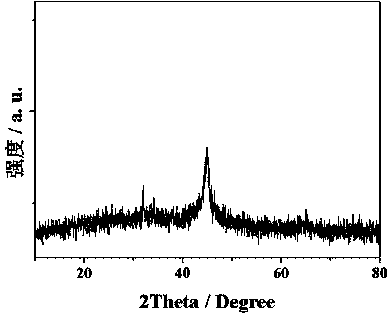
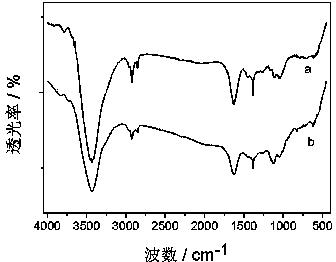
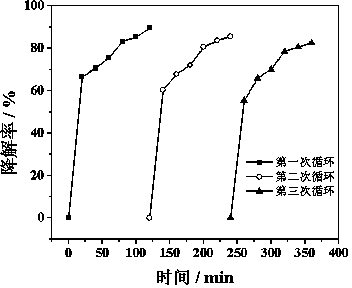
Organic wastewater treatment method based on polyaniline coated nanometer zero-valent iron
A nano-zero-valent iron, organic wastewater technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, oxidized water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. and other problems, to achieve the effect of low cost, simple preparation process and rapid degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Prepare 10mL of rhodamine B dye wastewater with a concentration of 2.5mg / L, adjust the pH value to 3.3 with HCl or NaOH, and pass in air to make the molecular oxygen concentration in the water 3.0mg / L, add 20.0mg of polyaniline-coated Nano-zero-valent iron (the mass ratio of polyaniline to nano-zero-valent iron is 1:10) and 1.0 mg of anthraquinone-2-sulfonic acid sodium salt are stirred magnetically at room temperature. After 120 minutes, the degradation rate of Rhodamine B was 88.5%.
[0029] Under the same experimental conditions, 18.0 mg of nano-zero-valent iron and 1.0 mg of anthraquinone-2-sulfonic acid sodium salt were added to 10 mL of rhodamine B dye wastewater, and the degradation rate of rhodamine B was 39.2% after 120 minutes of reaction.
Embodiment 2
[0031] Prepare 10mL of rhodamine B dye wastewater with a concentration of 30.0mg / L, adjust the pH value to 6.5 with HCl or NaOH, and pass in oxygen to make the molecular oxygen concentration in the water 8.0mg / L, add 20.0mg of polyaniline-coated Nano-zero-valent iron (the mass ratio of polyaniline to nano-zero-valent iron is 1:10) and 1.0 mg cobalamin are stirred magnetically at room temperature. After 120 minutes, the degradation rate of Rhodamine B was 72.4%.
[0032] Under the same experimental conditions, 18.0 mg nanometer zero-valent iron and 1.0 mg cobalamin were added to 10 mL rhodamine B dye wastewater, and the degradation rate of rhodamine B was 31.7% after 120 min of reaction.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Prepare 10mL of 2-chlorobiphenyl wastewater with a concentration of 1.0mg / L, adjust the pH value to 3.0 with HCl or NaOH, and pass in air to make the molecular oxygen concentration in the water 2.0mg / L, add 100.0mg of polyaniline to coat Type nano-sized zero-valent iron (the mass ratio of polyaniline to nano-sized zero-valent iron is 1:5) and 0.1 mg of anthraquinone-2-sulfonic acid sodium salt, and magnetically stirred at room temperature. After 120 minutes, the degradation rate of 2-chlorobiphenyl was 70.8%.
[0035] Under the same experimental conditions, 80.0 mg of nano-zero-valent iron and 0.1 mg of anthraquinone-2-sulfonic acid sodium salt were added to 10 mL of 2-chlorobiphenyl wastewater, and the degradation rate of 2-chlorobiphenyl was 33.5% after 120 minutes of reaction.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com