Method of degrading phosphate tri(2-chloroethyl) ester by adopting bacillus thuringiensis
A technology of Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus aureus, applied in the field of microbial degradation of organic pollutants, can solve the problem of low efficiency of organophosphorus flame retardants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
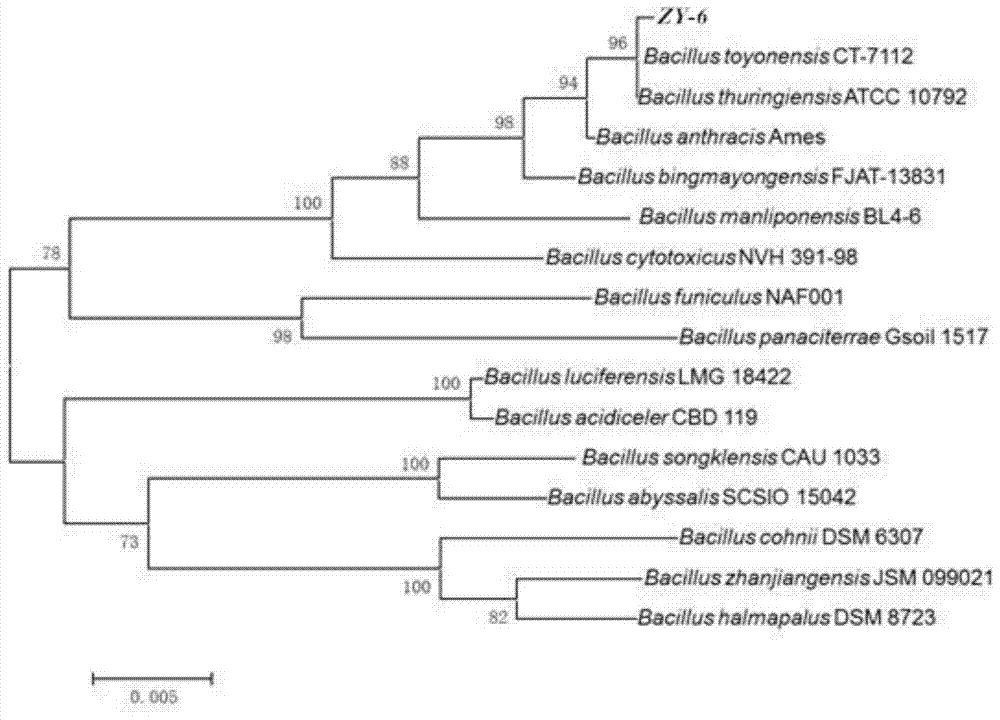
[0023] 1. Isolation of strains
[0024] (1) Collect the activated sludge from the sewage treatment plant and place it in a glass acclimation device with a length of 31.2cm, a width of 22.0cm and a height of 22.5cm, and use an air compressor without adding nutrients or exchanging water in and out. Intermittent aeration for 3 days. Then change the water, discharge about 10L of mud-water mixture in the device, add nutrient solution and carry out uninterrupted aeration. After cultivating for 10 days, start to add tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate-acetone solution when adding nutrient solution, keep the concentration of tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate in the device at about 1ppm, and according to the SBR process ( Water intake, aeration, standing, draining and idle) were carried out for domestication and cultivation, and the water was changed every other day for one month of cultivation and domestication. Preparation of culture medium: 0.6g / L glucose, 0.8g / L anhydrous sodium acetate,...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 Degradation Analysis of Tris(2-Chloroethyl) Phosphate by Bacillus thuringiensis
[0035] Under sterile conditions, Bacillus thuringiensis was inoculated into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 100mL of sterilized enrichment medium, placed in a constant temperature shaker, 30°C, 120rpm, and cultivated for 48h. The main components of enrichment medium EM (Enrichment Medium) are: 10g / L fish meal peptone, 5g / L yeast powder, 5g / L NaCl, 1000mL distilled water, pH=6.8~7.2.
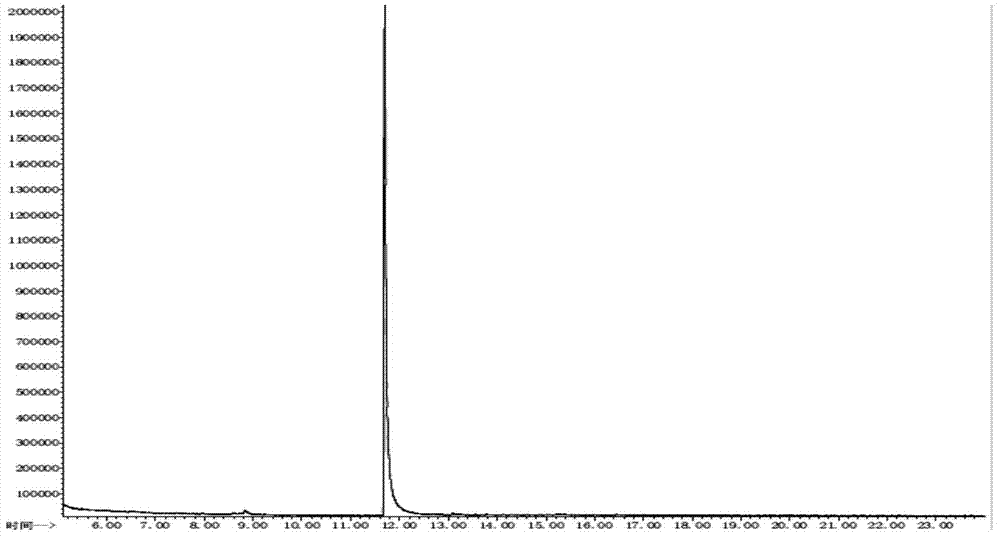
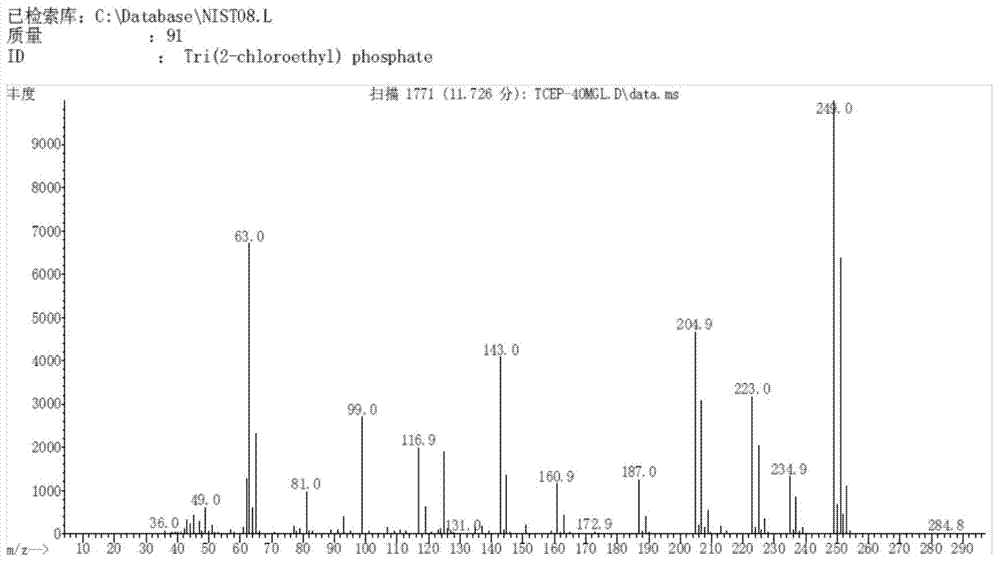
[0036] Centrifuge the enriched cultured bacteria in a 10mL sterilized centrifuge tube at a speed of 6000r / min for 10min, collect the bacteria, wash repeatedly with sterile normal saline and centrifuge for 2-3 times, and finally resuspend with an equal volume of normal saline Be made into the bacterium suspension of certain concentration, inoculate in the tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate degradation medium by the amount of 10% and carry out degradation experiment, the sample is measured by GC-MS, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com