Method for carrying out nucleic acid isothermal amplification by using paper-based microfluid
A paper-based microfluidics and isothermal amplification technology, applied in the field of microfluidics, can solve the problems of complex process, cumbersome process, and the cost cannot be disposable, and achieve the effect of simplifying the preparation process, fast analysis, and light weight.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Loop-mediated isothermal amplification detection of seven bacteria simultaneously using paper microfluidics
[0027] Use paper microfluidics to simultaneously detect whether the sample contains the following seven bacteria: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae , Acinetobacter baumannii, using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (loop-mediated isothermal amplification, LAMP), according to the following steps:
[0028] 1. The DNA solution of the extracted sample is ready for use, and the nucleic acid is quickly extracted by boiling.
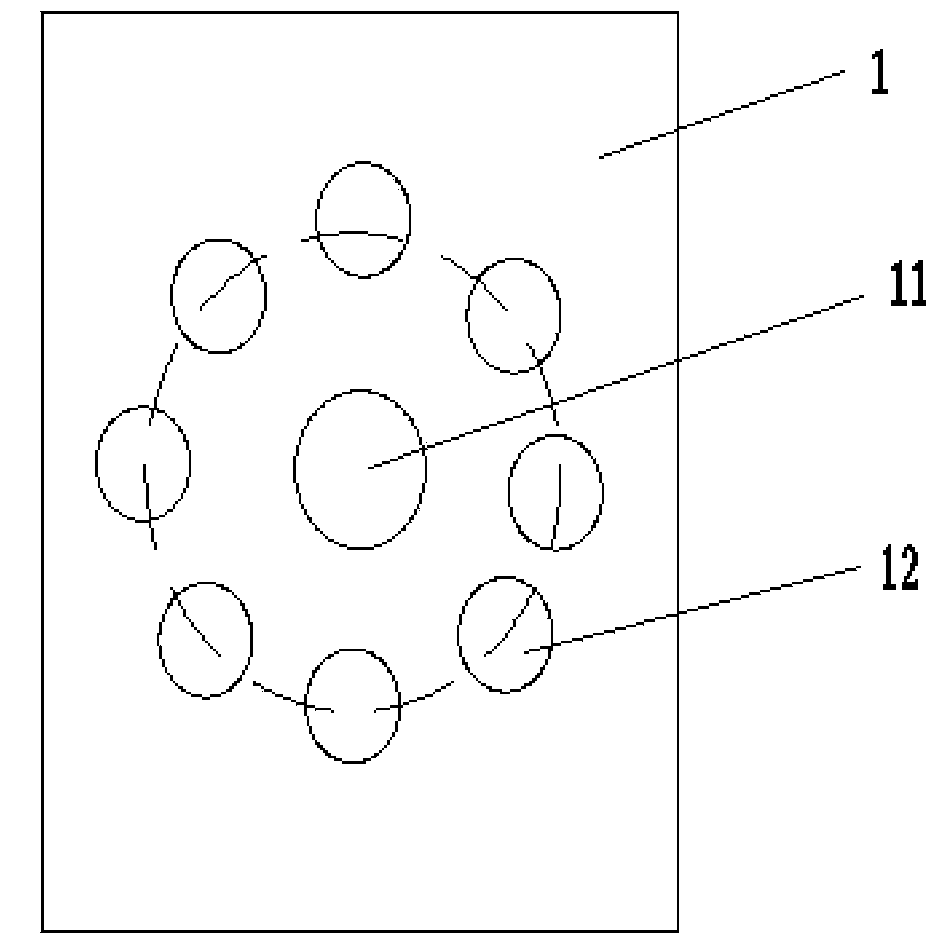
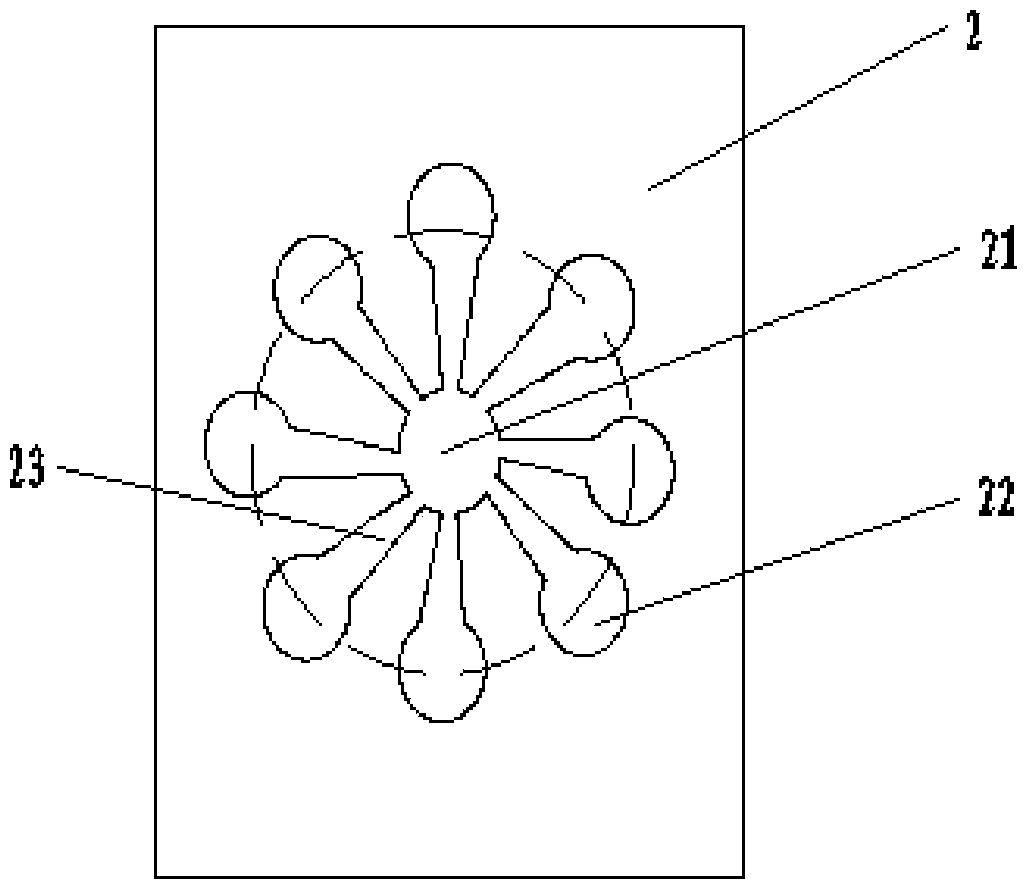
[0029] 2. Precipitate the LAMP primers of seven kinds of bacteria on the seven reaction zones 22 of paper microfluidics respectively. The genes detected by different bacteria and the primers used are shown in Table 1: through biotinylated primers and avidinized microcoagulation The gel was coupled, dried at room temperature and ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Loop-mediated isothermal amplification detection of seven bacteria simultaneously using paper microfluidics heated by resistance wire
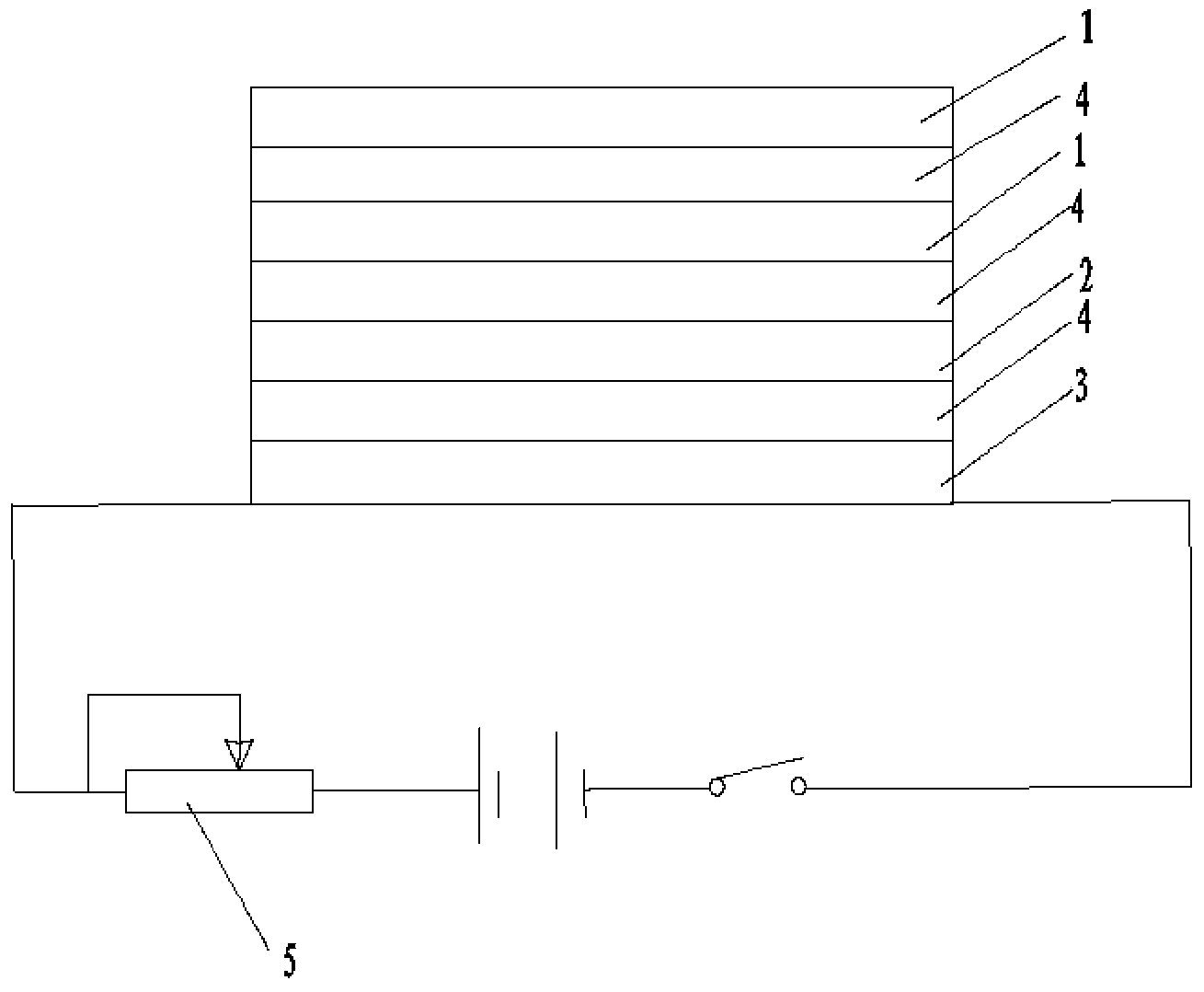
[0041] Others are the same as in Example 1, except that a heating layer 3 is pasted under the reaction layer 2 through a double-sided adhesive layer 4 without any patterns and holes. The heating layer 3 is made of filter paper, and its lower surface is provided with a resistance wire 31, preferably the resistance wire 31 is formed by spraying and depositing metal powder, and the resistance wire 31 and the variable resistor 5 are connected in series with a power supply and a switch through a wire. The magnitude of the current is changed through the adjustment of the variable resistor 5 , so as to regulate the temperature of the heating layer 3 . The metal indicator used is not HNB but orange-yellow Calcein.
[0042] When in use, drop the sample to be tested mixed with the metal indicator Calcein into the sample injection hole ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com