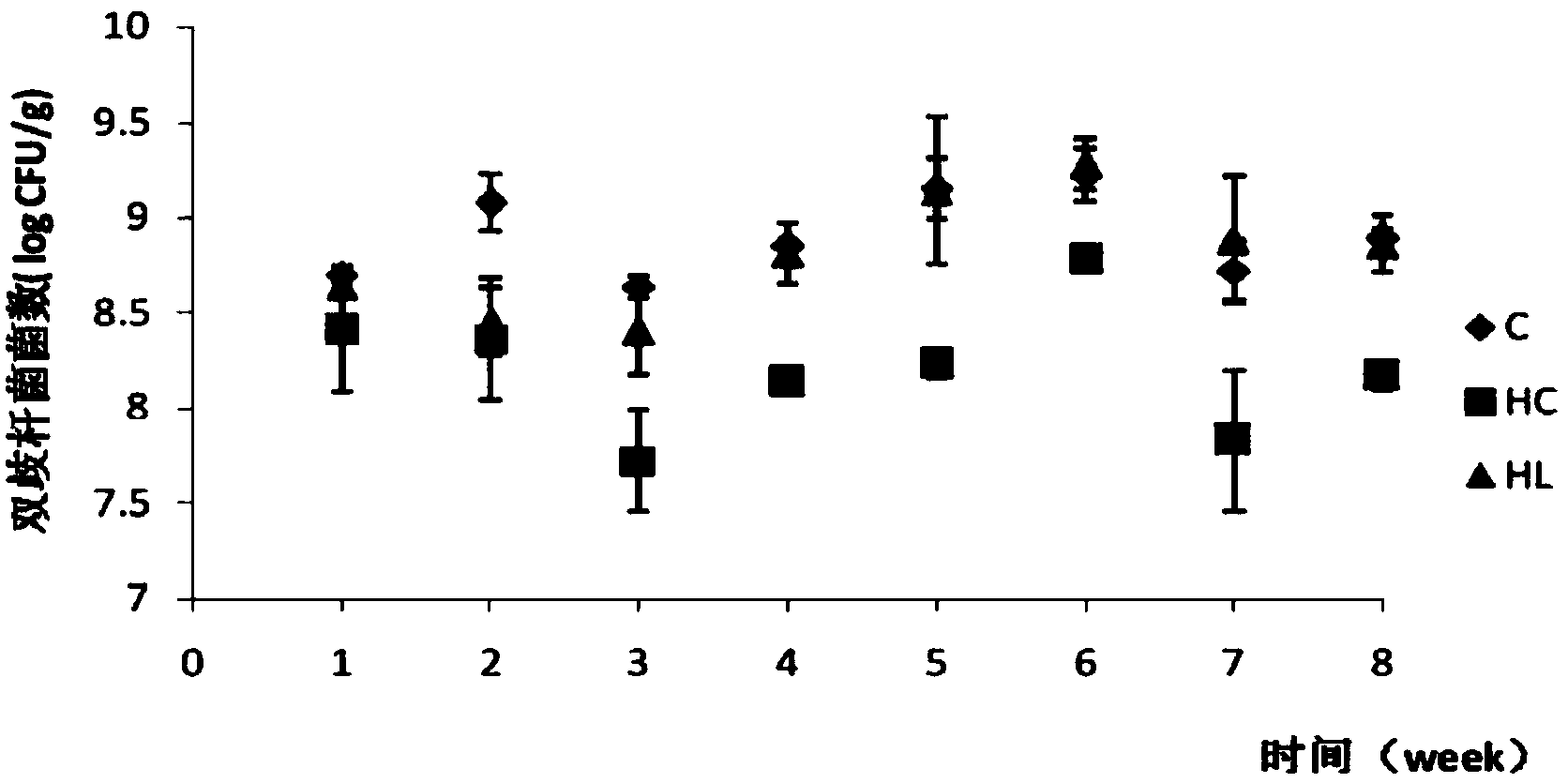
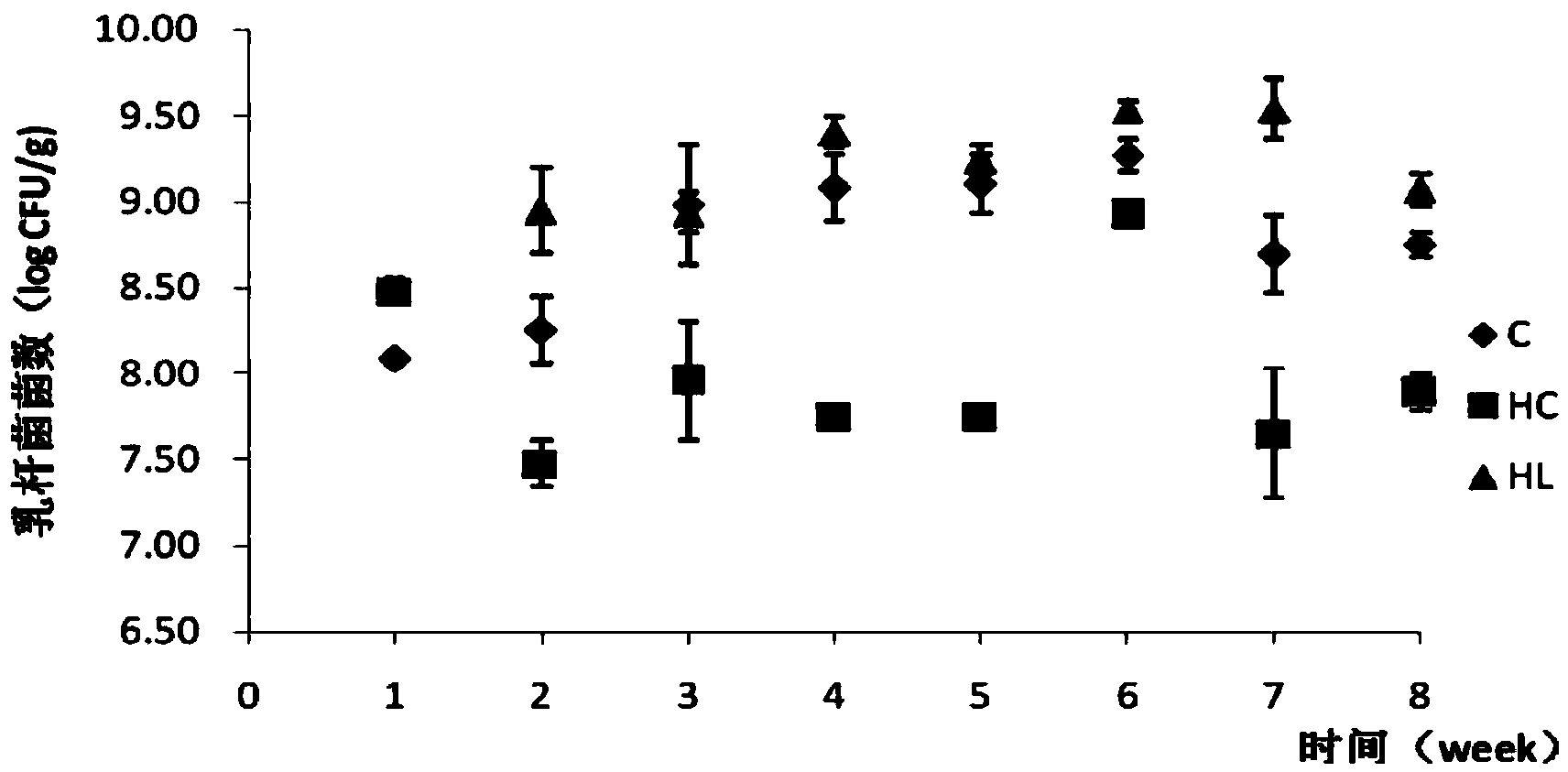
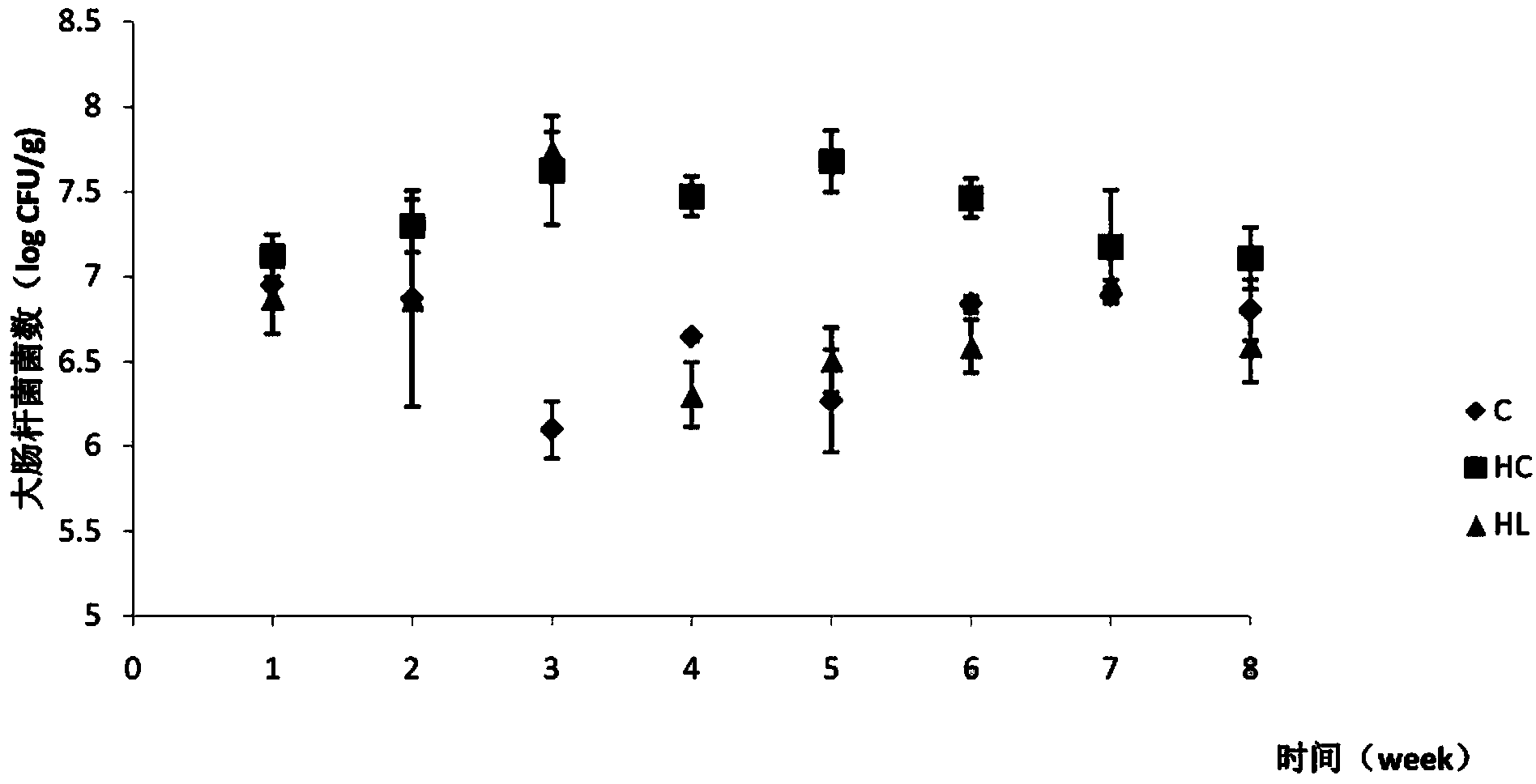Lactobacillus plantarum capable of lowering cholesterol
A Lactobacillus plantarum and cholesterol-lowering technology, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganisms, dairy products, etc., can solve the problems of low degradation rate and low application value, and achieve lower serum cholesterol, improve body immunity, and strong ability to degrade cholesterol Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Screening and identification of Lactobacillus plantarum Lp5 with high cholesterol-lowering ability according to the present invention
[0026] 1. Sample source
[0027] It comes from the traditional fermented yak milk product of Guoluo Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai Province, my country.
[0028] 2. Isolation and screening of lactic acid bacteria from traditional yak dairy products
[0029] Take 1ml of fermented yak milk product and dilute it with sterilized physiological saline at a ratio of 1:10, which is 10 -1 dilution. Then draw 1ml of the above diluent, and then dilute it 10 times, which is 10 -2 dilution, and so on. Pick 10 -6 Dilution: Pipette 100ul of the dilution into SL medium, culture anaerobically at 37°C for 48 hours, pick characteristic colonies, and further purify to obtain a pure isolated strain named Lp5.
[0030] 3. Identification of strains
Embodiment 2
[0037] The mensuration and contrast of embodiment 2 cholesterol-lowering ability
[0038] Adjust the number of Lactobacillus plantarum Lp5 to 1.0×10 9 cfu / mL, inoculate 10 ml of MRS liquid medium containing cholesterol 50 mg / ml according to 1% inoculum size, and culture statically at 37°C. Immediately after shaking, sample 1 mL, centrifuge at 4000 rpm / min for 5 min, absorb 0.5 mL of the supernatant, and use the o-phthalaldehyde method to determine the cholesterol content. After inoculation, the fermented liquid was cultured statically at 37°C for 48 hours, and then the cholesterol content in the supernatant was determined by the same method. The degradation rate of cholesterol was calculated by the following formula:
[0039] Cholesterol degradation rate = (cholesterol content in 0h supernatant - cholesterol content in 48h supernatant) / cholesterol content in 0h supernatant × 100%
[0040] Table 1 Lactobacillus plantarum L p 5 cholesterol lowering rate
[0041]
[0042]...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3: Digestive tract simulation test
[0044] The selected Lactobacillus plantarum Lp5 was subjected to artificial gastric juice and artificial intestinal juice tolerance experiments.
[0045] Test of tolerance to artificial gastric juice: After 2 generations of cell activation, the seed liquid was centrifuged at 5000r / min for 10 min, washed 3 times with sterilized normal saline, and then suspended. Take 1 mL of the bacterial suspension and put it in artificial gastric juice sterilized by filtration (including 9 mL of artificial gastric juice at pH 3.0), mix well and culture at a constant temperature of 37°C. Samples were taken at the beginning of the experiment and 3 hours later, and diluted 10 times with sterile saline. Select an appropriate dilution, take 0.1 mL of the bacterial suspension and spread it on the MRS plate, and set up 2 replicates. Count after 48 hours of anaerobic constant temperature cultivation at 37°C. The test results are shown in Table 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com