Method for preparing propylene from methanol
A technology for producing propylene and dimethyl ether from methanol is applied in the directions of producing hydrocarbons from oxygen-containing organic compounds, organic chemistry, etc., and can solve the problems of low reaction efficiency, complicated conversion reaction, easy coking and deactivation of catalysts, etc. The effect of improving the yield of propylene and reducing the generation of carbon deposits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0041] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
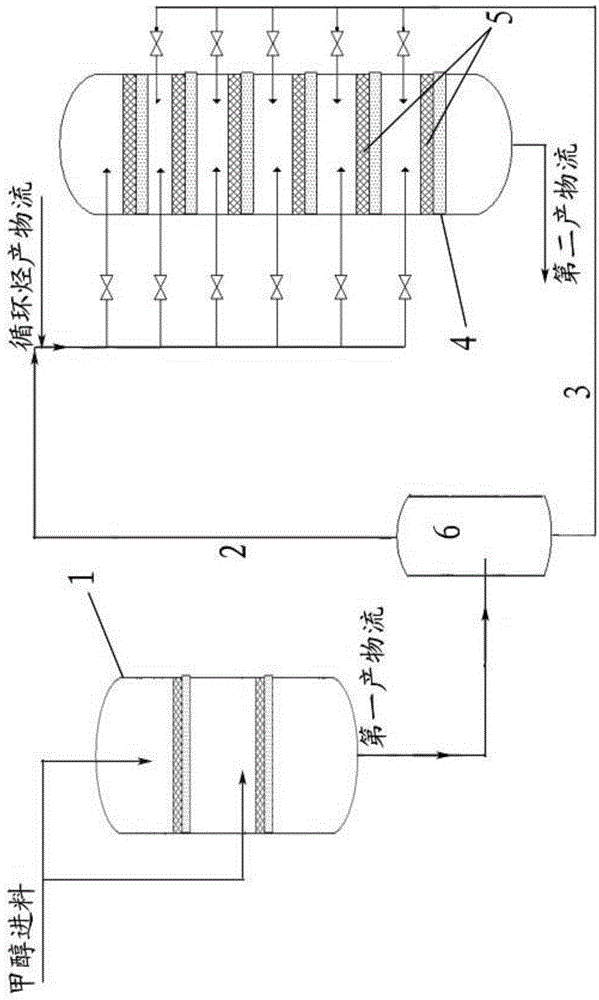
[0042] Such as figure 1 As shown, the reaction unit comprises a first reactor 1 (i.e. a DME reactor) and a second reactor 4 (i.e. an MTP reactor), and the first reactor 1 is vertically provided with 2 catalyst beds, The second reactor 4 is provided with 6 catalyst beds 5, wherein, the methanol feed of the first reactor 1 is divided into two streams: after the first feed is preheated, from the first reaction The top of device 1 enters to carry out the strong exothermic reaction of methanol dehydration to dimethyl ether; the second feed is sent to the Between the two catalyst beds in the first reactor 1, it is mixed with the reaction product of the first feed, absorbs the heat released by the strong exothermic reaction, and continues the reaction of synthesizing methanol from dimethyl ether.
[0043] The first product...
Embodiment 1
[0049] In order to evaluate the rationality of the new process based on methanol to propylene, such as figure 1 The shown model test device simulates the process conditions of industrial devices for experiments, wherein the catalyst in the first reactor (ie DME reactor) is γ-Al 2 o 3 (Select the DME-1 catalyst of Clariant Co., Ltd.), and fill in two layers. The catalyst filling method in the second reactor is as follows: uniformly mix catalysts A and C with a mass ratio of 1:1 and then fill them into the first to sixth catalyst beds of the second reactor.
[0050] Wherein, the feed amount of methanol to the first reactor is 2.5kg / h, and the total amount of catalyst loaded in the first reactor is 1.8kg, and the reaction pressure is 0.8MPa. The total amount of catalyst loaded in the second reactor is 2.5kg, and the reaction pressure is 0.09MPa.
[0051] After preheating 75wt% methanol raw material to about 280°C, it enters from the top of the first reactor, and the remaining ...
Embodiment 2
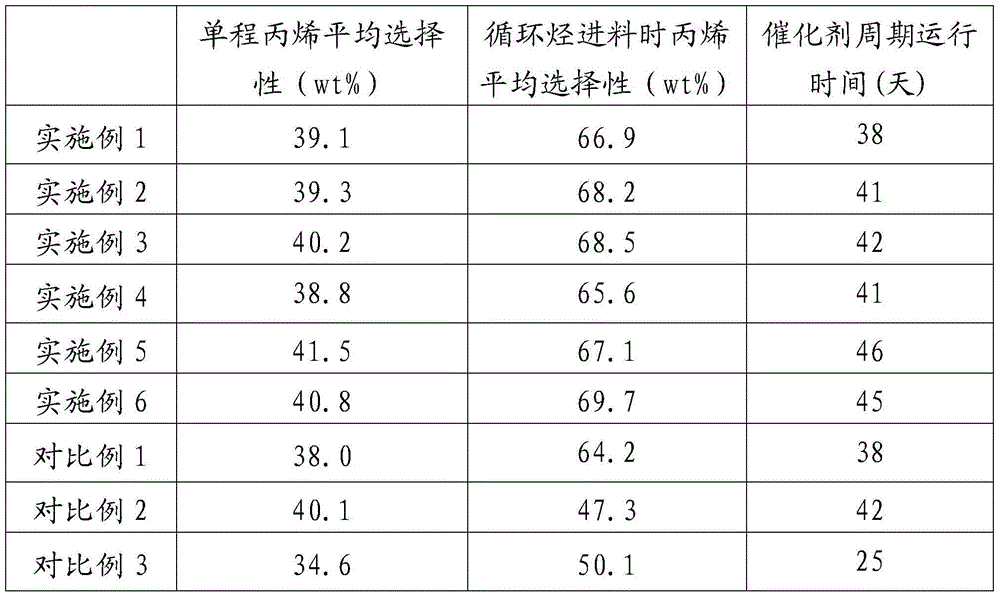
[0054] The difference from Example 1 is that the filling method of the catalyst in the second reactor is: the catalyst A is filled from the uppermost layer in the catalyst bed of the second reactor to the lower interlayer to the corresponding Catalyst bed, catalyst C is packed into the rest of the catalyst bed, and the mass ratio of catalysts A and C is 1:1. The experimental results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com