Method of cellulose catalytic conversion to prepare dihydric alcohol, hexahydric alcohol and gamma-valerolactone
A catalytic conversion and cellulose technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, molecular sieve catalysts, preparation of hydroxyl compounds, etc., to achieve the effects of small investment, easy industrialization, and low equipment requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
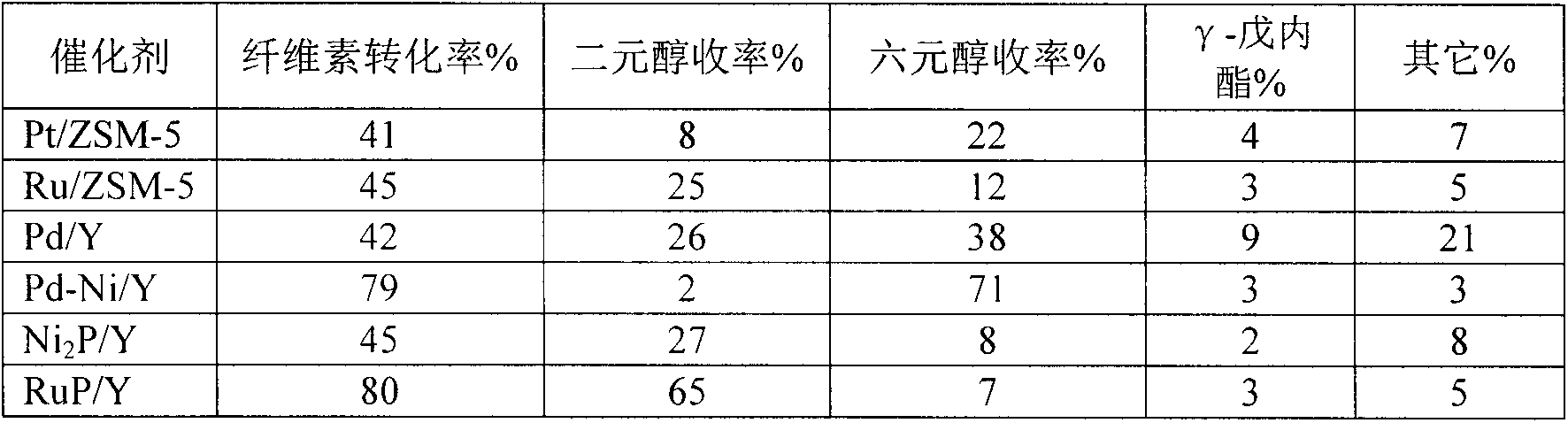
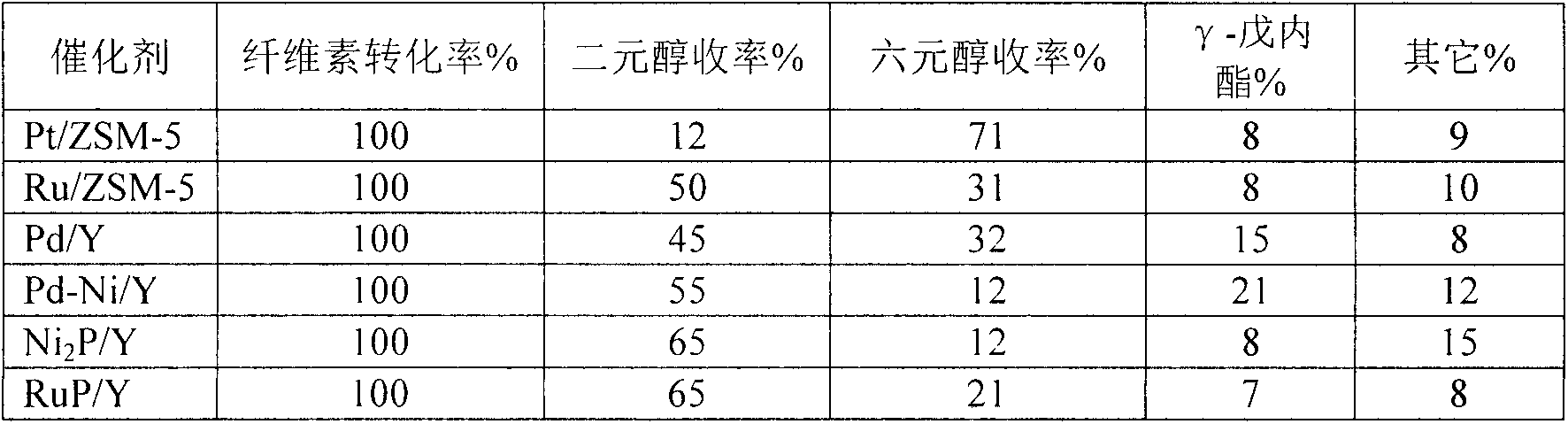
[0012] Preparation of molecular sieve-coated metal catalysts by hydrothermal synthesis: Pt(NH 3 ) 4 (NO 3 ) 2 , water glass, sodium metaaluminate, sodium hydroxide, deionized water to make nPt:nSiO 2 :nAl 2 o 3 : nNa 2 O:nH 2 The silica-alumina sol with O=0.51:70:1:12:2400 was placed in a crystallization kettle and crystallized at 160° C. for 3 days. The obtained sample was washed with deionized water to neutrality, and then dried in an oven at 120 °C for 12 h, then the catalyst precursor was subjected to NH 4 Cl exchange treatment, exchange the obtained catalyst in H 2 In the atmosphere, the temperature was raised to 400°C at a rate of 2°C / min and reduced for 3 hours to obtain a Pt / ZSM-5 catalyst, and Pt metal accounted for 1% of the weight of the catalyst. Pt(NH 3 ) 4 (NO 3 ) 2 into Ru(NH 3 ) 6 Cl 3 , to obtain Ru / ZSM-5 catalyst, Ru metal accounted for 5% of catalyst weight. . Catalyst coating success with 1-hexene (0.5nm, smaller than ZSM-5 pore size 0.55n...
Embodiment 2
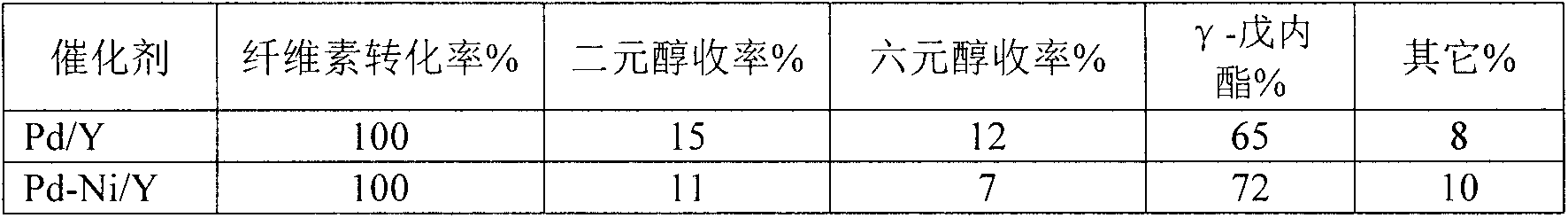
[0014] Synthesis of molecular sieve-coated metal catalysts by ion exchange: mix 5.0gNaY with 0.02mol / LPd(NH 3 ) 4 (NO 3 ) 2 The solution was ion-exchanged at 80°C for 4h, the obtained sample was filtered, washed with water, and then dried in an oven at 120°C for 12h, then the catalyst precursor was subjected to NH 4 Cl exchange treatment, exchange the obtained catalyst in H 2 In the atmosphere, the temperature was raised to 500°C for 3 hours at a rate of 2°C / min, and then the obtained sample was subjected to NH 4 Cl exchange treatment, exchange the obtained catalyst in N 2 In the atmosphere, the temperature was raised to 500°C at a rate of 2°C / min and reduced for 3 hours to obtain a Pd / Y catalyst, and Pt metal accounted for 2% of the weight of the catalyst. A Pt / ZSM-5 catalyst was obtained. 0.02mol / L Pd(NH 3 ) 4 (NO 3 ) 2 The solution was replaced with 0.01mol / LPd(NH 3 ) 4 (NO 3 ) 2 and Ni(NH 3 ) 6 Cl 2 solution to obtain a Pd-Ni / Y catalyst. The success of ca...
Embodiment 3
[0016] Synthesis of molecular sieve-coated metal phosphide catalysts by impregnation method: nickel nitrate and hypophosphorous acid were formulated into a 0.1mol / L nickel salt solution with a molar ratio of 1:4, 5.0g NaY was placed in the mixture, and the Impregnated and stirred for 6h, then evaporated to dryness at 100°C. The obtained sample was dried in an oven at 120°C for 12 hours, and then placed in H 2 In the atmosphere, the temperature was raised to 400°C for 3 hours at a rate of 5°C / min, and then the obtained sample was subjected to NH 4 Cl exchange treatment, exchange the obtained catalyst in N 2 In the atmosphere, the temperature was raised to 400°C at a rate of 2°C / min for 3 hours to obtain Ni 2 P / Y catalyst, Ni 2P accounts for 20% by weight of the catalyst. Replace the nickel nitrate solution used with Ru(NH 3 ) 6 (NO 3 ) 3 solution to obtain a RuP / Y catalyst, where RuP accounts for 5% by weight of the catalyst. The success of the catalyst coating was ver...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com