop (Ni) 2867.77mg / kg (Table 1.a).
[0031] Proceed as follows:
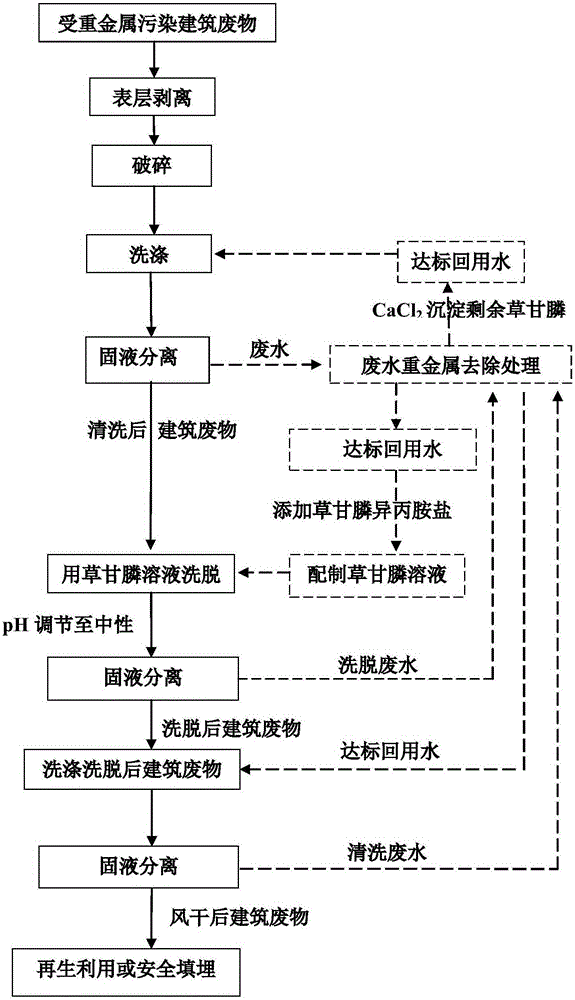
[0032]In the first step, the surface layer of the concrete blocks and bricks of the wall is stripped...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Elution and purification treatment of polluted construction waste in zinc smelter
[0051] Taking the polluted construction waste of a zinc smelting factory in Yunnan as an example, the electrolysis workshop and cleaning workshop of the factory were seriously polluted by zinc. The Zn contents in the workshop were 49280.00mg / kg and 29738.72mg / kg respectively (Table 2).
[0052] In the first step, the surface layer of the concrete blocks and bricks of the wall is stripped, and the construction waste with high heavy metal content in the surface layer is separated. Use commercially available industrial grade 2-8mo1 / L caustic soda solution (solid-to-liquid volume ratio 1:5) to carry out alkaline leaching of construction waste with high heavy metal content on the surface, and perform electrolytic treatment on the leaching solution to recover metal zinc.
[0053] The second step is the same as in Example 1.
[0054] The third step is to peel off the surface layer, break it, ...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Elution and purification treatment of polluted construction sand and gravel waste after demolition of a factory building
[0067] Taking the polluted concrete sand and gravel waste from a factory building in Shanghai as an example, the sand and gravel waste is mainly polluted by Cu and Zn. After stripping the surface construction waste, the Cu and Zn contents were measured to be 27155.32 mg / kg and 4087.06 mg / kg respectively (Table 3 ).
[0068] Proceed as follows:
[0069] The first step is to peel off the surface layer of concrete sand and gravel to separate the construction waste with high heavy metal content in the surface layer. Use commercially available industrial grade 2-8mo1 / L caustic soda solution (solid-to-liquid volume ratio: 1:5) to carry out alkaline leaching of construction waste with high heavy metal content on the surface, and perform electrolytic treatment on the leaching solution to recover metal zinc.
[0070] Second step, third step are identical w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com