Thermally enhanced wiring board with built-in heat sink and build-up circuitry
A heat sink, gain-type technology, applied in circuit thermal devices, circuits, printed circuits, etc., can solve problems such as limiting routing feasibility, reducing heat dissipation, and limiting heat dissipation, so as to be suitable for mass manufacturing and prevent thermal connection. The effect of false, high routing feasibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
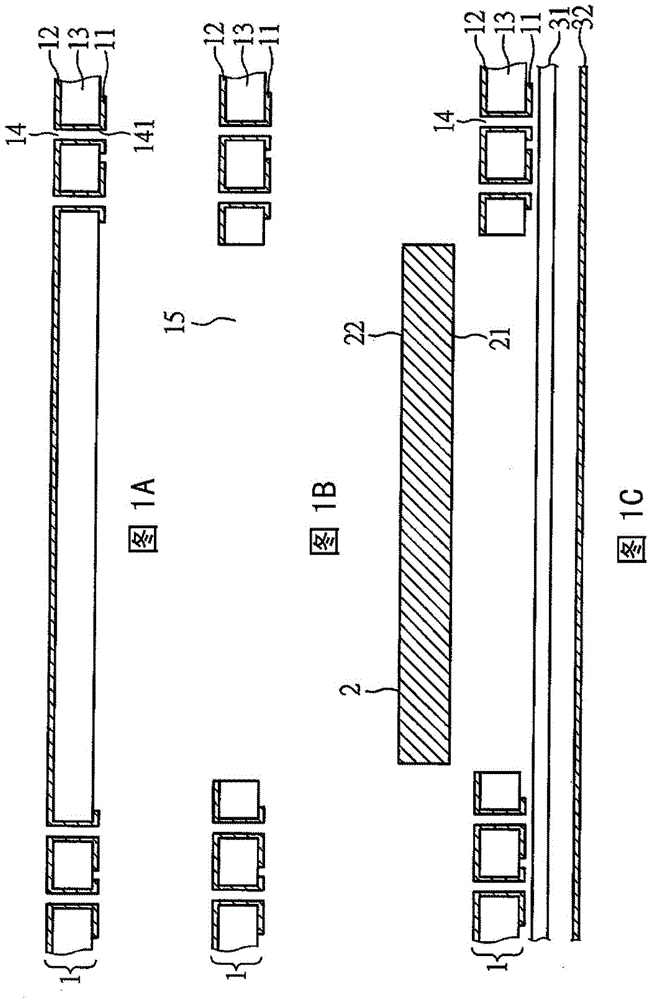
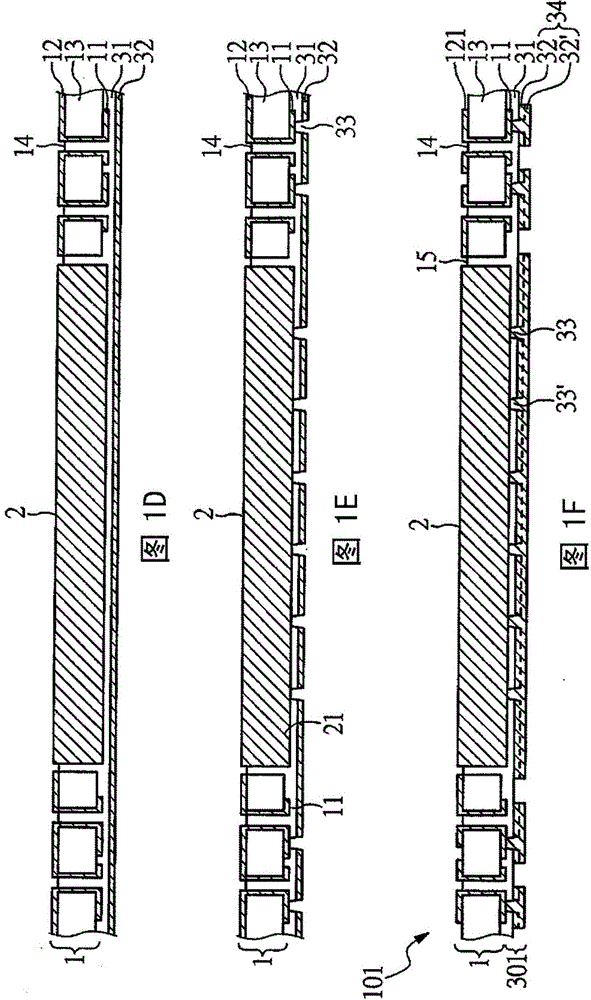
[0039] Figure 1A — 1F is a cross-sectional view of a method for manufacturing a thermally enhanced circuit board according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. The circuit board includes a reinforcement layer, a heat sink, and a build-up circuit electrically connected to the reinforcement layer.
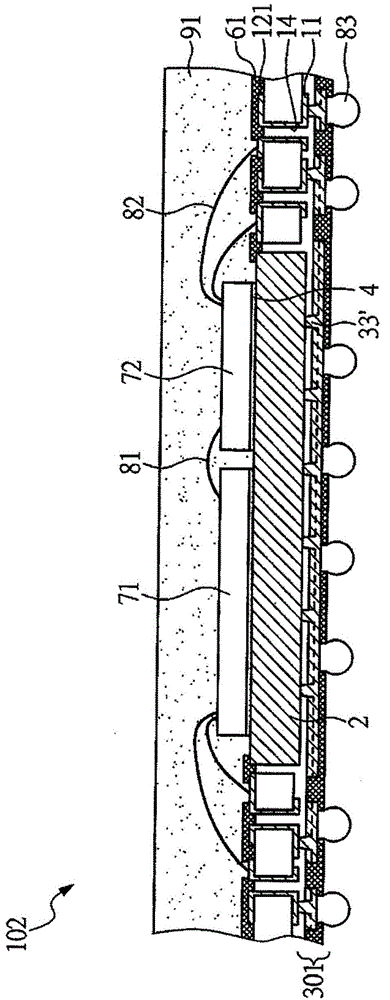
[0040] Such as Figure 1F As shown, the thermally enhanced circuit board 101 includes a reinforcement layer 1 , a heat sink 2 , and a build-up circuit 301 . The reinforcement layer 1 includes a first patterned circuit layer 11 , covered through holes 14 , a second patterned circuit layer 121 opposite to the first patterned circuit layer 11 and electrically connected to the first patterned circuit layer 11 , and via holes 15 , which is put into heat sink 2. The build-up circuit 301 includes a first dielectric layer 31 , a first blind hole 33 , and a first wire 34 . The build-up circuit 301 is respectively thermally connected to the heat sink 2 and electrically conne...
Embodiment 2
[0052] For the purpose of brevity, any statement in Example 1 may be incorporated into the same application section here, and the same statement will not be repeated.
[0053] Figure 2A and 2B is a cross-sectional view of a method for forming the positioning member 17 on the first dielectric layer 31 according to another preferred embodiment of the present invention; and Figure 2C for correspondence Figure 2B top view.
[0054] Figure 2A It is a structural cross-sectional view of a laminated substrate having a metal layer 16 , a first dielectric layer 31 and a support plate 35 . The metal layer 16 is shown as a copper layer with a thickness of 35 μm, however, the metal layer 16 can also be made of other various metal materials and is not limited to the copper layer. In addition, the metal layer 16 can be deposited on the first dielectric layer 31 in a single-layer or multi-layer structure by various techniques such as pressing, electroplating, electroless plating, eva...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Figure 4A-Figure 4DIt is a cross-sectional view of another circuit board manufacturing method according to another preferred embodiment of the present invention. The circuit board includes a heat sink, a positioning member, a reinforcing layer, and a double build-up circuit.
[0075] For the purpose of brevity, any statement in Example 1 may be incorporated into the same application section here, and the same statement will not be repeated.
[0076] Please refer to Figure 3A and Figure 3B The structure, after using the adhesive 4 and using the positioning piece 17 as a configuration guide, the heat sink 2 is arranged on the first dielectric layer 31, the positioning piece 17 and the heat sink 2 are aligned with the through hole 15 of the reinforcement layer 1 and extending into it, and using an adhesive 4 to place the reinforcement layer 1 on the first dielectric layer 31 . Such as Figure 4A As shown, the heat sink 2 and the through hole 15 of the reinforcing la...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com